Study finds medical financial hardship common in adult survivors of AYA cancers
2021-04-12
(Press-News.org) ATLANTA - APRIL 12, 2021 - New study finds higher medical financial hardship in adult survivors of adolescent and young adult (AYA) cancers than in adults without a history of cancer in the United States. The study appears in JNCI: The Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Experts have known that cancer and its treatment can cause significant financial hardship to cancer survivors and their families. However, the long-term economic implications for adult survivors of AYA cancers were not fully understood. In this study, investigators led by Amy D. Lu, MD, The Hospital for Sick Children, and Zhiyuan "Jason" Zheng, Ph.D., American Cancer Society, used data from the National Health Interview Survey (2010-2018) and analyzed responses from adult (>18 years) survivors of AYA cancers (ages 15-39 at diagnosis) and adults without a cancer history. The study explored the various aspects of financial hardships including material (for example, ability to pay bills), psychological (for example, worries about medical bills), and behavioral (for example, delaying or foregoing medical care) measures.
Key study findings include:
Adult survivors of AYA cancers were more likely than adults without a cancer history, to report material and behavioral financial hardship, including problems paying medical bills or delaying or forgoing care because of cost.
Adult survivors of AYA cancers were more likely to report greater intensity of medical financial hardship than their counterparts without a cancer history.
Adult survivors of AYA cancers were more likely to report cost-related medication non-adherence, such as skipping medication doses, taking less medication, and delaying filling a prescription to save money.
"Multiple aspects of financial hardship associated with a cancer diagnosis may last for many years for survivors of AYA cancers," said Dr. Zheng.
As the incidences of AYA cancers increases, understanding the spectrum of medical financial hardship is critical to those caring for and designing policies for adult survivors of AYA cancers, and in guiding ongoing research in this area.
"Healthcare providers can help support increased awareness and assessment of financial hardship, as well as subsequent connection to existing financial and vocational assistance/support services. State and federal policies may have a broader impact through implementation of provisions of the Affordable Care Act in increasing insurance coverage options including affordability and accessibility," said the authors.
INFORMATION:
Article: Lu AD, Zheng Z, Han X, Qi R, Zhao J, Yabroff KR, Nathan PC. Medical financial hardship in survivors of adolescent and young adult cancer in the United States. JNCI: The Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 2021. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djab013.
URL upon embargo: https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djab013
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-12
Study: "Untested Admissions: Examining Changes in Application Behaviors and Student Demographics Under Test-Optional Policies"
Author: Christopher Bennett (Vanderbilt University)
This study was published today in American Educational Research Journal.
Key Findings:
In undergraduate admissions, the adoption of test-optional policies at selective private institutions was linked to a 3-4 percent increase in enrollment of Pell Grant recipients, a 10-12 percent increase in enrollment of first-time Black, Latinx, and Native students, and a 6-8 percent increase in enrollment of first-time students who were women.
However, these gains translate into only a 1 percentage point increase in the ...
2021-04-12
Study: "Disproportionate Burden: Estimating the Cost of FAFSA Verification for Public Colleges and Universities"
Authors: Alberto Guzman-Alvarez (University of Pittsburgh), Lindsay C. Page (University of Pittsburgh)
This study was published today in Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis.
Main Findings:
The institutional compliance costs of the FAFSA verification mandate in 2014 totaled nearly $500 million, with the burden falling disproportionately on public institutions and community colleges in particular.
Twenty-two percent of an average community college's financial aid office ...
2021-04-12
Study: "21st Century Tracking and De Facto School Segregation: Excluding and Hoarding Access to College Prep"
Author: Heather E. Price (Marian University)
This study will be presented today at the AERA 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Session: Schools and Social Policy: Segregation, Housing, and Transportation
Date/Time: Monday, April 12, 9:30 a.m. - 11:00 a.m. ET
Main Finding:
The prevalence of Black, non-Hispanic students in high schools that do not offer any AP or IB courses in multi-school districts that fund college-prep curricula cannot be explained by resource or school factors.
Details:
Using national data, this study examined how the ...
