(Press-News.org) New research shows that people who experience big dips in blood sugar levels, several hours after eating, end up feeling hungrier and consuming hundreds more calories during the day than others.
A study published today in Nature Metabolism, from PREDICT, the largest ongoing nutritional research program in the world that looks at responses to food in real life settings, the research team from King's College London and health science company ZOE (including scientists from Harvard Medical School, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Massachusetts General Hospital, the University of Nottingham, Leeds University, and Lund University in Sweden) found why some people struggle to lose weight, even on calorie-controlled diets, and highlight the importance of understanding personal metabolism when it comes to diet and health.
The research team collected detailed data about blood sugar responses and other markers of health from 1,070 people after eating standardized breakfasts and freely chosen meals over a two-week period, adding up to more than 8,000 breakfasts and 70,000 meals in total. The standard breakfasts were based on muffins containing the same amount of calories but varying in composition in terms of carbohydrates, protein, fat and fibre. Participants also carried out a fasting blood sugar response test (oral glucose tolerance test), to measure how well their body processes sugar.
Participants wore stick-on continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) to measure their blood sugar levels over the entire duration of the study, as well as a wearable device to monitor activity and sleep. They also recorded levels of hunger and alertness using a phone app, along with exactly when and what they ate over the day.
Previous studies looking at blood sugar after eating have focused on the way that levels rise and fall in the first two hours after a meal, known as a blood sugar peak. However, after analyzing the data, the PREDICT team noticed that some people experienced significant 'sugar dips' 2-4 hours after this initial peak, where their blood sugar levels fell rapidly below baseline before coming back up.
Big dippers had a 9% increase in hunger, and waited around half an hour less, on average, before their next meal than little dippers, even though they ate exactly the same meals.
Big dippers also ate 75 more calories in the 3-4 hours after breakfast and around 312 calories more over the whole day than little dippers. This kind of pattern could potentially turn into 20 pounds of weight gain over a year.
Dr Sarah Berry from King's College London said, "It has long been suspected that blood sugar levels play an important role in controlling hunger, but the results from previous studies have been inconclusive. We've now shown that sugar dips are a better predictor of hunger and subsequent calorie intake than the initial blood sugar peak response after eating, changing how we think about the relationship between blood sugar levels and the food we eat."
Professor Ana Valdes from the School of Medicine at the University of Nottingham, who led the study team, said: "Many people struggle to lose weight and keep it off, and just a few hundred extra calories every day can add up to several pounds of weight gain over a year. Our discovery that the size of sugar dips after eating has such a big impact on hunger and appetite has great potential for helping people understand and control their weight and long-term health."
Comparing what happens when participants eat the same test meals revealed large variations in blood sugar responses between people. The researchers also found no correlation between age, bodyweight or BMI and being a big or little dipper, although males had slightly larger dips than females on average.
There was also some variability in the size of the dips experienced by each person in response to eating the same meals on different days, suggesting that whether you're a dipper or not depends on individual differences in metabolism, as well as the day-to-day effects of meal choices and activity levels.
Choosing foods that work together with your unique biology could help people feel fuller for longer and eat less overall.
Lead author on the study, Patrick Wyatt from ZOE, notes, "This study shows how wearable technology can provide valuable insights to help people understand their unique biology and take control of their nutrition and health. By demonstrating the importance of sugar dips, our study paves the way for data-driven, personalized guidance for those seeking to manage their hunger and calorie intake in a way that works with rather than against their body."
Tim Spector, Professor of Genetic Epidemiology at King's College London and scientific co-founder of ZOE, concludes, "Food is complex and humans are complicated, but our research is finally starting to open up the black box between diet and health. We're excited to have been able to turn this cutting-edge science into an at-home nutrition and microbiome test so that everyone has the opportunity to discover their unique responses to food to best support their metabolism and gut health."
INFORMATION:
Between 2018 and 2020, 1,4 million EU citizens signed the petition 'End the Cage Age', with the aim of ending cage housing for farm animals in Europe. In response to this citizens initiative, the European Parliament requested a study by Utrecht University researchers on the possibilities to end cage housing. On 13 April, the scientists will present their report 'End the Cage Age - Looking for Alternatives' to the European Parliament.
In the report, behavioural biologists, animal scientists, veterinarians and ethicists from Utrecht University's Faculty of Veterinary Medicine analysed the available scientific literature on alternatives to cage housing. "Our focus was on laying hens and pigs" says Bas Rodenburg, Professor of Animal Welfare at Utrecht University. "Because these ...
Many women "risk" allowing natural grey hair to show in order to feel authentic, a new study shows.
Researchers from the University of Exeter surveyed women who chose not to dye their grey hair, and found a "conflict" between looking natural and being seen as competent.
