Acrylamide derivatives for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) Design, synthesis, molecular modeling, and biological evaluation of acrylamide derivatives as potent inhibitors of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is a viable target for the development of therapeutics to treat cancer and immunological diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriasis and multiple sclerosis (MS).
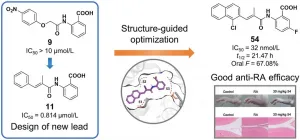
The authors designed and synthesized a series of acrylamide-based novel DHODH inhibitors as potential RA treatment agents. 2-Acrylamidobenzoic acid analog 11 was identified as the lead compound for structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies. The replacement of the phenyl group with naphthyl moieties improved inhibitory activity significantly to double-digit nanomolar range. Further structure optimization revealed that an acrylamide with small hydrophobic groups (Me, Cl or Br) at the 2-position was preferred. Moreover, adding a fluoro atom at the 5-position of the benzoic acid enhanced the potency. The optimization efforts led to potent compounds 42 and 53?55 with IC50 values of 41, 44, 32, and 42 nmol/L, respectively.
The most potent compound 54 also displayed favorable pharmacokinetic (PK) profiles and encouraging in vivo anti-arthritic effects in a dose-dependent manner.
INFORMATION:
Article reference: Fanxun Zeng, Shiliang Li, Guantian Yang, Yating Luo, Tiantian Qi, Yingfan Liang, Tingyuan Yang, Letian Zhang, Rui Wang, Lili Zhu, Honglin Li, Xiaoyong Xu, Design, synthesis, molecular modeling, and biological evaluation of acrylamide derivatives as potent inhibitors of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2021, ISSN 2211-3835, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.008
Keywords: DHODH, De novo pyrimidine biosynthesis, DHODH inhibitors, Acrylamide derivatives, Rheumatoid arthritis
The Journal of the Institute of Materia Medica, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association.
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (APSB) is a monthly journal, in English, which publishes significant original research articles, rapid communications and high-quality reviews of recent advances in all areas of pharmaceutical sciences -- including pharmacology, pharmaceutics, medicinal chemistry, natural products, pharmacognosy, pharmaceutical analysis and pharmacokinetics.
For more information please visit https://www.journals.elsevier.com/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/
Editorial Board: https://www.journals.elsevier.com/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/editorial-board
APSB is available on ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b).
Submissions to APSB may be made using Editorial Manager® (https://www.editorialmanager.com/apsb/default.aspx).
CiteScore: 10.5
Impact Factor: 7.097
5-Year Impact Factor: 7.865
Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP): 2.210
SCImago Journal Rank (SJR): 1.792
ISSN 2211-3835
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-08
Orchids of the Boreal zone are rare species. Most of the 28,000 species of the Orchid family actually live in the tropics. In the Boreal zone, ground orchids can hardly tolerate competition from other plants -- mainly forbs or grasses. So they are often pushed into ecotones -- border areas between meadows and forests, or between forests and swamps.
Furthermore, there has been a decline in wild orchids all over North America and Eurasia, caused in part by human-induced destruction of their habitats, the transformation of ecosystems, and the harvesting of flowers from the wild.
In the Novosibirsk region, ...
2021-04-08
Pioneering research led by experts from the University of Exeter's Living Systems Institute has provided new insight into formation of the human embryo.
The team of researchers discovered an unique regenerative property of cells in the early human embryo.
The first tissue to form in the embryo of mammals is the trophectoderm, which goes on to connect with the uterus and make the placenta. Previous research in mice found that trophectoderm is only made once.
In the new study, however, the research team found that human early embryos are able to regenerate trophectoderm. They also showed that human embryonic stem cells grown in the laboratory can similarly ...
2021-04-08
Every year, our planet encounters dust from comets and asteroids. These interplanetary dust particles pass through our atmosphere and give rise to shooting stars. Some of them reach the ground in the form of micrometeorites. An international program conducted for nearly 20 years by scientists from the CNRS, the Université Paris-Saclay and the National museum of natural history with the support of the French polar institute, has determined that 5,200 tons per year of these micrometeorites reach the ground. The study will be available in the journal Earth & Planetary Science Letters from April 15.
