INFORMATION:
The research was supported by grants awarded to Bosworth from the National Science Foundation and the National Eye Institute.
RIT researcher finds that sign-language exposure impacts infants as young as 5 months old
Eye-tracking studies show different eye-gaze patterns in babies with deaf, signing parents compared to babies with hearing, speaking parents
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) While it isn't surprising that infants and children love to look at people's movements and faces, recent research from Rochester Institute of Technology's National Technical Institute for the Deaf studies exactly where they look when they see someone using sign language. The research uses eye-tracking technology that offers a non-invasive and powerful tool to study cognition and language learning in pre-verbal infants.
NTID researcher and Assistant Professor Rain Bosworth and alumnus Adam Stone studied early-language knowledge in young infants and children by recording their gaze patterns as they watched a signer. The goal was to learn, just from gaze patterns alone, whether the child was from a family that used spoken language or signed language at home.
They tested two groups of hearing infants and children that differ in their home language. One "control" group had hearing parents who spoke English and never used sign language or baby signs. The other group had deaf parents who only used American Sign Language at home. Both sets of children had normal hearing in this study. The control group saw sign language for the first time in the lab, while the native signing group was familiar with sign language.
The study, published in Developmental Science, showed that the non-signing infants and children looked at areas on the signer called "signing space," in front of the torso. The hands predominantly fall in this area about 80 percent of the time when signing. However, the signing infants and children looked primarily at the face, barely looking at the hands.
According to the findings, the expert sign-watching behavior is already present by about 5 months of age.
"This is the earliest evidence, that we know of, for effects of sign-language exposure," said Bosworth. "At first, it does seem counter-intuitive that the non-signers are looking at the hands and signers are not. We think signers keep their gaze on the face because they are relying on highly developed and efficient peripheral vision. Infants who are not familiar with sign language look at the hands in signing space perhaps because that is what is perceptually salient to them."
Another possible reason why signing babies keep their gaze on the face could be because they already understand that the face is very important for social interactions, added Bosworth.
"We think the reason perceptual gaze control matures so rapidly is because it supports later language learning, which is more gradual," Bosworth said. "In other words, you have to be able to know where to look before you learn the language signal."
Bosworth says more research is needed to understand the gaze behaviors of deaf babies who are or are not exposed to sign language.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Stanford researchers and others illuminate mystery of sea turtles' epic migrations
2021-04-08
"Not all those who wander are lost ... "
--J.R.R. Tolkien
Known as "the lost years," it is a little-understood journey that unfolds over thousands of miles and as much as two decades or more. Now, a Stanford-led study illuminates secrets of the North Pacific loggerhead turtles' epic migration between their birthplace on the beaches of Japan and reemergence years later in foraging grounds off the coast of Baja California. The study, published April 8 in Frontiers in Marine Science, provides evidence for intermittent passages of warm water that allow sea turtles to cross otherwise inhospitably cold ocean barriers. The findings could help inform the design of conservation measures to protect sea turtles and other migratory sea creatures amid climatic ...
Mars didn't dry up in one go
2021-04-08
The Perseverance rover has just landed on Mars. Meanwhile, its precursor Curiosity continues to explore the base of Mount Sharp (officially Aeolis Mons), a mountain several kilometres high at the centre of the Gale crater. Using the telescope on the ChemCam instrument to make detailed observations of the steep terrain of Mount Sharp at a distance, a French-US team headed by William Rapin, CNRS researcher at the Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (CNRS/Université Toulouse III/CNES) (1), has discovered that the Martian climate recorded there alternated between dry and wetter periods, before drying up completely about 3 billion years ago. Spacecraft in orbit ...
Heart failure and stroke rising in men under 40
2021-04-08
Heart failure and stroke are unusual diagnoses among younger people. But they are now clearly on the rise in men below the age of 40, according to a University of Gothenburg study. The scientists have found links to obesity and low fitness in the upper teens.
The present study, published in Journal of Internal Medicine, includes data on 1,258,432 men who, at an average age of 18.3 years, enlisted for military service in Sweden between 1971 and 1995.
Particulars of the men's weight, height and physical fitness on enlistment were merged with data in the National Board of Health and Welfare's National Patient Register and Cause of Death Register for the period 1991-2016. From when they enlisted, the men were thus monitored over a period exceeding 20 years.
The proportion ...
Lockdown for genome parasites
2021-04-08
Researchers at GMI - Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences - uncover an ingenious mechanism by which Arabidopsis safeguards the integrity of its genome. The paper is published in the journal Nature Cell Biology.
Is it possible for one single gene product to silence undesirable genetic elements? Can such a strong effect be seen in the regulation of Transposable Elements (TEs), or genome parasites? If yes, how does this gene product singlehandedly keep transposons in check? New research from Frédéric Berger's group at GMI provides answers to these questions and dissects a mechanism of gene silencing that has long remained shrouded in mystery.
Genome parasites
Although jumping transposons promote ...
