(Press-News.org) April 8, 2021 - Routinely collected data on patients undergoing spinal fusion surgery do not provide a valid basis for assessing and comparing hospital performance on patient safety outcomes, reports a study in Spine. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
At a time when hospitals are increasingly subject to online rankings or "pay-for-performance" reimbursement programs, metrics based on hospital administrative data are "unreliable for profiling hospital performance," concludes the new research by Jacob K. Greenberg, MD, MSCI, of Washington University in St Louis and colleagues. They write, "These results provide important insights into the advisability of using administrative billing data to benchmark hospital quality in spine surgery."
Study finds unacceptably low hospital 'rankability' for spinal fusion
The researchers analyzed more than 367,000 spinal fusion surgery procedures performed in nine states between 2010 and 2017, drawn from nine state inpatient databases. Performed in patients with degenerative spine disease, spinal fusion is a common and costly inpatient surgical procedure. The study included data on approximately 154,000 procedures in the upper (cervical) spine and 213,000 in the lower (thoracic and lumbar) spine.
The analysis focused on serious complications such as return to the operating room, myocardial infarction (heart attack), death, or prolonged hospital stay. The study was designed to determine whether a metric based on publicly available information from state inpatient databases would be reliable for benchmarking and comparing performance between hospitals.
The researchers calculated a risk/reliability-adjusted complication rate to account for differences in the characteristics (case mix) of patients treated at each hospital. They then used a "rankability" measure to assess whether the metric could distinguish true differences in hospital performance from random fluctuations due to chance (signal-to-noise ratio).
Overall, 4.4 percent of patients undergoing cervical spinal fusion had serious complications. For this group of patients, rankability was consistently low - indicating that "rank-based profiling efforts would lead to widely varying results over time," Dr. Greenberg and colleagues write.
For patients undergoing thoracic and lumbar spinal fusion, the serious complication rate was 7.7 percent. Rankability was higher than for cervical spinal fusion. However, the metric's ability to compare complication rates between hospitals was still just slight to moderate depending on the year, indicating most differences across hospitals were due to chance.
The authors noted that rankability increases with the volume of spinal fusion procedures performed. However, only about one-third of hospitals performed sufficient numbers of thoracic-lumbar fusions to produce reliable estimates. Less than five percent performed enough cervical fusions for reliable rankings.
Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers increasingly use complication rates or other safety metrics to adjust payments to doctors and hospitals for various conditions and procedures. Complication rates are not yet used in national benchmarking for spine surgery, but are widely used for hip and knee replacement surgery. "While payers are increasingly focused on implementing pay-for-performance measures, quality metrics must reliably reflect true differences in performance among the hospitals profiled," according to the authors.
The new analysis - including hundreds of thousands of procedures performed at hospitals across the United States - suggests that state inpatient data on complications are inappropriate for use in ranking and comparing hospital performance for spinal fusion procedures. Dr. Greenberg and colleagues conclude: "These results indicate that such metrics derived from administrative billing data should not be used in high-stakes applications, such as public reporting or pay-for-performance."
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "Administrative Data are Unreliable for Ranking Hospital Performance Based on Serious Complications after Spine Fusion."
DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000004017
About Spine
Recognized internationally as the leading journal in its field, Spine (http://www.spinejournal.com) is an international, peer-reviewed, bi-weekly periodical that considers for publication original articles in the field of spine. It is the leading subspecialty journal for the treatment of spinal disorders. Only original papers are considered for publication with the understanding that they are contributed solely to Spine. According to the latest ISI Science Citation Impact Factor, Spine is the most frequently cited spinal deformity journal among general orthopaedic journals and subspecialty titles.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the clinicians, nurses, accountants, lawyers, and tax, finance, audit, risk, compliance, and regulatory sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with advanced technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2019 annual revenues of €4.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 19,000 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students with advanced clinical decision support, learning and research and clinical intelligence. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
For more information, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
In a medical records study covering thousands of children, a U.S.-Canadian team led by researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine concludes that while surgery to correct congenital heart disease (CHD) within 10 years after birth may restore young hearts to healthy function, it also may be associated with an increased risk of hypertension -- high blood pressure -- within a few months or years after surgery. ...
Waste materials from the pulp and paper industry have long been seen as possible fillers for building products like cement, but for years these materials have ended up in the landfill. Now, researchers at UBC Okanagan are developing guidelines to use this waste for road construction in an environmentally friendly manner.
The researchers were particularly interested in wood-based pulp mill fly ash (PFA), which is a non-hazardous commercial waste product. The North American pulp and paper industry generates more than one million tons of ash annually by burning wood in ...
