Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein
Balance of potency and metabolic stability
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein: Balance of potency and metabolic stability
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.07.016
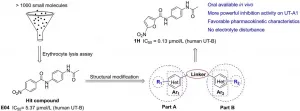
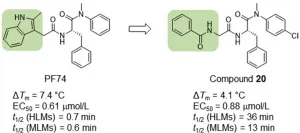
Of all known small molecules targeting human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) capsid protein (CA), PF74 represents by far the best characterized chemotype, due to its ability to confer antiviral phenotypes in both early and late phases of viral replication. However, the prohibitively low metabolic stability renders PF74 a poor antiviral lead. The authors report on their medicinal chemistry efforts toward identifying novel and metabolically stable small molecules targeting the PF74 binding site. Specifically, they replaced the inter-domain-interacting, electron-rich indole ring of PF74 with less electron-rich isosteres, including imidazolidine-2,4-dione, pyrimidine-2,4-dione, and benzamide, and identified four potent antiviral compounds (10, 19, 20 and 26) with markedly improved metabolic stability. Compared to PF74, analog 20 exhibited similar submicromolar potency, and much longer (51-fold) half-life in human liver microsomes (HLMs). Molecular docking corroborated that 20 binds to the PF74 binding site, and revealed distinct binding interactions conferred by the benzamide moiety. Collectively, the authors data support compound 20 as a promising antiviral lead.
INFORMATION:
Article reference: Lei Wang, Mary C. Casey, Sanjeev Kumar, V. Vernekar, Rajkumar Lalji Sahani, Karen A. Kirby, Haijuan Du, Huanchun Zhang, Philip R. Tedbury, Jiashu Xie, Stefan G. Sarafianos, Zhengqiang Wang, Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein: Balance of potency and metabolic stability, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2021, ISSN 2211-3835, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.07.016
Keywords: HIV-1, Capsid protein, PF74, Microsomal stability
The Journal of the Institute of Materia Medica, the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association.
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (APSB) is a monthly journal, in English, which publishes significant original research articles, rapid communications and high-quality reviews of recent advances in all areas of pharmaceutical sciences -- including pharmacology, pharmaceutics, medicinal chemistry, natural products, pharmacognosy, pharmaceutical analysis and pharmacokinetics.
For more information please visit https://www.journals.elsevier.com/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/
Editorial Board: https://www.journals.elsevier.com/acta-pharmaceutica-sinica-b/editorial-board
APSB is available on ScienceDirect.
Submissions to APSB may be made using Editorial Manager®.
CiteScore: 10.5
Impact Factor: 7.097
5-Year Impact Factor: 7.865
Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP): 2.210
SCImago Journal Rank (SJR): 1.792
ISSN 2211-3835
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-08
A consortium of researchers from Russia, Belarus, Japan, Germany and France led by a Skoltech scientist have uncovered the way in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis survives in iron-deficient conditions by utilizing rubredoxin B, a protein from a rubredoxin family that play an important role in adaptation to changing environmental conditions. The new study is part of an effort to study the role of M. tuberculosis enzymes in developing resistance to the human immune system and medication. The paper was published in the journal Bioorganic Chemistry.
According to the World Health Organization, every year 10 million people fall ill with tuberculosis and about 1.5 million die from it, making it the world's top infectious killer. ...
2021-04-08
A great need for better pain treatment
After an appendectomy, a quarter (24.8%) of all children wanted a stronger pain treatment in the first 24 hours after their operation. Among children who had a tonsillectomy, this was one-fifth (20.2%). Analysis of the data showed that this desire was primarily associated with sleep impairments and with movement pain. The lead author of the study, Prof. Ulrike M. Stamer, explained: "We are dealing with a large number of affected patients. Appendectomies and tonsillectomies are the most common operations performed on children overall. Just under a quarter of these cases strongly signal a desire for
improvement".
A comprehensive, multicentre study
This study is based on the international pain registry "PAIN OUT infant", which was established ...
2021-04-08
TAMPA, Fla. (April 8, 2021) -- A dysfunctional immune system significantly contributes to the development of cancer. Several therapeutic strategies to activate the immune system to target cancer cells have been approved to treat different types of cancer, including melanoma. However, some patients do not show beneficial clinical responses to these novel and very promising immunotherapies. In a new article published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers demonstrate how an important defect in STING gene expression in melanoma cells contributes to their evasion from immune cell detection and destruction.