Participants in the study - mostly from English-speaking countries - belonged to online groups whose members allow their natural grey hair to show, and the researchers noted "solidarity and sisterhood" among these women.
"We are all constrained by society's norms and expectations when it comes to appearance, but expectations are more rigorous for women - especially older women," said lead author Vanessa Cecil, of the University of Exeter.
"The 'old woman' is an undesirable character in Western societies, being seen ...
Why is sugar not transparent? Because light that penetrates a piece of sugar is scattered, altered and deflected in a highly complicated way. However, as a research team from TU Wien (Vienna) and Utrecht University (Netherlands) has now been able to show, there is a class of very special light waves for which this does not apply: for any specific disordered medium--such as the sugar cube you may just have put in your coffee--tailor-made light beams can be constructed that are practically not changed by this medium, but only attenuated. The light beam penetrates the medium, and a light pattern arrives on the other ...
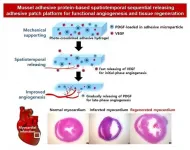
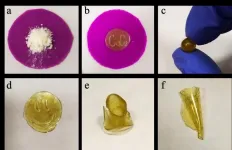
Blood vessels deliver nutrients and oxygen to each organ in our body. They are difficult to completely restore to their original conditions once damaged by myocardial infarction or severe ischemic diseases. This is because various angiogenic growth factors must be applied sequentially in order to restore the vascular structure. Recently, a research team at POSTECH has bioengineered a novel adhesive patch platform that can efficiently deliver blood vessel-forming growth factors spatiotemporally using mussel adhesive protein (MAP), a bio-adhesive material that is made from mussels harmless to humans.
A POSTECH research team led by Professor Hyung Joon ...
Squirrels and other tree-dwelling rodents evolved to have bigger brains than their burrowing cousins, a study suggests.
This greater brain power has given them key abilities needed to thrive in woodland habitats, including better vision and motor skills, and improved head and eye movements, researchers say.
Scientists have shed light on how the brains of rodents - a diverse group that accounts for more than 40 per cent of all mammals - have changed since they evolved around 50 million years ago.
Few studies looking into factors affecting brain size in mammals have taken account ...
New Orleans, LA - A study led by Hui-Yi Lin, Ph.D., Professor of Biostatistics, and a team of researchers at LSU Health New Orleans Schools of Public Health and Medicine has found that adequate levels of five antioxidants may reduce infection with the strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) associated with cervical cancer development. Findings are published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Although previous studies have suggested that the onset of HPV-related cancer development may be activated by oxidative stress, the association had not been clearly understood. This study evaluated associations between 15 antioxidants and vaginal HPV infection status -- no, low-risk, and oncogenic/high-risk HPV (HR-HPV) -- in 11,070 women aged 18-59 who participated ...
In 2018, Pompeu Fabra University launched its Planetary Wellbeing initiative, a long-term institutional strategy spurred by the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) and based on the Planetary Health project promoted by the Rockefeller Foundation and The Lancet.
Fifteen academics and public officials, led by the three directors of the initiative, Josep Maria Antó, scientific director of ISGlobal; Josep Lluís Martí, UPF vice-rector for innovation projects, and Jaume Casals, UPF rector, are the authors of an academic article published in the journal ...
Cancer is one of the top causes of death worldwide. The cancer burden is related not only to genetic predisposition, but also to environmental pollution and socioeconomic factors such as lifestyle. Consequently, the burden of this disease is not uniform across all countries. In fact, the public health of China, a country known for the rapid change in its development status in the last few decades, has undergone a paradigm shift with respect to cancer incidence and mortality.
To better understand the cancer burden of the country, a team of researchers from Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College reviewed the data of GLOBOCAN 2020, an online database of cancer incidence and mortality compiled by the International Agency for Research ...
Researchers at the Laboratory of Cluster Catalysis at St Petersburg University have synthesised polymers from biomass. What makes them different is that they can be easily recycled.
Today, our life is simply unthinkable without polymers. Plastics, fibres, films, paint and lacquer coating - they are all polymers. We use them both in our everyday life and in industry. Yet the goods made from polymers, e.g. bottles, bags, or disposable tableware, are used just once or for a short period of time before they are thrown away. Due to the chemical compounds that they may release during recycling, they pose a real threat to our environment.
There ...
Study: "Students Enrolled in Late-Start-Time Districts Report Higher Academic Achievement and Sleeping More"
Authors: Julio Caesar (Bloomington Public Schools), Rik Lamm (University of Minnesota), Michael C. Rodriguez (University of Minnesota), David J. Heistad (Bloomington Public Schools)
This study will be presented today at the AERA 2021 Annual Meeting.
Session: Organizational Effects Examining Academic Achievement and Student Support
Date/Time: Saturday, April 10, 2:30 p.m. - 4:00 p.m. ET
Main Finding:
Later school start times are linked ...