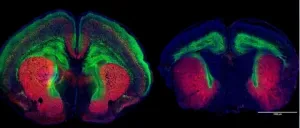
JUPITER, FL -- Damage to the autism-associated gene Dyrk1a, sets off a cascade of problems in developing mouse brains, resulting in abnormal growth-factor signaling, undergrowth of neurons, smaller-than-average brain size, and, eventually, autism-like behaviors, a new study from Scripps Research, Florida, finds.
The study from neuroscientist Damon Page, PhD, describes a new mechanism underlying the brain undergrowth seen in individuals with Dyrk1a mutations. Page's team used those insights to target the affected pathway with an existing medicine, a growth hormone. It restored normal brain growth in the Dyrk1a mutant mice, Page says.
"As of now, there's simply no targeted treatments available for individuals with autism spectrum ...
When you think of ways to treat opioid use disorder, you might think methadone clinics and Narcotics Anonymous meetings. You probably don't imagine stretches and strengthening exercises.
But Anne Swisher--professor at the West Virginia University School of Medicine--is working to address opioid misuse in an unconventional way: through physical therapy. She and her colleagues have enhanced physical therapy instruction at WVU to emphasize the profession's role in preventing and treating opioid use disorder.
"Students have different interests and passions within the profession, and they find their niche," said Swisher, a researcher and director of scholarship in the Division of Physical Therapy. "No matter what their passion is, there ...
EVANSTON, Ill. -- Five-star ratings are no guarantee to lead you to the perfect barber who truly understands your hair or to the espresso machine that brews a perfect cup of coffee.
That's because most products online are now rated positively, making it harder than ever to truly discern whether they will succeed in the marketplace.
A new study from Northwestern University Kellogg School of Management and the University of Massachusetts Boston was able to predict the success of movies, commercials, books and restaurants by relying on the "emotionality" of reviews instead of the star rating.
The researchers explored box office revenue of 2,400 movies, sales of 1.6 million books and real-world reservations at ...
Astronomers at Western University have discovered the most rapidly rotating brown dwarfs known. They found three brown dwarfs that each complete a full rotation roughly once every hour. That rate is so extreme that if these "failed stars" rotated any faster, they could come close to tearing themselves apart. Identified by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, the brown dwarfs were then studied by ground-based telescopes including Gemini North, which confirmed their surprisingly speedy rotation.
Three brown dwarfs have been discovered spinning faster than any other found before. Astronomers at Western University in Canada first measured the rotation speeds of these brown dwarfs using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and confirmed them with follow-up ...
Taiwan is an island of extremes: severe earthquakes and typhoons repeatedly strike the region and change the landscape, sometimes catastrophically. This makes Taiwan a fantastic laboratory for geosciences. Erosion processes, for example, occur up to a thousand times faster in the center of the island than in its far south. This difference in erosion rates influences the chemical weathering of rocks and yields insights into the carbon cycle of our planet on a scale of millions of years. A group of researchers led by Aaron Bufe and Niels Hovius of the German Research Center for Geosciences (GFZ) has now taken advantage of the different erosion rates and investigated how uplift and erosion of rocks determine the balance of carbon emissions ...
Having a responsive, supportive partner minimizes the negative impacts of an individual's depression or external stress on their romantic relationship, according to research by a University of Massachusetts Amherst social psychologist.
Paula Pietromonaco, professor emerita of psychological and brain sciences, drew on data from her Growth in Early Marriage project (GEM) to investigate what she had discovered was an under-studied question. Findings are published in the journal Social Psychological and Personality Science.
"I was really surprised that although there's a ton of work out there on depression, there ...
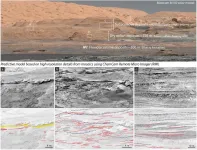
Boulder, Colo., USA: Gale Crater's central sedimentary mound (Aeolis Mons or, informally, Mount Sharp) is a 5.5-km-tall remnant of the infilling and erosion of this ancient impact crater. Given its thickness and age, Mount Sharp preserves one of the best records of early Martian climatic, hydrological, and sedimentary history.
In this paper, published today in Geology, William Rapin and colleagues present the first description of key facies in the sulfate-bearing unit, recently observed in the distance by the rover, and propose a model for changes in depositional environments.
The basal part of this sedimentary sequence is ahead of the Curiosity rover traverse and was recently analyzed with unprecedented resolution by the rover ...
While it isn't surprising that infants and children love to look at people's movements and faces, recent research from Rochester Institute of Technology's National Technical Institute for the Deaf studies exactly where they look when they see someone using sign language. The research uses eye-tracking technology that offers a non-invasive and powerful tool to study cognition and language learning in pre-verbal infants.
NTID researcher and Assistant Professor Rain Bosworth and alumnus Adam Stone studied early-language knowledge in young infants and children by recording their gaze patterns as they watched a signer. The goal was to learn, just from gaze patterns alone, ...