Grave goods show gendered roles for Neolithic farmers
2021-04-14
(Press-News.org) Grave goods, such as stone tools, have revealed that Neolithic farmers had different work-related activities for men and women.
Researchers at the University of York analysed 400 stone objects found in graves at cemetery sites across Europe and noted there were differences in size, weight, and raw material dependent on whether the body was a male or a female.
Archaeologists had previously thought that polished stone tools in this period were used for woodworking, but analysis now shows a much wider range of tasks, with different activities for men and women.
The tools found in female graves were most likely used for the working of animal skins and hide, and tools for the men were associated with hunting and potential conflict. The researchers concluded that the different roles of men and women were a crucial part of the transition to farming in human societies.
Dr Penny Bickle, from the University of York's Department of Archaeology, said: "The gendered roles, far from being a sign of early gender inequalities, actually shows how dynamic farming societies were and how aware they were of the different skills of members of their community.
"The tasks attributed to women were difficult manual work and complemented the work of the men as equal contributors to their community. The fact that you see these objects in the graves of men and women, demonstrates how marked out and valued they were for these jobs."
The evidence also demonstrated that these roles would have varied depending on where the community was from. In eastern areas, there is evidence to suggest women moved around more than men, and regardless of sex, shell ornamentation and jewellery were carried in their graves. In the west, men moved around more and had tools more associated with hunting than women.
Alba Masclans Latorre, a postdoctoral researcher from Barcelona and the lead on the study, said: "Women's roles and contributions to these very early human societies are often downplayed; but here we show that they took an active role in shaping early farming communities.
"So important was their role that these activities were chosen to mark them out in death, but we see the same in the graves of men, suggesting that there were indeed specific gendered roles, but all of these jobs were hugely significant to the proper functioning of their society."
INFORMATION:
The research, funded by the Fyssen Foundation, is published in the journal PLOS ONE.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-14
Researchers at HSE University have identified the genes that play a crucial role in breast cancer metastasis. The results of the study were published in the journal PLOS ONE.
Every human cell includes a huge number of various molecules: DNA, RNA, proteins, etc. One of the essential classes of molecules that interact with each other are microRNAs, along with their target genes and transcription factors. MicroRNAs are small molecules, which can directly reduce the concentration (expression) of target genes, while transcription factors are able to both increase and reduce the expression of ...
2021-04-14
A new state-by-state analysis shows a statistical association between high adherence to mask wearing and reduced rates of COVID-19 in the U.S. Charlie Fischer and colleagues at the Boston University School of Public Health in Massachusetts present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on April 14.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, different states have enacted different policies on mask wearing, with some states having no mask requirements and others requiring masks in all public spaces. Understanding the link between mask wearing and COVID-19 rates could help inform policies to mitigate stress on healthcare systems, economic instability, and death.
To help clarify the effects of mask wearing, Fischer and colleagues examined publicly ...
2021-04-14
Combining immune-boosting drugs with radiation and surgery increased the survival and anticancer immune response in mouse models of mesothelioma in preclinical research by Princess Margaret Cancer Centre researchers.
In a series of exciting experiments using mouse models of mesothelioma cancer, researchers found that combining two immunotherapy drugs can amplify the anti-tumour response first triggered by a short course of radiation, conferring long-lasting control and resistance against cancer. These response rates are improved further by adding surgery to remove the remaining tumour.
Better treatments are urgently needed for mesothelioma patients, as ...
2021-04-14
INDIANAPOLIS, IN AND BERKELEY, CA (April 14, 2021) - Researchers from Indiana University School of Medicine and OMGYES have conducted the first-ever, large-scale, nationally representative study focused on women's techniques for increasing their own pleasure from vaginal penetration. The findings, published today in the scientific journal, PLOS ONE, identify and name four distinct methods: Angling, Pairing, Rocking and Shallowing.
The research was led by Dr. Devon J. Hensel, Associate Professor of Research at Indiana University School of Medicine, and Dr. Christiana von Hippel, an OMGYES Research Scientist.
"For the first time, we have ...
2021-04-14
Berkeley -- Engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have created a tiny wireless implant that can provide real-time measurements of tissue oxygen levels deep underneath the skin. The device, which is smaller than the average ladybug and powered by ultrasound waves, could help doctors monitor the health of transplanted organs or tissue and provide an early warning of potential transplant failure.
The technology, created in collaboration with physicians at the University of California, San Francisco, also paves the way for the creation of a variety of miniaturized sensors that could track other key biochemical markers in the body, ...
2021-04-14
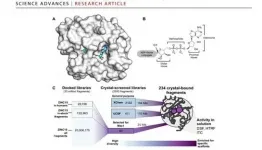
New research published in Science Advances provides a template for how to develop directly-acting antivirals with novel modes of action, that would combat COVID-19 by suppressing the SARS-CoV-2 viral infection. The study focused on the macrodomain part of the Nsp3 gene product that SARS-CoV-2 uses to suppress the host cell's natural antiviral response. This part of the virus's machinery, also known as Mac1, is essential for its reproduction: previous studies have shown that viruses that lack it cannot replicate in human cells, suggesting that blocking ...
2021-04-14
"Family clustering is a confirmed phenomenon associated with Covid-19, and harrowing stories of this disease ravaging families continue to be reported," a new article explains in the March-April issue of the Hastings Center Report. In one extreme example, 28 extended family members in California reportedly tested positive for Covid-19. Two of the family members who quarantined together required hospitalization, and one of them died from the infection. In family clustering cases, multiple loved ones may suffer from the symptoms of Covid-19 and be hospitalized, in quarantine, or recovering; and family ...
2021-04-14
The slurred speech, poor coordination, and sedative effects of drinking too much alcohol may actually be caused by the breakdown of alcohol products produced in the brain, not in the liver as scientists currently think. That is the finding of a new study led by researchers from the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. It was published recently in the journal Nature Metabolism and provides new insights into how alcohol may affect the brain and the potential for new treatments to treat alcohol misuse.
It is well known that the liver is the major organ ...
2021-04-14
One of the technical challenges the current data revolution faces is finding an efficient way to route the data. This task is usually performed by electronic switches, while the data itself is transferred using light confined in optical waveguides. For this reason, conversion from an optical to an electronic signal and back-conversion are required, which costs energy and limits the amount of transferable information. These drawbacks are avoidable with a full optical switch operation. One of the most promising approaches is based on microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), thanks ...
2021-04-14
Most people by now have memorized the public health guidelines meant to help minimize transmission of COVID-19: wash your hands, wear a mask, keep six feet apart from others. That part is easy.
What some may not realize is that upholding these guidelines in certain urban areas can present new challenges.
For example, how are you supposed to stay six feet apart from other people when the standard width of a sidewalk is only four feet? What do you do when you want to cross an intersection that requires pressing a button to activate the pedestrian signal, but you are avoiding touching any surfaces?
The COVID-19 pandemic has drastically altered the way individuals interact with other people and their environment, but some public health guidelines meant to protect ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Grave goods show gendered roles for Neolithic farmers