Micrometeorites have always fallen on our planet. These interplanetary dust particles from comets or asteroids are particles of a few tenths to hundredths of a millimetre that have passed ...
2021-04-08
Scientists have made a pivotal breakthrough in understanding the way in which cells communicate with each other.
A team of international researchers, including experts from the University of Exeter's Living Systems Institute, has identified how signalling pathways of Wnt proteins - which orchestrate and control many cell developmental processes - operate on both molecular and cellular levels.
Various mechanisms exist for cells to communicate with each other, and many are essential for development. This information exchange between cells is often based on signalling proteins that activate specific intracellular signalling cascades to control cell behaviour at a distance.
Wnt proteins are produced by a relatively small group ...
2021-04-08
The damaging effects of life under Nazi rule have long been known with many victims having experienced periods of protracted emotional and physical torture, malnutrition and mass exposure to disease. But recent research from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem show that even for those who survived, their health and mortality continued to be directly impacted long after the end of the Holocaust.
The study, led by Drs. Iaroslav Youssim and Hagit Hochner from the School of Public Health at the Faculty of Medicine and published in the American Journal of Epidemiology, investigated mortality rates from ...
2021-04-08
Short pieces of DNA--jumping genes--can bounce from one place to another in our genomes. When too many DNA fragments move around, cancer, infertility, and other problems can arise. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor & HHMI Investigator Leemor Joshua-Tor and a research investigator in her lab, Jonathan Ipsaro, study how cells safeguard the genome's integrity and immobilize these restless bits of DNA. They found that one of the jumping genes' most needed resources may also be their greatest vulnerability.
The mammalian genome is full of genetic elements that have the potential to move from place to place. One type is an LTR retrotransposon (LTR). In normal cells, these elements don't ...
2021-04-08
ITHACA, N.Y. - Research shows people turn to religion in times of fear and uncertainty - and March 2020 was one of those times.
To find the impact of religion during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, Landon Schnabel, the Robert and Ann Rosenthal Assistant Professor of Sociology in the College of Arts and Sciences, analyzed responses from 11,537 Americans surveyed March 19-24, 2020, shortly after the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global health pandemic.
Religion protected mental health of members of several ...
2021-04-08
Image inpainting is a computer vision technique in which pixels missing from an image are filled in. It is often used to remove unwanted objects from an image or to recreate missing regions of occluded images. Inpainting is a common tool for predicting missing image data, but it's challenging to synthesize the missing pixels in a realistic and coherent way.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have presented a frequency-based inpainting method that enables the use of both frequency and spatial information to generate missing image portions. Publishing in the Journal of Electronic Imaging (JEI), Hiya Roy et al. detail the technique in " END ...
2021-04-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio - It's one thing to decide among two or three snacks available at a friend's house. But what do people do when they're faced with a vending machine offering 36 different options?
A new study using eye-tracking technology suggests that the amount of time people spend looking at individual items may actually help them decide. Findings showed that people tended to choose snacks they spent more time looking at, sometimes even over snacks that they rated more highly.
"We could do pretty well predicting what people would choose based just ...
2021-04-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Avian brood parasites lay their eggs in the nests of other bird species, forcing the hosts to do the hard work of raising the unrelated young. A team of scientists wanted to simulate the task of piercing an egg - a tactic that only a minority of host birds use to help grasp and eject the foreign eggs. Their study offers insight into some of the physical challenges the discriminating host birds face.
The new findings appear in the Journal of Experimental Biology.
Take cowbirds, for example. Their eggs look nothing like the host birds' eggs, "yet most of their hosts do not reject the parasite eggs," said study co-author Mark Hauber, a professor of evolution, ecology and behavior at the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Acrylamide derivatives for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis