(Press-News.org) When you think of ways to treat opioid use disorder, you might think methadone clinics and Narcotics Anonymous meetings. You probably don't imagine stretches and strengthening exercises.
But Anne Swisher--professor at the West Virginia University School of Medicine--is working to address opioid misuse in an unconventional way: through physical therapy. She and her colleagues have enhanced physical therapy instruction at WVU to emphasize the profession's role in preventing and treating opioid use disorder.
"Students have different interests and passions within the profession, and they find their niche," said Swisher, a researcher and director of scholarship in the Division of Physical Therapy. "No matter what their passion is, there is a way they can make a difference, whether it's by preventing people from starting down the road of opioids--by minimizing pain medication and doing movement interventions--or whether it's by helping people in the recovery process become healthier overall."
Swisher and her team devised a model to show doctor of physical therapy students how key topics in their curriculum--such as women's health, pediatric care and sports therapy--could all address opioid use disorder in various ways.
Their model--which was published in prestigious rehabilitation journal Physical Therapy--is innovative because it goes beyond musculoskeletal issues and addresses how physical therapists can assist people across the lifespan, from neonatal to hospice settings. It also illustrates how physical therapists can help improve human movement across what Swisher calls the "whole addiction spectrum."
"In our curriculum, our students learn about all of these different aspects--what to do with somebody who's critically ill, the appropriate developmental milestones for children, how to help older people stay active--but it was really just a matter of connecting it all together," she said.
For instance, by making it easier for pregnant women to manage their aches and pains without opioids, physical therapists can help prevent neonatal abstinence syndrome in newborns. By combining special exercises with pharmacological treatment, they can reduce opioid use in patients after spinal surgery. And by promoting healthy physical activity in general, they can support people as they recover from opioid use disorder.
"I think it comes back to movement," Swisher said. "One of the catchphrases we like to use is, 'Motion is lotion for the joints.' And we know that regular physical activity releases the body's own opioid chemicals. That's the so-called 'runner's high' that makes us feel good. Physical therapists can partner with people to work through their barriers to becoming more physically active."
What are some of those barriers? Well, it depends. An overweight patient may find movement difficult because he has knee pain. A patient recovering from hip surgery may fear the pain of exercise so much that she avoids attempting it. And a new mom may find caring for her baby so overwhelming that even a walk around the block feels herculean.
"Pain is always a perception," Swisher said. "It is always influenced by your own experiences, your motivation. If you get a tattoo to celebrate something monumental, you're causing tissue damage, but you don't perceive that as painful as putting your hand on the stove accidentally. We're educating our students--and our colleagues--to understand that whole context working with pain."
As described in the article, she and her team also incorporated their model into the clinical rotations that DPT students complete in rural Appalachian communities. As part of their rotations, the students choose a topic to develop into an educational program for a specific population in their community. They research issues specific to that community and consider those issues when designing the program.
"So, you get a small group of students who love women's health," Swisher said. "Maybe they develop an exercise program for women who have had babies that might have chronic pelvic pain."
All of the programs are stored electronically so that as the students make their way through their rotations, they can access each other's programs and work with their own clinical supervisors to tailor them to the communities they're serving.
"I think when we're looking at any kind of healthcare provider going into these rural communities that are really struggling with addiction, you have to look at those psychosocial and emotional reasons why people might find a desire to escape some pain, whether they perceive it as physical pain or whether it becomes more of an emotional pain," Swisher said. "We have to consider how we as physical therapists interact with people as complex, bio-psychosocial individuals."
The complex, bio-psychosocial individuals who call Appalachia home have been disproportionately affected by the opioid crisis. Appalachians are more likely to die prematurely than people who live elsewhere in the United States, and opioid-related deaths are a main reason for this disparity, reports the Appalachian Regional Commission.
West Virginia, in particular, has been hit hard. In 2018, the state had the nation's highest rate of opioid-involved overdose deaths, according to the National Institutes of Health. That same year, healthcare providers in the state wrote 69.3 opioid prescriptions for every 100 West Virginians. The national average? Just 51.4.
Preparing the next generation of physical therapists to deal with opioid use disorder is important because "there's such a huge issue here in Appalachia, especially in rural communities," Swisher said.
"If you're a physical therapist, you don't need a special certification in opioid recovery to influence something across this whole addiction spectrum," she said. "Just do the things that you do as a physical therapist, in your area."
INFORMATION:
Research reported in this publication was supported by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Service Administration under Award Number 1H79TI081724, via the West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of SAMHSA or WV DHHR.
Citation
Title: Physical Therapist Roles During the Opioid Epidemic in Rural Appalachia: Preparing Students to Educate Communities
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/pzaa215
Link: https://academic.oup.com/ptj/article-abstract/101/2/pzaa215/6044309
EVANSTON, Ill. -- Five-star ratings are no guarantee to lead you to the perfect barber who truly understands your hair or to the espresso machine that brews a perfect cup of coffee.
That's because most products online are now rated positively, making it harder than ever to truly discern whether they will succeed in the marketplace.
A new study from Northwestern University Kellogg School of Management and the University of Massachusetts Boston was able to predict the success of movies, commercials, books and restaurants by relying on the "emotionality" of reviews instead of the star rating.
The researchers explored box office revenue of 2,400 movies, sales of 1.6 million books and real-world reservations at ...
