INFORMATION:
Fostered flamingos just as friendly
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) Flamingo chicks raised by foster parents from another flamingo species develop normally, scientists say.
Six Chilean flamingo chicks were reared by Andean flamingos - a species of similar size and behaviour - at WWT Slimbridge Wetland Centre in the summer of 2018.
University of Exeter scientists studied the chicks' behaviour after they re-joined the Chilean flamingo flock early in 2019.
The results showed fostering had no negative effects, with fostered flamingos still forming stable social ties - making "friends" and behaving like parent-reared birds.
"Slimbridge's Andean flamingos hadn't nested for about 20 years," said Dr Paul Rose, of the University of Exeter.
"But in the hot summer of 2018 - probably due to the high temperatures - they made nests and laid eggs.
"Unfortunately, the eggs turned out to be infertile, possibly due to the age of the birds - some of them are approaching their 60s.
"To give them enrichment (allowing them to behave naturally), keepers placed six eggs from the Chilean flamingo flock to be raised by the Andean flamingos.
"This gave us a rare opportunity to study the effects of fostering - although it should be noted that these species are remarkably similar, and this would not have been attempted otherwise."
Peter Kidd, then a student on Exeter's MSc Animal Behaviour course, observed and recorded the chicks' behaviour from April to July 2019 (after their return to their own flock).
These observations were used to study integration and social networks.
"The six fostered chicks and seven parent-reared chicks quickly bonded back together," Kidd said.
"We found very slight behavioural differences - small enough to be explained by individual variation - and all chicks became embedded in the wider social network of the group.
"They all had favoured 'friends' to spend time with, which is normal flamingo behaviour."
Species including the Andean flamingo rare in captivity (only two flocks worldwide) and are classified as "vulnerable" in the wild.
Flamingos can be challenging to breed regularly in captivity, so the findings about successful fostering may help zoo conservation programmes.
"Foster rearing appears to be a safe method for conservation breeding of these species if done correctly," Dr Rose said.
"It is important to note that this fostering event went so smoothly because of the expert flamingo knowledge within the animal care teams at WWT."
The paper, published in the Journal of Zoo and Botanical Gardens, is entitled: "Influences of rearing environment on behaviour and welfare of captive Chilean flamingos: a case study on foster-reared and parent-reared birds."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
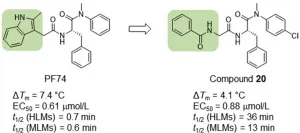
Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein
2021-04-08
Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein: Balance of potency and metabolic stability
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.07.016
Of all known small molecules targeting human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) capsid protein (CA), PF74 represents by far the best characterized chemotype, due to its ability to confer antiviral phenotypes in both early and late phases of viral replication. However, the prohibitively low metabolic stability renders PF74 a poor antiviral lead. The authors report on their medicinal chemistry efforts ...
New study explains Mycobacterium tuberculosis high resistance to drugs and immunity
2021-04-08
A consortium of researchers from Russia, Belarus, Japan, Germany and France led by a Skoltech scientist have uncovered the way in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis survives in iron-deficient conditions by utilizing rubredoxin B, a protein from a rubredoxin family that play an important role in adaptation to changing environmental conditions. The new study is part of an effort to study the role of M. tuberculosis enzymes in developing resistance to the human immune system and medication. The paper was published in the journal Bioorganic Chemistry.
According to the World Health Organization, every year 10 million people fall ill with tuberculosis and about 1.5 million die from it, making it the world's top infectious killer. ...
One in four children want better pain treatment
2021-04-08
A great need for better pain treatment
After an appendectomy, a quarter (24.8%) of all children wanted a stronger pain treatment in the first 24 hours after their operation. Among children who had a tonsillectomy, this was one-fifth (20.2%). Analysis of the data showed that this desire was primarily associated with sleep impairments and with movement pain. The lead author of the study, Prof. Ulrike M. Stamer, explained: "We are dealing with a large number of affected patients. Appendectomies and tonsillectomies are the most common operations performed on children overall. Just under a quarter of these cases strongly signal a desire for
improvement".
A comprehensive, multicentre study
This study is based on the international pain registry "PAIN OUT infant", which was established ...
