INFORMATION:
This work was supported by CNES, the French Space Agency, for overseeing the construction of the ChemCam instrument and operating it together with Los Alamos National Laboratory (New Mexico, USA).
Note:
(1) The other team members work at the Laboratoire de géologie de Lyon : Terre, Planètes, Environnement (CNRS/ENS de Lyon/Université Lyon 1) and the Laboratoire de Planétologie et Géodynamique (CNRS/Université de Nantes/Université d'Angers) in France; at UC Santa Cruz, US Geological Survey, California Insitute of Technoloy and Los Alamos National Laboratory in the USA.
Mars didn't dry up in one go
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) The Perseverance rover has just landed on Mars. Meanwhile, its precursor Curiosity continues to explore the base of Mount Sharp (officially Aeolis Mons), a mountain several kilometres high at the centre of the Gale crater. Using the telescope on the ChemCam instrument to make detailed observations of the steep terrain of Mount Sharp at a distance, a French-US team headed by William Rapin, CNRS researcher at the Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (CNRS/Université Toulouse III/CNES) (1), has discovered that the Martian climate recorded there alternated between dry and wetter periods, before drying up completely about 3 billion years ago. Spacecraft in orbit around Mars had already provided clues about the mineral composition of the slopes of Mount Sharp. But now, ChemCam has successfully made detailed observations of the sedimentary beds from the planet's surface, revealing the conditions under which they formed. Moving up through the terrain observed, which is several hundred metres thick, the types of bed change radically. Lying above the lake-deposited clays that form the base of Mount Sharp, wide, tall, cross-bedded structures are a sign of the migration of wind-formed dunes during a long, dry climate episode. Higher up still, thin alternating brittle and resistant beds are typical of river floodplain deposits, marking the return of wetter conditions. The climate of Mars therefore likely underwent several large-scale fluctuations between dry conditions and river and lake environments, until the generally arid conditions observed today took hold. During its extended mission, Curiosity is scheduled to climb the foothills of Mount Sharp and drill into its various beds. It will test this model, characterise in more details how the ancient climate evolved, and possibly understand the origin of these major fluctuations.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Heart failure and stroke rising in men under 40
2021-04-08
Heart failure and stroke are unusual diagnoses among younger people. But they are now clearly on the rise in men below the age of 40, according to a University of Gothenburg study. The scientists have found links to obesity and low fitness in the upper teens.
The present study, published in Journal of Internal Medicine, includes data on 1,258,432 men who, at an average age of 18.3 years, enlisted for military service in Sweden between 1971 and 1995.
Particulars of the men's weight, height and physical fitness on enlistment were merged with data in the National Board of Health and Welfare's National Patient Register and Cause of Death Register for the period 1991-2016. From when they enlisted, the men were thus monitored over a period exceeding 20 years.
The proportion ...
Lockdown for genome parasites
2021-04-08
Researchers at GMI - Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences - uncover an ingenious mechanism by which Arabidopsis safeguards the integrity of its genome. The paper is published in the journal Nature Cell Biology.
Is it possible for one single gene product to silence undesirable genetic elements? Can such a strong effect be seen in the regulation of Transposable Elements (TEs), or genome parasites? If yes, how does this gene product singlehandedly keep transposons in check? New research from Frédéric Berger's group at GMI provides answers to these questions and dissects a mechanism of gene silencing that has long remained shrouded in mystery.
Genome parasites
Although jumping transposons promote ...
Fostered flamingos just as friendly
2021-04-08
Flamingo chicks raised by foster parents from another flamingo species develop normally, scientists say.
Six Chilean flamingo chicks were reared by Andean flamingos - a species of similar size and behaviour - at WWT Slimbridge Wetland Centre in the summer of 2018.
University of Exeter scientists studied the chicks' behaviour after they re-joined the Chilean flamingo flock early in 2019.
The results showed fostering had no negative effects, with fostered flamingos still forming stable social ties - making "friends" and behaving like parent-reared birds.
"Slimbridge's Andean flamingos hadn't nested for about 20 years," said Dr Paul Rose, of the University of Exeter.
"But in the ...
