Leaking calcium in neurons an early sign of Alzheimer's pathology
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) New Haven, Conn. -- Alzheimer's disease is known for its slow attack on neurons crucial to memory and cognition. But why are these particular neurons in aging brains so susceptible to the disease's ravages, while others remain resilient?
A new study led by researchers at the Yale School of Medicine has found that susceptible neurons in the prefrontal cortex develop a "leak" in calcium storage with advancing age, they report April 8 in the journal Alzheimer's & Dementia, The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association. This disruption of calcium storage in turns leads to accumulation of phosphorylated, or modified, tau proteins which cause the neurofibrillary tangles in the brain that are a hallmark of Alzheimer's.
These changes occur slowly, building over many years, and can be seen within neurons in the brains of very old monkeys, the researchers report.
"Altered calcium signaling with advancing age is linked to early-stage tau pathology in the neurons that subserve higher cognition," said corresponding author Amy Arnsten, the Albert E. Kent Professor of Neuroscience and professor of psychology and member of the Kavli Institute of Neuroscience at Yale University.
These vulnerable neurons face another problem. As they age, they tend to lose a key regulator of calcium signaling, a protein called calbindin, which protects neurons from calcium overload, and is abundant in the neurons of younger individuals.
"With age, these neurons face a double whammy, with an excessive calcium leak that initiates toxic actions, as well as diminished levels of the protectant, calbindin," said Arnsten.
Neurons in the prefrontal cortex require relatively high levels of calcium to perform their cognitive operations, but the calcium must be tightly regulated. However, as regulation is lost with increasing age, neurons become susceptible to tau pathology and degeneration. Essentially, neurons "eat" themselves from within.
"Understanding these early pathological changes may provide strategies to slow or prevent disease progression," Arnsten said.
INFORMATION:
The study is a collaboration between the labs of Arnsten and Angus Nairn at Yale; Dibyadeep Datta and Shannon N. Leslie are co-first authors of the research.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - New insights into the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infections could bring better treatments for COVID-19 cases.
An international team of researchers unexpectedly found that a biochemical pathway, known as the immune complement system, is triggered in lung cells by the virus, which might explain why the disease is so difficult to treat. The research is published this week in the journal Science Immunology.
The researchers propose that the pairing of antiviral drugs with drugs that inhibit this process may be more effective. Using an in vitro model using human lung ...
2021-04-08
MADISON, WI, April 8, 2021 - USDA Forest Service scientists have delivered a new comprehensive assessment of the invasive species that confront America's forests and grasslands, from new arrivals to some that invaded so long ago that people are surprised to learn they are invasive.
The assessment, titled "Invasive Species in Forests and Rangelands of the United States: A Comprehensive Science Synthesis for the United States Forest Sector," serves as a one-stop resource for land managers who are looking for information on the invasive species that are already affecting the landscape, the species that may threaten the landscape, and what is known about control ...
2021-04-08
Nobel laureate in physics Richard Feynman once described turbulence as "the most important unsolved problem of classical physics."
Understanding turbulence in classical fluids like water and air is difficult partly because of the challenge in identifying the vortices swirling within those fluids. Locating vortex tubes and tracking their motion could greatly simplify the modeling of turbulence.
But that challenge is easier in quantum fluids, which exist at low enough temperatures that quantum mechanics -- which deals with physics on the scale of atoms or subatomic particles -- govern their behavior.
In a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Florida State University researchers ...
2021-04-08
The network of nerves connecting our eyes to our brains is sophisticated and researchers have now shown that it evolved much earlier than previously thought, thanks to an unexpected source: the gar fish.
Michigan State University's Ingo Braasch has helped an international research team show that this connection scheme was already present in ancient fish at least 450 million years ago. That makes it about 100 million years older than previously believed.
"It's the first time for me that one of our publications literally changes the textbook that I am teaching with," said Braasch, as assistant professor in the Department of Integrative Biology in the College ...
2021-04-08
URBANA, Ill. - When scientists need to understand the effects of new infant formula ingredients on brain development, it's rarely possible for them to carry out initial safety studies with human subjects. After all, few parents are willing to hand over their newborns to test unproven ingredients.
Enter the domestic pig. Its brain and gut development are strikingly similar to human infants - much more so than traditional lab animals, rats and mice. And, like infants, young pigs can be scanned using clinically available equipment, including non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI. That means researchers can test nutritional interventions in pigs, look at their effects on the developing brain via MRI, and make educated predictions about how those ...
2021-04-08
Modern human-like brains evolved comparatively late in the genus Homo and long after the earliest humans first dispersed from Africa, according to a new study. By analyzing the impressions left behind by the ancient brains that once sat inside now fossilized skulls, the authors discovered that the brains of the earliest Homo retained a primitive, great ape-like organization of the frontal lobe. The findings challenge the long-standing assumption that human-like brain organization is a hallmark of early Homo and suggest that the evolutionary history of the human brain is more complex than previously thought. Our modern brains are larger and structurally different than those of our closest living relatives, ...
2021-04-08
Researchers present a new, low-temperature method for injection-molding transparent fused silica glass, similar to how many plastic objects are manufactured. According to the authors, the process offers the possibility of producing complex and high-quality glass components using the same fabrication methods that allowed polymers to become one of the most important materials of the 21st century. The optical, thermal, mechanical and chemical properties of silicate glasses make them an ideal non-carbon based, high-performance material with applications ranging from packaging and architecture to high-throughput fiber optic ...
2021-04-08
Using a novel genetic editing system termed intMEMOIR, researchers reveal the cell lineage histories of individual cells within their native tissue context, according to a new study. The new approach provides a powerful new tool for recording cell lineage in diverse cellular systems. During multicellular development, a cell's spatial position and lineage play important roles in cell fate determination. The ability to visualize lineage relationships directly within their native tissues can provide valuable insight into the factors that affect development and disease. This promise has spurred the development of several ...
2021-04-08
X-ray emissions from the Crab Pulsar are more intense during giant radio pulses (GRPs), researchers report. The new findings provide constraints on the mechanisms underlying GRPs and may provide insights into other transient radio phenomena observed throughout the Universe. Pulsars, or rapidly spinning neutron stars, emit pulses of electromagnetic radiation from their magnetospheres and are observed from Earth as regular sequences of radio pulses. Most radio pulses from these distant objects are of a consistent intensity. Occasionally, however, sporadic and short-lived ...
2021-04-08
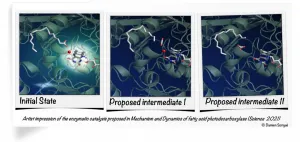
The functioning of the enzyme FAP, useful for producing biofuels and for green chemistry, has been decrypted. This result mobilized an international team of scientists, including many French researchers from the CEA, CNRS, Inserm, École Polytechnique, the universities of Grenoble Alpes, Paris-Saclay and Aix Marseille, as well as the European Synchrotron (ESRF) and synchrotron SOLEIL. The study is published in Science on April 09, 2021.
The researchers decrypted the operating mechanisms of FAP (Fatty Acid Photodecarboxylase), which is naturally present in microscopic algae such as Chlorella. The enzyme had been identified in 2017 as able to use light energy to form hydrocarbons from fatty acids ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Leaking calcium in neurons an early sign of Alzheimer's pathology