(Press-News.org) April 15, 2021 - Decades after their days on the gridiron, middle-aged men who played football in high school are not experiencing greater problems with concentration, memory, or depression compared to men who did not play football, reports a study in Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Men who played high-school football did not report worse brain health compared with those who played other contact sports, noncontact sports, or did not participate in sports during high school," according to the new research, led by Grant L. Iverson, PhD, of Harvard Medical School. The study offers reassurance that playing high-school football is not, in itself, a risk factor for cognitive or mood disorders or other problems that have been linked to a history of repeated concussions in professional football players.
No increase in cognitive, mood, or pain problems in high-school football players
The researchers analyzed responses to an online survey completed by 407 men aged 35 to 55 years. Of these, 123 reported playing football in high school. The study excluded men with recent concussions or those who played semi-professional football.
Rates of a wide range of brain health problems were assessed for the ex-football players, compared to men who played other contact sports, non-contact sports, or no sports. Men who played contact sports, especially football, had more concussions than the other two groups: more than 80 percent of men who played high-school football reported at least one concussion.
Overall, the former football players were no more likely to have problems with brain health in their mid-thirties to mid-fifties. High-school sports experience was unrelated to problems with depression, anxiety, or anger; concentration or memory problems; or headaches, migraines, neck or back pain, or chronic pain. For football and other contact sports, rates of brain health problems were unrelated to years playing sports.
There were a few significant differences between groups. Men who played high-school football were more likely to report sleep problems: 39 percent, compared to about 20 to 30 percent of the other groups. Ex-football players were also more likely to be prescribed medications for headaches or chronic pain.
The study identified several factors that predicted an increased rate of memory problems, including sleep difficulties, anxiety, history of concussions, and feeling depressed. Although some of these factors were more common among former football players, playing football itself was not a significant predictor.
Reports of long-term neurological abnormalities among former National Football League (NFL) players have raised concerns over the brain health of men who played football at the high-school level. Previous studies have found no increase in mental health, cognitive, or mood problems in former high-school football players. The new research - partly supported by the NFL - is the first to focus on middle-aged men.
Dr. Iverson and colleagues emphasize that, "without question," some men who played high-school football will develop problems with psychological health and cognitive function later in life. However, these risks "do not seem to be greater than the rates in men who did not play football."
The researchers note that there are strong associations between depression and anxiety, headaches and migraine, chronic pain, and memory problems, which commonly occur together and are "mutually amplifying." Dr. Iverson and colleagues conclude, "[E]vidence-based treatment and rehabilitation for these problems can substantially reduce symptoms and improve functioning and quality of life."
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "High-School Football and Midlife Brain Health Problems."
DOI: 10.1097/JSM.0000000000000898
About Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine
Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine is an international refereed journal published for clinicians with a primary interest in sports medicine practice. The journal publishes original research and reviews covering diagnostics, therapeutics, and rehabilitation in healthy and physically challenged individuals of all ages and levels of sport and exercise participation. CJSM is the official journal of the American Medical Society for Sports Medicine, the American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine, the Australasian College of Sports Physicians, and the Canadian Academy of Sport Medicine.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the clinicians, nurses, accountants, lawyers, and tax, finance, audit, risk, compliance, and regulatory sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with advanced technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2020 annual revenues of €4.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 19,200 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
For more information, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive type of breast cancer with a high fatality rate. Currently, chemotherapy is the major treatment option, but the clinical result is unsatisfactory. A research team led by biologists at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has identified and characterised a set of specific super-enhancers that stimulate the activity of the related critical cancer genes. The research has also discovered that the deletion of certain specific super-enhancers can reduce tumour cell growth. The latest findings may help discover new effective drug targets for TNBC patients to improve their survival chance.
Traditionally, cancer research ...
A key portion of MIT's campus overlaps with Kendall Square, the bustling area in East Cambridge where students, residents, and tech employees scurry around in between classes, meetings, and meals. Where are they all going? Is there a way to make sense of this daily flurry of foot traffic?
In fact, there is: MIT Associate Professor Andres Sevtsuk has made Kendall Square the basis of a newly published model of pedestrian movement that could help planners and developers better grasp the flow of foot traffic in all cities.