Several different mechanisms have been discovered ...
2021-04-08
Genome mining combined metabolic shunting and OSMAC strategy of an endophytic fungus leads to the production of diverse natural products
Endophytic fungi are promising producers of bioactive small molecules. Bioinformatic analysis of the genome of an endophytic fungus Penicillium dangeardii revealed 43 biosynthetic gene clusters, exhibited its strong ability to produce numbers of secondary metabolites. However, this strain mainly produce rubratoxins alone with high yield in varied culture conditions, suggested most gene clusters are silent. Efforts for mining the cryptic gene clusters in P. dangeardii, including epigenetic regulation and one-strain-many-compounds (OSMAC) approach were failed probably due to the high yield of rubratoxins. A metabolic ...
2021-04-08
A team of archaeologists in north-west the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has uncovered the earliest evidence of dog domestication by the region's ancient inhabitants.
The discovery came from one of the projects in the large-scale archaeological surveys and excavations of the region commissioned by the Royal Commission for AlUla (RCU).
The researchers found the dog's bones in a burial site that is one of the earliest monumental tombs identified in the Arabian Peninsula, roughly contemporary with such tombs already dated further north in the Levant.
Evidence ...
2021-04-08
Indole, and structures derived from it, are a component of many natural substances, such as the amino acid tryptophan. A new catalytic reaction produces cyclopenta[b]indoles--frameworks made of three rings that are joined at the edges--very selectively and with the desired spatial structure. As a research team reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie, the rates of the different steps of the reaction play a critical role.
Indole derivates are widely distributed in nature; they are part of serotonin and melatonin, as well as many alkaloids--some of which are used as drugs, for example, as treatments for Parkinson's disease. Indole is an aromatic six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring along one edge. The five-membered ring has a double bond and ...
2021-04-08
Using a surprisingly simple technique, researchers in the University of Arizona Department of Neuroscience have succeeded in approximating how many brain cells make up the brains of several species of bees, ants and wasps. The work revealed that certain species of bees have a higher density of brain cells than even some species of birds, whereas ants turned out to have fewer brain cells than originally expected.
Published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, the study marks the first time the new cell counting method has been applied to invertebrate animals and provides a robust and reproducible protocol for other research groups studying the brains of ...
2021-04-08
Discovery of novel diarylamides as orally active diuretics targeting urea transporters
Urea transporters (UT) play a vital role in the mechanism of urine concentration and are recognized as novel targets for the development of salt-sparing diuretics. Thus, UT inhibitors are promising for development as novel diuretics. In this study the authors discovered a novel UT inhibitor with a diarylamide scaffold by high-throughput screening. Optimization of the inhibitor led to the identification of a promising preclinical candidate, N-[4-(acetylamino)phenyl]-5-nitrofuran-2-carboxamide ...
2021-04-08
The full assembly of human chromosome 8 is reported this week in Nature. While on the outside this chromosome looks typical, being neither short nor long or distinctive, its DNA content and arrangement are of interest in primate and human evolution, in several immune and developmental disorders, and in chromosome sequencing structure and function generally.
This linear assembly is a first for a human autosome - a chromosome not involved in sex determination. The entire sequence of chromosome 8 is 146,259,671 bases. The completed assembly fills in the gap of more than 3 million bases missing from the current reference genome.
The Nature paper is titled "The structure, function and evolution of a complete chromosome 8."
One of several intriguing characteristics ...
2021-04-08
Using DNA structures as scaffolds, Tim Liedl, a scientist of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich, has shown that precisely positioned gold nanoparticles can serve as efficient energy transmitters.
Since the inception of the field in 2006, laboratories around the world have been exploring the use of 'DNA origami' for the assembly of complex nanostructures. The method is based on DNA strands with defined sequences that interact via localized base pairing. "With the aid of short strands with appropriate sequences, we can connect specific regions of long DNA molecules together, rather like forming three-dimensional structures by folding a flat sheet of paper in certain ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein
Balance of potency and metabolic stability