INFORMATION:
Injection molding transparent glass like a plastic
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) Researchers present a new, low-temperature method for injection-molding transparent fused silica glass, similar to how many plastic objects are manufactured. According to the authors, the process offers the possibility of producing complex and high-quality glass components using the same fabrication methods that allowed polymers to become one of the most important materials of the 21st century. The optical, thermal, mechanical and chemical properties of silicate glasses make them an ideal non-carbon based, high-performance material with applications ranging from packaging and architecture to high-throughput fiber optic and photonic devices. However, despite being one of the oldest and most relevant materials used by humans today, the technology used to manufacture glass has remained virtually unchanged for centuries. Glass processing requires that it be melted at high temperatures - approaching 2,000 degrees Celsius for some glasses - which not only makes the process highly energy intensive, but also difficult to scale industrially. As a result, many components are made using thermoplastic polymers, which can be processed at lower temperatures and using scalable industrial replication techniques like injection molding (IM). Here, Markus Mader and colleagues demonstrate a novel approach in which a plastic, silica-based nanocomposite can be used for low-temperature injection molding to manufacture glass. Using established IM process technologies and low-temperature (~1,300°C) sintering, the authors could produce precise and highly transparent glass components in as little as five seconds per piece. "Mader et al. have demonstrated the use of pelletized glass-forming composites that are compatible with conventional, low-temperature injection molding - a process used in the high-volume manufacture of polymeric components," writes Rebecca Dylla-Spears in a related Perspective.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
IntMEMOIR traces cell lineage though development and within native tissues
2021-04-08
Using a novel genetic editing system termed intMEMOIR, researchers reveal the cell lineage histories of individual cells within their native tissue context, according to a new study. The new approach provides a powerful new tool for recording cell lineage in diverse cellular systems. During multicellular development, a cell's spatial position and lineage play important roles in cell fate determination. The ability to visualize lineage relationships directly within their native tissues can provide valuable insight into the factors that affect development and disease. This promise has spurred the development of several ...
Enhanced X-Ray emissions coincide with giant radio pulses from crab pulsar
2021-04-08
X-ray emissions from the Crab Pulsar are more intense during giant radio pulses (GRPs), researchers report. The new findings provide constraints on the mechanisms underlying GRPs and may provide insights into other transient radio phenomena observed throughout the Universe. Pulsars, or rapidly spinning neutron stars, emit pulses of electromagnetic radiation from their magnetospheres and are observed from Earth as regular sequences of radio pulses. Most radio pulses from these distant objects are of a consistent intensity. Occasionally, however, sporadic and short-lived ...
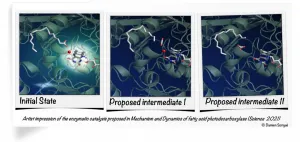
Green chemistry and biofuel: the mechanism of a key photoenzyme decrypted
2021-04-08
The functioning of the enzyme FAP, useful for producing biofuels and for green chemistry, has been decrypted. This result mobilized an international team of scientists, including many French researchers from the CEA, CNRS, Inserm, École Polytechnique, the universities of Grenoble Alpes, Paris-Saclay and Aix Marseille, as well as the European Synchrotron (ESRF) and synchrotron SOLEIL. The study is published in Science on April 09, 2021.
The researchers decrypted the operating mechanisms of FAP (Fatty Acid Photodecarboxylase), which is naturally present in microscopic algae such as Chlorella. The enzyme had been identified in 2017 as able to use light energy to form hydrocarbons from fatty acids ...
Two studies support key role for immune system in shaping SARS-CoV-2 evolution
2021-04-08
Two studies published in the open-access journal PLOS Pathogens provide new evidence supporting an important role for the immune system in shaping the evolution of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. These findings--and the novel technology behind them--improve understanding of how new SARS-CoV-2 strains arise, which could help guide treatment and vaccination efforts.
For the first study, Rachel Eguia of Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington, and colleagues sought to better understand SARS-CoV-2 by investigating a closely related virus that has circulated widely for a far longer period of time: the common-cold virus ...
Giant radio pulses from pulsars are hundreds of times more energetic than previously believed
2021-04-08
A group led by scientists from the RIKEN Cluster for Pioneering Research, using coordinated observations of the Crab pulsar in a number of frequencies, have discovered that the "giant radio pulses" which it emits include an increase in x-ray emissions in addition to the radio and visible light emissions that had been previously observed. This finding, published in Science, implies that these pulses are hundreds of times more energetic than previously believed and could provide insights into the mysterious phenomenon of "fast radio bursts (FRBs)."
Giant radio pulses--a phenomenon where extremely short, millisecond-duration pulses of radio waves are emitted--have ...
Blocking a protein could help overcome cancer resistance to PARP inhibitors
2021-04-08
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have found that blocking a specific protein could increase tumour sensitivity to treatment with PARP inhibitors. Their work published in Science , suggests combining treatments could lead to improved therapy for patients with inheritable breast cancers.
Some cancers, including certain breast, ovarian and prostate tumours, are caused by a fault in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes, which are important for DNA repair. Treatment for these cancers has greatly improved thanks to the discovery of PARP inhibitors, drugs which capitalise on this weakness in the cancer ...
New discovery uncovers secret switch that could revolutionise heart attack treatment
2021-04-08
Scientists at the Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute in Sydney have discovered a critical new gene that it is hoped could help human hearts repair damaged heart muscle after a heart attack.
Researchers have identified a genetic switch in zebrafish that turns on cells allowing them to divide and multiply after a heart attack, resulting in the complete regeneration and healing of damaged heart muscle in these fish.
It's already known that zebrafish can heal their own hearts, but how they performed this incredible feat remained unknown, until now. In research recently published in the prestigious journal, Science, the team at the Institute drilled down into a critical ...
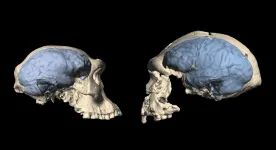
Modern human brain originated in Africa around 1.7 million years ago
2021-04-08
Modern humans are fundamentally different from our closest living relatives, the great apes: We live on the ground, walk on two legs and have much larger brains. The first populations of the genus Homo emerged in Africa about 2.5 million years ago. They already walked upright, but their brains were only about half the size of today's humans. These earliest Homo populations in Africa had primitive ape-like brains - just like their extinct ancestors, the australopithecines. So when and where did the typical human brain evolve?
CT comparisons of skulls reveal modern brain structures
An international ...
Novel algorithm reveals birdsong features that may be key for courtship
2021-04-08
Researchers have developed a new algorithm capable of identifying features of male zebra finch songs that may underlie the distinction between a short phrase sung during courtship, and the same phrase sung in a non-courtship context. Sarah Woolley of McGill University in Montreal, Canada, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology.
Like many animals, male zebra finches adjust their vocal signals for their audience. They may sing the same sequence of syllables during courtship interactions with females as ...
Scientists discover 'jumping' genes that can protect against blood cancers
2021-04-08
DALLAS - April 8, 2021 - New research has uncovered a surprising role for so-called "jumping" genes that are a source of genetic mutations responsible for a number of human diseases. In the new study from Children's Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI), scientists made the unexpected discovery that these DNA sequences, also known as transposons, can protect against certain blood cancers.
These findings, published in Nature Genetics, led scientists to identify a new biomarker that could help predict how patients will respond to cancer therapies and find new therapeutic targets for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the deadliest type of blood cancer in adults and children.
Transposons ...