Fostered flamingos just as friendly
2021-04-08
Flamingo chicks raised by foster parents from another flamingo species develop normally, scientists say.
Six Chilean flamingo chicks were reared by Andean flamingos - a species of similar size and behaviour - at WWT Slimbridge Wetland Centre in the summer of 2018.
University of Exeter scientists studied the chicks' behaviour after they re-joined the Chilean flamingo flock early in 2019.
The results showed fostering had no negative effects, with fostered flamingos still forming stable social ties - making "friends" and behaving like parent-reared birds.
"Slimbridge's Andean flamingos hadn't nested for about 20 years," said Dr Paul Rose, of the University of Exeter.
"But in the ...
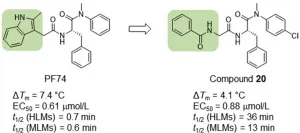
Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein
2021-04-08
Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein: Balance of potency and metabolic stability
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.07.016
Of all known small molecules targeting human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) capsid protein (CA), PF74 represents by far the best characterized chemotype, due to its ability to confer antiviral phenotypes in both early and late phases of viral replication. However, the prohibitively low metabolic stability renders PF74 a poor antiviral lead. The authors report on their medicinal chemistry efforts ...
New study explains Mycobacterium tuberculosis high resistance to drugs and immunity
2021-04-08
A consortium of researchers from Russia, Belarus, Japan, Germany and France led by a Skoltech scientist have uncovered the way in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis survives in iron-deficient conditions by utilizing rubredoxin B, a protein from a rubredoxin family that play an important role in adaptation to changing environmental conditions. The new study is part of an effort to study the role of M. tuberculosis enzymes in developing resistance to the human immune system and medication. The paper was published in the journal Bioorganic Chemistry.
According to the World Health Organization, every year 10 million people fall ill with tuberculosis and about 1.5 million die from it, making it the world's top infectious killer. ...
One in four children want better pain treatment
2021-04-08
A great need for better pain treatment
After an appendectomy, a quarter (24.8%) of all children wanted a stronger pain treatment in the first 24 hours after their operation. Among children who had a tonsillectomy, this was one-fifth (20.2%). Analysis of the data showed that this desire was primarily associated with sleep impairments and with movement pain. The lead author of the study, Prof. Ulrike M. Stamer, explained: "We are dealing with a large number of affected patients. Appendectomies and tonsillectomies are the most common operations performed on children overall. Just under a quarter of these cases strongly signal a desire for
improvement".
A comprehensive, multicentre study
This study is based on the international pain registry "PAIN OUT infant", which was established ...
Moffitt investigators identify STING gene methylation allows melanoma to evade the immune system
2021-04-08
TAMPA, Fla. (April 8, 2021) -- A dysfunctional immune system significantly contributes to the development of cancer. Several therapeutic strategies to activate the immune system to target cancer cells have been approved to treat different types of cancer, including melanoma. However, some patients do not show beneficial clinical responses to these novel and very promising immunotherapies. In a new article published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers demonstrate how an important defect in STING gene expression in melanoma cells contributes to their evasion from immune cell detection and destruction.
Several different mechanisms have been discovered ...
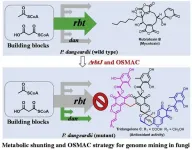
Endophytic fungi as promising producers of bioactive small molecules
2021-04-08
Genome mining combined metabolic shunting and OSMAC strategy of an endophytic fungus leads to the production of diverse natural products
Endophytic fungi are promising producers of bioactive small molecules. Bioinformatic analysis of the genome of an endophytic fungus Penicillium dangeardii revealed 43 biosynthetic gene clusters, exhibited its strong ability to produce numbers of secondary metabolites. However, this strain mainly produce rubratoxins alone with high yield in varied culture conditions, suggested most gene clusters are silent. Efforts for mining the cryptic gene clusters in P. dangeardii, including epigenetic regulation and one-strain-many-compounds (OSMAC) approach were failed probably due to the high yield of rubratoxins. A metabolic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
Buck Institute launches Healthspan Horizons to turn long-term health data into Actionable healthspan insights
University of Ottawa Heart Institute, the University of Ottawa and McGill University launch ARCHIMEDES to advance health research in Canada
The world’s largest brain research prize awarded for groundbreaking discoveries on how we sense touch and pain
Magnetofluids help to overcome challenges in left atrial appendage occlusion
Brain-clearing cells offer clues to slowing Alzheimer’s disease progression
mRNA therapy restores fertility in genetically infertile mice
Cloaked stem cells evade immune rejection in mice, pointing to a potential universal donor cell line
Growth in telemedicine has not improved mental health care access in rural areas, study finds
Pitt scientists engineer “living eye drop” to support corneal healing
Outcomes of older adults with advanced cancer who prefer quality of life vs prolonging survival
[Press-News.org] RIT researcher finds that sign-language exposure impacts infants as young as 5 months oldEye-tracking studies show different eye-gaze patterns in babies with deaf, signing parents compared to babies with hearing, speaking parents