Astronomers at Western University have discovered the most rapidly rotating brown dwarfs known. They found three brown dwarfs that each complete a full rotation roughly once every hour. That rate is so extreme that if these "failed stars" rotated any faster, they could come close to tearing themselves apart. Identified by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, the brown dwarfs were then studied by ground-based telescopes including Gemini North, which confirmed their surprisingly speedy rotation.
Three brown dwarfs have been discovered spinning faster than any other found before. Astronomers at Western University in Canada first measured the rotation speeds of these brown dwarfs using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and confirmed them with follow-up ...
Taiwan is an island of extremes: severe earthquakes and typhoons repeatedly strike the region and change the landscape, sometimes catastrophically. This makes Taiwan a fantastic laboratory for geosciences. Erosion processes, for example, occur up to a thousand times faster in the center of the island than in its far south. This difference in erosion rates influences the chemical weathering of rocks and yields insights into the carbon cycle of our planet on a scale of millions of years. A group of researchers led by Aaron Bufe and Niels Hovius of the German Research Center for Geosciences (GFZ) has now taken advantage of the different erosion rates and investigated how uplift and erosion of rocks determine the balance of carbon emissions ...
Having a responsive, supportive partner minimizes the negative impacts of an individual's depression or external stress on their romantic relationship, according to research by a University of Massachusetts Amherst social psychologist.
Paula Pietromonaco, professor emerita of psychological and brain sciences, drew on data from her Growth in Early Marriage project (GEM) to investigate what she had discovered was an under-studied question. Findings are published in the journal Social Psychological and Personality Science.
"I was really surprised that although there's a ton of work out there on depression, there ...
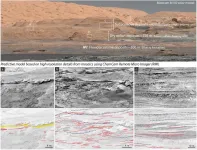
Boulder, Colo., USA: Gale Crater's central sedimentary mound (Aeolis Mons or, informally, Mount Sharp) is a 5.5-km-tall remnant of the infilling and erosion of this ancient impact crater. Given its thickness and age, Mount Sharp preserves one of the best records of early Martian climatic, hydrological, and sedimentary history.
In this paper, published today in Geology, William Rapin and colleagues present the first description of key facies in the sulfate-bearing unit, recently observed in the distance by the rover, and propose a model for changes in depositional environments.
The basal part of this sedimentary sequence is ahead of the Curiosity rover traverse and was recently analyzed with unprecedented resolution by the rover ...
While it isn't surprising that infants and children love to look at people's movements and faces, recent research from Rochester Institute of Technology's National Technical Institute for the Deaf studies exactly where they look when they see someone using sign language. The research uses eye-tracking technology that offers a non-invasive and powerful tool to study cognition and language learning in pre-verbal infants.
NTID researcher and Assistant Professor Rain Bosworth and alumnus Adam Stone studied early-language knowledge in young infants and children by recording their gaze patterns as they watched a signer. The goal was to learn, just from gaze patterns alone, ...
"Not all those who wander are lost ... "
--J.R.R. Tolkien
Known as "the lost years," it is a little-understood journey that unfolds over thousands of miles and as much as two decades or more. Now, a Stanford-led study illuminates secrets of the North Pacific loggerhead turtles' epic migration between their birthplace on the beaches of Japan and reemergence years later in foraging grounds off the coast of Baja California. The study, published April 8 in Frontiers in Marine Science, provides evidence for intermittent passages of warm water that allow sea turtles to cross otherwise inhospitably cold ocean barriers. The findings could help inform the design of conservation measures to protect sea turtles and other migratory sea creatures amid climatic ...
The Perseverance rover has just landed on Mars. Meanwhile, its precursor Curiosity continues to explore the base of Mount Sharp (officially Aeolis Mons), a mountain several kilometres high at the centre of the Gale crater. Using the telescope on the ChemCam instrument to make detailed observations of the steep terrain of Mount Sharp at a distance, a French-US team headed by William Rapin, CNRS researcher at the Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (CNRS/Université Toulouse III/CNES) (1), has discovered that the Martian climate recorded there alternated between dry and wetter periods, before drying up completely about 3 billion years ago. Spacecraft in orbit ...
Heart failure and stroke are unusual diagnoses among younger people. But they are now clearly on the rise in men below the age of 40, according to a University of Gothenburg study. The scientists have found links to obesity and low fitness in the upper teens.
The present study, published in Journal of Internal Medicine, includes data on 1,258,432 men who, at an average age of 18.3 years, enlisted for military service in Sweden between 1971 and 1995.
Particulars of the men's weight, height and physical fitness on enlistment were merged with data in the National Board of Health and Welfare's National Patient Register and Cause of Death Register for the period 1991-2016. From when they enlisted, the men were thus monitored over a period exceeding 20 years.
The proportion ...
Researchers at GMI - Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences - uncover an ingenious mechanism by which Arabidopsis safeguards the integrity of its genome. The paper is published in the journal Nature Cell Biology.
Is it possible for one single gene product to silence undesirable genetic elements? Can such a strong effect be seen in the regulation of Transposable Elements (TEs), or genome parasites? If yes, how does this gene product singlehandedly keep transposons in check? New research from Frédéric Berger's group at GMI provides answers to these questions and dissects a mechanism of gene silencing that has long remained shrouded in mystery.
Genome parasites
Although jumping transposons promote ...