Sevtsuk's work emphasizes the functionality of a neighborhood's elements, above and beyond its physical form, making the model one that could be ...
A new scientific discovery in Australia by Flinders University has recorded for the first time how ghost currents and sediments can 'undo' the force of gravity.
The new theory, just published in the Journal of Marine Systems, helps explain obscure events in which suspended sediment particles mysteriously move upward, not downward, on the slope of submarine canyons of the deep sea.
While this activity seems to contradict the laws of gravity, Flinders University physical oceanographer Associate Professor Jochen Kaempf has found an answer, devising the first scientific explanation of the observed upslope sediment transport.
"To put it simply, the vehicle of this transport are currents that, while carrying ...
Many long for a return to a post-pandemic "normal," which, for some, may entail concerts, travel, and large gatherings. But how to keep safe amid these potential public health risks?
One possibility, according to a new study, is dogs. A proof-of-concept investigation published today in the journal PLOS ONE suggests that specially trained detection dogs can sniff out COVID-19-positive samples with 96% accuracy.
"This is not a simple thing we're asking the dogs to do," says Cynthia Otto, senior author on the work and director of the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine Working Dog Center. "Dogs have to ...
Do freshwater snails make good tennis players? One of them certainly has the name for it.
Enter Travunijana djokovici, a new species of aquatic snail named after famous Serbian tennis player Novak Djokovic.
Slovak biospeleologist Jozef Grego and Montenegrin zoologist Vladimir Pesic of the University of Montenegro discovered the new snail in a karstic spring near Podgorica, the capital of Montenegro, during a field trip in April 2019. Their scientific article, published in the open-access, peer-reviewed journal Subterranean Biology, says they named it after Djokovic "to acknowledge his inspiring enthusiasm and energy."
"To discover some of the world's rarest animals that inhabit the unique underground habitats of the Dinaric karst, to reach inaccessible cave and spring habitats ...
WASHINGTON (April 15, 2021) -- Clusters of a virus known to cause stomach flu are resistant to detergent and ultraviolet disinfection, according to new research co-led by END ...
Since the 1970s, the Standard Model of Physics has served as the basis from which particle physics are investigated. Both experimentalists and theoretical physicists have tested the Standard Model's accuracy, and it has remained the law of the land when it comes to understanding how the subatomic world behaves.
This week, cracks formed in that foundational set of assumptions. Researchers of the "Muon g-2" collaboration from the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) in the United States published further experimental findings that show that muons--heavy subatomic relatives of electrons--may have a larger "magnetic moment" than earlier Standard Model estimates had predicted, indicating that an unknown particle or force might be influencing ...
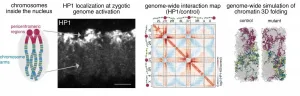
The DNA molecule is not naked in the nucleus. Instead, it is folded in a very organized way by the help of different proteins to establish a unique spatial organization of the genetic information. This 3D spatial genome organization is fundamental for the regulation of our genes and has to be established de novo by each individual during early embryogenesis. Researchers at the MPI of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg in collaboration with colleagues from the Friedrich Mischer Institute in Basel now reveal a yet unknown and critical role of the protein HP1a in the 3D genome re-organization after fertilisation. The study published in the scientific journal Nature identifies HP1a as an epigenetic regulator that is involved in establishing ...
Leesburg, VA, April 15, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting found that as the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 transitions from a numerical score to pass or fail--as early as January 2022--radiology residency program directors will likely rely on USMLE Step 2 Clinical Knowledge (CK) scores as an objective and standardized metric to screen applicants.
"However," wrote lead investigator Rebecca Zhang of the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Baltimore, "program directors remain unsure whether they will ...
Leesburg, VA, April 15, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting found that in the setting of a high pretest probability of COVID-19 infection or with a quick turnaround of the rapid real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) COVID-19 test, a chest x-ray (CXR) scoring system may be used prospectively to predict patient outcomes.
"We developed an accurate and reliable tool for classifying COVID-19 severity, which can be used both at the attending chest radiologist and junior resident level. This study identifies the laboratory, clinical and radiographic data that predict important patient outcomes such as death, intubation, and the need for chronic renal replacement ...