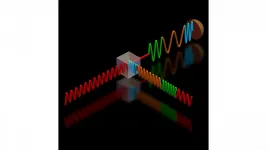
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, April 20, 2021 -- Fiber optic technology is the holy grail of high-speed, long-distance telecommunications. Still, with the continuing exponential growth of internet traffic, researchers are warning of a capacity crunch.
In AVS Quantum Science, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the University of Maryland show how quantum-enhanced receivers could play a critical role in addressing this challenge.
The scientists developed a method to enhance receivers based on quantum physics properties to dramatically increase network performance while significantly reducing the error bit rate (EBR) and energy consumption.
Fiber optic technology relies on receivers to detect optical signals and convert them into electrical signals. The conventional detection process, largely as a result of random light fluctuations, produces "shot noise," which decreases detection ability and increases EBR.
To accommodate this problem, signals must continually be amplified as pulsating light becomes weaker along the optic cable, but there is a limit to maintaining adequate amplification when signals become barely perceptible.
Quantum-enhanced receivers that process up to two bits of classical information and can overcome the shot noise have been demonstrated to improve detection accuracy in laboratory environments. In these and other quantum receivers, a separate reference beam with a single-photon detection feedback is used so the reference pulse eventually cancels out the input signal to eliminate the shot noise.
The researchers' enhanced receiver, however, can decode as many as four bits per pulse, because it does a better job in distinguishing among different input states.
To accomplish more efficient detection, they developed a modulation method and implemented a feedback algorithm that takes advantage of the exact times of single photon detection. Still, no single measurement is perfect, but the new "holistically" designed communication system yields increasingly more accurate results on average.
"We studied the theory of communications and the experimental techniques of quantum receivers to come up with a practical telecommunication protocol that takes maximal advantage of the quantum measurement," author Sergey Polyakov said. "With our protocol, because we want the input signal to contain as few photons as possible, we maximize the chance that the reference pulse updates to the right state after the very first photon detection, so at the end of the measurement, the EBR is minimized."
INFORMATION:
The article "Practical quantum-enhanced receivers for classical communication" is authored by Ivan Burenkov, M.V. Jabir, and Sergey V. Polyakov. The article appears in AVS Quantum Science (DOI: 10.1116/5.0036959) and can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1116/5.0036959.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
AVS Quantum Science, co-published by AIP Publishing and AVS, is a truly intradisciplinary journal that reaches from its foundations in quantum science into a breadth of areas from condensed matter and atomic, molecular and optical physics, to biology, chemistry, and materials science, as well as computer science and engineering. The journal places a strong emphasis on focused and comprehensive reviews and features perspectives and original research.
ABOUT AVS
AVS is an interdisciplinary, professional society with some 4,500 members worldwide. Founded in 1953, AVS hosts local and international meetings, publishes four journals, serves members through awards, training and career services programs and supports networking among academic, industrial, government, and consulting professionals. Its members come from across the fields of chemistry, physics, biology, mathematics, engineering and business and share a common interest in basic science, technology development and commercialization related to materials, interfaces, and processing. https://www.avs.org
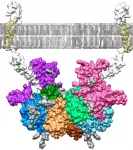
Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany and the Institute of Molecular Biology of Barcelona in Spain have discovered how the blood plasma protein fetuin-B binds to the enzyme meprin β and used a computer model to visualize their findings. These results could lead to the development of new drugs to treat serious diseases such as Alzheimer's and cancer. Meprin β releases proteins from cell membranes, thus controlling important physiological functions in the human body. However, a dysregulation of this process can trigger the development of Alzheimer's and ...
Earthquake early warnings can be delivered successfully using a small network of off-the-shelf smartphones attached to building baseboards, according to a study conducted in Costa Rica last year.
In his presentation at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)'s 2021 Annual Meeting, Ben Brooks of the U.S. Geological Survey said the ASTUTI (Alerta Sismica Temprana Utilizando Teléfonos Inteligentes) network of more than 80 stations performed comparably to scientific-grade warning systems.
During six months' of ASTUTI operation, there were 13 earthquakes that caused noticeable ...