2021-04-12
BEER-SHEVA, Israel...April 13, 2021 - Researchers at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) have for the first time identified new drug candidates based on molecules isolated from probiotic Kefir yogurt for combating pathogenic bacteria and treating various inflammatory conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and COVID-19 related cytokine storms.
The research, published in Microbiome, a leading peer-reviewed publication was led by Orit Malka, a Ph.D. student of Prof. Raz Jelinek, GU vice president and dean for research and development.
"These results are notable, since this is the first demonstration that virulence of human pathogenic bacteria can be mitigated ...
2021-04-12
Study: "Paying for Whose Performance? Teacher Incentive Pay and the Black-White Test Score Gap"
Authors: Andrew J. Hill (Montana State University), Daniel B. Jones (University of Pittsburgh)
This study was published today in Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis.
Key Finding:
Teacher incentive pay programs that focused on raising student achievement in high-need high schools expanded the test score gap between Black and White students by between 64 percent and 85 percent.
Details:
The Black-White test score gap has proven to be one of the most persistent phenomena in American education, for reasons that cannot be entirely explained by student characteristics or school and teacher quality.
Teacher performance pay is increasingly common in the United States ...
2021-04-12
GEOGRAFI A new study by a University of Copenhagen researcher finds that thawing permafrost in Alaska causes colder water in smaller rivers and streams. This surprising consequence of climate change could affect the survival of fish species in the Arctic's offshore waters.
Arctic stream
The study's researchers discovered that thawing permafrost causes groundwater to run deeper, where it becomes cooler than when it flows near the soil surface.
Rising global temperatures are causing frozen Arctic soil - permafrost - to thaw. In a new study, researchers have discovered something surprising: small ...
2021-04-12
Tsukuba, Japan - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disorder worldwide, affecting as much as a quarter of humanity. It is characterized by fat accumulation in liver cells and may progress to inflammation, cirrhosis and liver failure. Now, researchers at the University of Tsukuba reveal the positive effects, beyond the expected weight-loss benefit, of exercise on the liver.
NAFLD is associated with unhealthy behaviors such as overeating and a sedentary lifestyle. In Japan 41% of middle-aged men have NAFLD and 25% will progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and hepatic dysfunction.
Weight reduction is fundamental to NAFLD management. Unfortunately, ...
2021-04-12
Tsukuba, Japan--Liver disease, from metabolic and bacterial causes, is a growing concern. What connects these dots? The gut, or more specifically, bacteria in the gut. Bacteria that cause inflammation in the mouth are transported through the digestive tract to the gut and liver, where they can cause liver inflammation. Lipopolysaccharides, important structural molecules in some bacteria, act as endotoxins, producing systemic effects that can manifest as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Now, a multidisciplinary team from the University of Tsukuba show that exercise could be used to improve the oral environment in people with NAFLD, potentially leading to a new treatment for the disease.
These ...
2021-04-12
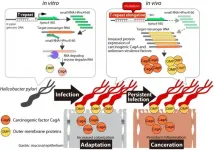
Osaka, Japan - Humans are exposed to many types of bacteria daily, the majority of which are harmless. However, some bacteria are pathogenic, which means they can cause disease. An extremely common pathogenic bacterial infection is Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in the stomach, where it can lead to chronic inflammation (gastritis), ulcers, and even cancer. A group of researchers from Osaka University have determined a specific molecular mechanism that H. pylori uses to adapt to growing in the human stomach for long periods of time.
In a report published in Nature Communications, this group found that a small RNA molecule called HPnc4160 plays a key role in how H. pylori invades the stomach ...
2021-04-12
Researchers at the University of Calgary and The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids), in Toronto, have discovered genetic risk factors for OCD that could help pave the way for earlier diagnosis and improved treatment for children and youth.
"Our group made the first finding of a genome-wide significant risk gene relevant to childhood OCD," says Dr. Paul Arnold, MD, PhD, co-principal investigator, a professor and director of The Mathison Centre for Mental Health Research & Education at the Cumming School of Medicine. "We've known that OCD runs in families, but we hadn't identified and validated specific genetic risks of OCD symptoms in children and youth until now."
The research drew on ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study finds medical financial hardship common in adult survivors of AYA cancers