First patient-derived organoid model for cervical cancer
2021-04-13
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the group of Hans Clevers (Hubrecht Institute) developed the first patient-derived organoid model for cervical cancer. They also modelled the healthy human cervix using organoids. In close collaboration with the UMC Utrecht, Princess Máxima Center for pediatric oncology and the Netherlands Cancer Institute, the researchers used the organoid-based platform to study sexually transmitted infections for a herpes virus. The model can potentially also be used to study the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is one of the main causes of cervical cancer. The results were published in Cell Stem Cell on the 13th of April.
Cervical cancer is a common gynecological malignancy, often caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). However, good models to study human cervical tissues were lacking. Reason enough for the group of Hans Clevers to develop an organoid-based model for the healthy cervix and associated malignancies including cervical cancer. The project was conducted in close collaboration with researchers from the UMC Utrecht, the Princess Máxima Center for pediatric oncology and the Netherlands Cancer Institute.
Mini organs
The researchers obtained human cervical tissue from either healthy patients or patients with different types of cervical cancer. From these tissues they grew organoids; tiny 3D structures of about half a millimeter in size that closely mimic organ function. The organoids derived from healthy tissue closely resemble the tissue architecture and gene expression profiles of the actual human cervix. Therefore, the organoids hold great promise for studying what happens when a virus infects the human cervix. Kadi Lõhmussaar, first author on the paper, explains: "For our study, we used a herpes virus - herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) - to demonstrate the potential of the model for research into sexually transmitted infections."
Prospectively, the model could also be applied to study the human papillomavirus (HPV) and how that virus causes cancer. "Cervical cancer is often caused by HPV-infection, but research into this virus was complicated as the virus is difficult to culture in the lab. Our new model might be able to overcome this obstacle," says Lõhmussaar.
Tumoroids
The organoids grown from cancerous tissue - also called tumoroids - closely resemble actual tumors. They show mutation- and gene expression profiles that are typical for cancer and they carry similar morphological abnormalities. The researchers also found that the tumoroids respond differently to common chemotherapeutics, paving way to the era of precision medicine. "Hopefully in the future, we can predict which chemotherapy will work best for specific patients based on results obtained in the tumoroids."
Biobanks
The organoids can be derived via patients' Pap-brush material. The study shows that the tiny bit of tissue obtained from this procedure is sufficient for starting an organoid culture. This opens up the possibility to not only look at fixed cells under the microscope, but also do in-depth analyses of the living cells that might be on their way to become cancerous. Additionally, given that the Pap-brush is non-invasive for patients, the new organoid model provides the research community with a relatively easy access to the tissue of interest and a new model system. Lõhmussaar: "This will hopefully facilitate a rapid generation of additional organoid-based cervical cancer biobanks worldwide. That would offer new means for advancing research into cervical biology and associated diseases."
INFORMATION:
Publication
'Patient-derived organoids as a pioneering platform to study cervical cancer'. Kadi Lõhmussaar, Rurika Oka, Jose Espejo Valle-Inclan, Milou H. H. Smits, Hila Wardak, Jeroen Korving, Harry Begthel, Natalie Proost, Marieke van de Ven, Onno W. Kranenburg, Trudy G. N. Jonges, Ronald P. Zweemer, Sebastiaan Veersema, Ruben van Boxtel, Hans Clevers. Cell Stem Cell (2021).
Hans Clevers is group leader at the Hubrecht Institute and the Princess Máxima Center for Pediatric Oncology, professor of Molecular Genetics at Utrecht University, and Oncode Investigator.
About the Hubrecht Institute
The Hubrecht Institute is a research institute focused on developmental and stem cell biology. It encompasses 21 research groups that perform fundamental and multidisciplinary research, both in healthy systems and disease models. The Hubrecht Institute is a research institute of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW), situated on Utrecht Science Park. Since 2008, the institute is affiliated with the UMC Utrecht, advancing the translation of research to the clinic. The Hubrecht Institute has a partnership with the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). For more information, visit http://www.hubrecht.eu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-13
(Boston)--How could studying gastrointestinal cells help the fight against COVD-19, which is a respiratory disease? According to a team led by Gustavo Mostoslavsky, MD, PhD, at the BU/BMC Center for Regenerative Medicine (CReM) and Elke Mühlberger, PhD, from the National Emerging Infectious Diseases Laboratories (NEIDL) at Boston University, testing how SARS-CoV-2 affects the gut can potentially serve to test novel therapeutics for COVID-19.
In order to study SARS-CoV-2, models are needed that can duplicate disease development in humans, identify potential targets and enable drug testing. BU researchers have created human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC)-derived intestinal organoids or 3-D models that can be infected and replicated ...