The famous 1700 Cascadia earthquake that altered the coastline of western North America and sent a tsunami across the Pacific Ocean to Japan may have been one of a sequence of earthquakes, according to new research presented at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)'s 2021 Annual Meeting.
Evidence from coastlines, tree rings and historical documents confirm that there was a massive earthquake in the U.S. Cascadia Subduction Zone on 26 January 1700. The prevailing hypothesis is that one megathrust earthquake, estimated at magnitude 8.7 to 9.2 and involving the entire tectonic plate boundary in the region, was responsible ...
When hydraulic fracturing operations ground to a halt last spring in the Kiskatinaw area of British Columbia, researchers expected seismic quiescence in the region. Instead, hundreds of small earthquakes occurred for months after operations shut down, according to a new study.
In her presentation at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)'s 2021 Annual Meeting, Rebecca Salvage of the University of Calgary said about 65% of these events could not be attributed to either natural seismicity or active fluid injection from hydraulic fracturing operations.
Salvage and her colleagues instead suggest the latent earthquakes may be the result of aseismic slip, driven by fluid from previous hydraulic fracture injections keeping rock pore pressures elevated.
"Because there are lots of faults ...
BOSTON - New research from Boston Medical Center identifies elevated mortality risk for women with back pain when compared to women without back pain. Back pain was not associated with mortality among men indicating long-term consequences of back pain may differ by sex. The overall findings suggest that mild back pain (pain that does not keep a person from exercising or doing daily activities) is unlikely to impact the length of one's life, but risk of mortality was increased among adults with more severe back pain. Published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine, this new study raises ...
The lack of accountability, poor communication and insufficient planning plaguing the government’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic -- especially in its early months -- have roots in how the nation responded to 9/11, Hurricane Katrina and the H1N1 swine flu, a new study involving the University of Washington found.
Focusing on the way government agencies assemble and allocate resources - the procurement system - researchers said the successes and shortcomings of responses to other large-scale crises show that a more centralized approach can achieve goals faster and more effectively.
"In the moment of disasters, we prioritize saving ...
Using a widely known field of mathematics designed mainly to study how digital and other forms of information are measured, stored and shared, scientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine and Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center say they have uncovered a likely key genetic culprit in the development of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
ALL is the most common form of childhood leukemia, striking an estimated 3,000 children and teens each year in the United States alone.
Specifically, the Johns Hopkins team used "information theory," applying an analysis that relies on strings of zeros and ones -- the binary system of symbols common to computer languages and codes -- to identify variables or outcomes of a particular process. In the case of human ...
BOSTON - Recent research links certain cells that line the human airway with different infant diseases. The work, which is published in Cell Reports and was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), could lead to new prevention and treatment strategies for these conditions.
The human airway--from the windpipe to the lungs--is lined with epithelial cells, including a type called pulmonary neuroendocrine cells (PNECs) that communicate with the nervous system and secrete different factors and hormones. Increased numbers and clusters of PNECs have been observed in various breathing-related illnesses, but the cells' roles in health ...
WASHINGTON, April 20, 2021 -- Forensic science includes the analysis of blood backspatter involved in gunshot wounds, but scientific questions about the detailed role of fluids in these situations remained unresolved.
To search for answers about how blood droplets from a gunshot wound can reverse direction while in flight, University of Illinois at Chicago and Iowa State University researchers explored the influence of propellant gases on blood backspatter.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, the researchers report using numeric modeling to capture the behavior of gun muzzle gases and predict the reversal of blood droplet flight, which was captured experimentally. Their experiments also show the breakup of blood droplets, ...
WASHINGTON, April 20, 2021 -- In 2009, music producer Phil Spector was convicted for the 2003 murder of actress Lana Clarkson, who was shot in the face from a very short distance. He was dressed in white clothes, but no bloodstains were found on his clothing -- even though significant backward blood spatter occurred.
How could his clothing remain clean if he was the shooter? This real-life forensic puzzle inspired University of Illinois at Chicago and Iowa State University researchers to explore the fluid physics involved.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, the researchers present theoretical results revealing an interaction of the incoming vortex ring of propellant muzzle gases with backward blood spatter.
A detailed analytical theory of ...