Moffitt investigators identify STING gene methylation allows melanoma to evade the immune system
2021-04-08
TAMPA, Fla. (April 8, 2021) -- A dysfunctional immune system significantly contributes to the development of cancer. Several therapeutic strategies to activate the immune system to target cancer cells have been approved to treat different types of cancer, including melanoma. However, some patients do not show beneficial clinical responses to these novel and very promising immunotherapies. In a new article published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers demonstrate how an important defect in STING gene expression in melanoma cells contributes to their evasion from immune cell detection and destruction.
Several different mechanisms have been discovered ...
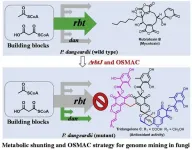
Endophytic fungi as promising producers of bioactive small molecules
2021-04-08
Genome mining combined metabolic shunting and OSMAC strategy of an endophytic fungus leads to the production of diverse natural products
Endophytic fungi are promising producers of bioactive small molecules. Bioinformatic analysis of the genome of an endophytic fungus Penicillium dangeardii revealed 43 biosynthetic gene clusters, exhibited its strong ability to produce numbers of secondary metabolites. However, this strain mainly produce rubratoxins alone with high yield in varied culture conditions, suggested most gene clusters are silent. Efforts for mining the cryptic gene clusters in P. dangeardii, including epigenetic regulation and one-strain-many-compounds (OSMAC) approach were failed probably due to the high yield of rubratoxins. A metabolic ...
Archaeologists uncover earliest evidence of domesticated dogs in Arabian Peninsula
2021-04-08
A team of archaeologists in north-west the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has uncovered the earliest evidence of dog domestication by the region's ancient inhabitants.
The discovery came from one of the projects in the large-scale archaeological surveys and excavations of the region commissioned by the Royal Commission for AlUla (RCU).
The researchers found the dog's bones in a burial site that is one of the earliest monumental tombs identified in the Arabian Peninsula, roughly contemporary with such tombs already dated further north in the Levant.
Evidence ...
The fastest one wins
2021-04-08
Indole, and structures derived from it, are a component of many natural substances, such as the amino acid tryptophan. A new catalytic reaction produces cyclopenta[b]indoles--frameworks made of three rings that are joined at the edges--very selectively and with the desired spatial structure. As a research team reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie, the rates of the different steps of the reaction play a critical role.
Indole derivates are widely distributed in nature; they are part of serotonin and melatonin, as well as many alkaloids--some of which are used as drugs, for example, as treatments for Parkinson's disease. Indole is an aromatic six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring along one edge. The five-membered ring has a double bond and ...
'Bug brain soup' expands menu for scientists studying animal brains
2021-04-08
Using a surprisingly simple technique, researchers in the University of Arizona Department of Neuroscience have succeeded in approximating how many brain cells make up the brains of several species of bees, ants and wasps. The work revealed that certain species of bees have a higher density of brain cells than even some species of birds, whereas ants turned out to have fewer brain cells than originally expected.
Published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, the study marks the first time the new cell counting method has been applied to invertebrate animals and provides a robust and reproducible protocol for other research groups studying the brains of ...
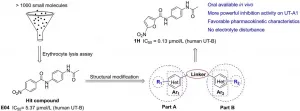
Novel diarylamides as orally active diuretics targeting urea transporters
2021-04-08
Discovery of novel diarylamides as orally active diuretics targeting urea transporters
Urea transporters (UT) play a vital role in the mechanism of urine concentration and are recognized as novel targets for the development of salt-sparing diuretics. Thus, UT inhibitors are promising for development as novel diuretics. In this study the authors discovered a novel UT inhibitor with a diarylamide scaffold by high-throughput screening. Optimization of the inhibitor led to the identification of a promising preclinical candidate, N-[4-(acetylamino)phenyl]-5-nitrofuran-2-carboxamide ...
Complete chromosome 8 sequence reveals novel genes and disease risks
2021-04-08
The full assembly of human chromosome 8 is reported this week in Nature. While on the outside this chromosome looks typical, being neither short nor long or distinctive, its DNA content and arrangement are of interest in primate and human evolution, in several immune and developmental disorders, and in chromosome sequencing structure and function generally.
This linear assembly is a first for a human autosome - a chromosome not involved in sex determination. The entire sequence of chromosome 8 is 146,259,671 bases. The completed assembly fills in the gap of more than 3 million bases missing from the current reference genome.
The Nature paper is titled "The structure, function and evolution of a complete chromosome 8."
One of several intriguing characteristics ...