2021-04-13
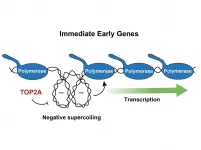
The (when stretched) two-metre-long DNA molecule in each human cell is continuously being unpacked and packed again to enable the expression of genetic information. When genes must be accessed for transcription, the DNA double helix unwinds and the strands separate from each other so that all the elements needed for gene expression can access the relevant DNA region. This process results in the accumulation of DNA supercoiling that needs to be resolved. A study recently published by Felipe Cortés, Head of the Topology and DNA Breaks Group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), and the members of his team, in cooperation with Silvia Jimeno González, Professor ...
2021-04-13
Understanding the effects of specific mutations in gene regulatory regions - the sections of DNA and RNA that turn genes on and off - is important to unraveling how the genome works, as well as normal development and disease. But studying a large variety of mutations in these regulatory regions in a systematic way is a monumental task. While progress has been made in cell lines and yeast, few studies in live animals have been done, especially in large populations.
Experimental and computational biologists at the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC) have teamed up to establish an approach to induce thousands of different mutations in up to 1 million ...
2021-04-13
Electrochemical processes could be used to convert CO2 into useful starting materials for industry. To optimise the processes, chemists are attempting to calculate in detail the energy costs caused by the various reaction partners and steps. Researchers from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and Sorbonne Université in Paris have discovered how small hydrophobic molecules, such as CO2, contribute to the energy costs of such reactions by analysing how the molecules interact in water at the interface. The team describes the results in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, PNAS for short, published online on 13 April 2021.
To conduct the ...
2021-04-13
The time children and adolescents spend on screen time entertainment -computers, mobile phones, television and video games- adversely affects their eating habits. This is the main conclusion drawn from a research carried out by EpiPHAAN (Epidemiology, Physical Activity, Accelerometry and Nutrition) research group of the University of Malaga, which further establishes that parents' education level is also associated with the adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
This research was conducted within the PASOS Study -Physical Activity, Sedentarism, lifestyles and Obesity in Spanish youth- of Gasol Foundation, which analyzed more than ...
2021-04-13
Cancer patients from the UK were 1.5 times more likely to die following a diagnosis with COVID-19 than cancer patients from European countries.
This is the finding of a study of over 1000 patients - 924 from European countries and 468 from the UK - during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. The research team, led by Imperial College London, say the study highlights the need for UK cancer patients to be prioritised for vaccination.
The study tracked data between 27 February to 10 September 2020, across 27 centres in six countries: Italy, Spain, France, Belgium, Germany and the UK.
The results, published in the European Journal of Cancer, showed that 30 days after a COVID-19 diagnosis, 40.38 per cent of UK cancer patients had died, versus 26.5 per cent of ...
2021-04-13
Artificial intelligence could be one of the keys for limiting the spread of infection in future pandemics. In a new study, researchers at the University of Gothenburg have investigated how machine learning can be used to find effective testing methods during epidemic outbreaks, thereby helping to better control the outbreaks.
In the study, the researchers developed a method to improve testing strategies during epidemic outbreaks and with relatively limited information be able to predict which individuals offer the best potential for testing.
"This can be a first step towards society ...
2021-04-13
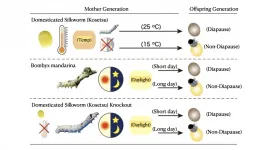
Diapause is a phenomenon in which animals and insects foresee changes in the environment and actively reduce metabolism, or halt regular differentiation and development. It is an adaptation strategy for adverse environments such as surviving winters, but also to encourage uniform growth of the generational group. By knocking out genes that allow the silkworm to detect temperature, researchers at Shinshu University et al. found that the silk moth diapause changes from temperature to photoperiod, or day length. This is not only valuable as an elucidation of the molecular mechanism in the environmental response mechanism of organisms such as insects, but also a very important finding in exploring the process of domestication of silk ...
2021-04-13
Scientists from the Skoltech Space Center (SSC) have developed nanosatellite interaction algorithms for scientific measurements using a tetrahedral orbital formation of CubeSats that exchange data and apply interpolation algorithms to create local maps of physical measurements in real time. The study presents an example of geomagnetic field measurement, which shows that these data can be used by other satellites for attitude control and, therefore, provided on a data-as-a-service basis. The research was published in the journal Advances in Space Research.
SSC is the research ...
2021-04-13
Despite increasing concern over the intrusion of algorithms in daily life, people may be more willing to trust a computer program than their fellow humans, especially if a task becomes too challenging, according to new research from data scientists at the University of Georgia.
From choosing the next song on your playlist to choosing the right size pants, people are relying more on the advice of algorithms to help make everyday decisions and streamline their lives.
"Algorithms are able to do a huge number of tasks, and the number of tasks that they are able to do is expanding practically every day," said Eric Bogert, a Ph.D. student in the Terry College of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] First patient-derived organoid model for cervical cancer