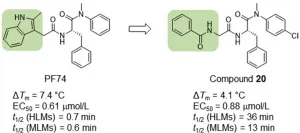
Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein
2021-04-08
Novel PF74-like small molecules targeting the HIV-1 capsid protein: Balance of potency and metabolic stability
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2020.07.016
Of all known small molecules targeting human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) capsid protein (CA), PF74 represents by far the best characterized chemotype, due to its ability to confer antiviral phenotypes in both early and late phases of viral replication. However, the prohibitively low metabolic stability renders PF74 a poor antiviral lead. The authors report on their medicinal chemistry efforts ...
New study explains Mycobacterium tuberculosis high resistance to drugs and immunity
2021-04-08
A consortium of researchers from Russia, Belarus, Japan, Germany and France led by a Skoltech scientist have uncovered the way in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis survives in iron-deficient conditions by utilizing rubredoxin B, a protein from a rubredoxin family that play an important role in adaptation to changing environmental conditions. The new study is part of an effort to study the role of M. tuberculosis enzymes in developing resistance to the human immune system and medication. The paper was published in the journal Bioorganic Chemistry.
According to the World Health Organization, every year 10 million people fall ill with tuberculosis and about 1.5 million die from it, making it the world's top infectious killer. ...
One in four children want better pain treatment
2021-04-08
A great need for better pain treatment
After an appendectomy, a quarter (24.8%) of all children wanted a stronger pain treatment in the first 24 hours after their operation. Among children who had a tonsillectomy, this was one-fifth (20.2%). Analysis of the data showed that this desire was primarily associated with sleep impairments and with movement pain. The lead author of the study, Prof. Ulrike M. Stamer, explained: "We are dealing with a large number of affected patients. Appendectomies and tonsillectomies are the most common operations performed on children overall. Just under a quarter of these cases strongly signal a desire for
improvement".
A comprehensive, multicentre study
This study is based on the international pain registry "PAIN OUT infant", which was established ...
Moffitt investigators identify STING gene methylation allows melanoma to evade the immune system
2021-04-08
TAMPA, Fla. (April 8, 2021) -- A dysfunctional immune system significantly contributes to the development of cancer. Several therapeutic strategies to activate the immune system to target cancer cells have been approved to treat different types of cancer, including melanoma. However, some patients do not show beneficial clinical responses to these novel and very promising immunotherapies. In a new article published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, Moffitt Cancer Center researchers demonstrate how an important defect in STING gene expression in melanoma cells contributes to their evasion from immune cell detection and destruction.
Several different mechanisms have been discovered ...
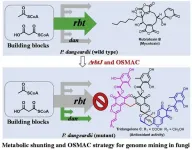
Endophytic fungi as promising producers of bioactive small molecules
2021-04-08
Genome mining combined metabolic shunting and OSMAC strategy of an endophytic fungus leads to the production of diverse natural products
Endophytic fungi are promising producers of bioactive small molecules. Bioinformatic analysis of the genome of an endophytic fungus Penicillium dangeardii revealed 43 biosynthetic gene clusters, exhibited its strong ability to produce numbers of secondary metabolites. However, this strain mainly produce rubratoxins alone with high yield in varied culture conditions, suggested most gene clusters are silent. Efforts for mining the cryptic gene clusters in P. dangeardii, including epigenetic regulation and one-strain-many-compounds (OSMAC) approach were failed probably due to the high yield of rubratoxins. A metabolic ...
Archaeologists uncover earliest evidence of domesticated dogs in Arabian Peninsula
2021-04-08
A team of archaeologists in north-west the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia has uncovered the earliest evidence of dog domestication by the region's ancient inhabitants.
The discovery came from one of the projects in the large-scale archaeological surveys and excavations of the region commissioned by the Royal Commission for AlUla (RCU).
The researchers found the dog's bones in a burial site that is one of the earliest monumental tombs identified in the Arabian Peninsula, roughly contemporary with such tombs already dated further north in the Levant.
Evidence ...
The fastest one wins
2021-04-08
Indole, and structures derived from it, are a component of many natural substances, such as the amino acid tryptophan. A new catalytic reaction produces cyclopenta[b]indoles--frameworks made of three rings that are joined at the edges--very selectively and with the desired spatial structure. As a research team reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie, the rates of the different steps of the reaction play a critical role.
Indole derivates are widely distributed in nature; they are part of serotonin and melatonin, as well as many alkaloids--some of which are used as drugs, for example, as treatments for Parkinson's disease. Indole is an aromatic six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring along one edge. The five-membered ring has a double bond and ...