(Press-News.org) Using a novel molecular-data-storage technique, researchers at the University of Texas at Austin have encoded a quote from Jane Austen's classic novel Mansfield Park in a series of oligomers, which a third party could read back without prior knowledge of the structures that encoded the passage. The findings, published April 21st in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science, illustrate a method to encode data that allows for greater information density than DNA-based approaches and that relies on urethane-like plastics--highly accessible and structurally modifiable chemical feedstocks--instead of nucleic acids.
"This work is another step toward the long-term goal of using synthetic sequence-defined polymers for information storage," says Eric Anslyn, a chemistry professor at the University of Texas at Austin and an author of the study. "It sets the stage and hopefully inspires further work towards the practical use of molecules to usefully store information."
As society churns out enormous quantities of data, scientists are continuously seeking dense, durable, and cost-effective ways to store information. Molecular approaches offer a particularly appealing solution because they can retain information at far higher densities than leading silicon-based technologies.
"In theory, any kind of information can be encoded in polymers," says Anslyn. "In practical terms, we have seen books and pictures, among many other things, stored in molecules."
However, despite their enormous information-storage potential, polymers such as plastics have lacked sufficiently inexpensive, efficient, and large-scale reproducible approaches to "writing" and "reading" information.
To overcome these challenges, Samuel Dahlhauser, a researcher at the University of Texas, and colleagues encoded a selected passage from Mansfield Park into a series of oligourethanes by using a new technique. The passage reads: "If one scheme of happiness fails, human nature turns to another; if the first calculation is wrong, we make a second better: we find comfort somewhere."
"This particular passage was chosen because we felt it was uplifting in these trying times, and it is easily understood without the context in the book," says Dahlhauser.
First, the researchers compressed the text into a bitstring (a sequence of binary digits) by using an algorithm before converting it into the hexadecimal numeral system, which consists of 16 symbols and enables computers to organize large binary digit strings. The 158-character hexadecimal string was next synthesized into 18 oligourethanes, each 10 monomers long. To decode the freshly encoded information, the researchers worked backwards. They sequenced the oligomers by using self-immolation, in which the compounds spontaneously fragmented into monomers through a cascade of reactions, and fed the sequencing data into decoder software, which assigned the molecules to their corresponding hexadecimal characters. Ultimately, the team succeeded in reproducing the wholly intact passage with complete accuracy.
To further verify the technique, the researchers asked a colleague who was unaffiliated with the project to "read" the encoded material by following a set of instructions. The participant correctly deciphered all but two characters on his first try and, when given a slightly modified set of instructions, correctly deciphered all of the monomers on his second attempt.
"Our future work will address the error rates in the reading and writing, as well as the limitations of oligourethanes as a medium for information storage," says Anslyn. "Likewise, we hope to utilize the rapid characterization techniques presented here to explore their applications in self-assembly, combinatorial chemistry, and catalysis."
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by the Army Research Office, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and the Welch Reagents Chair.
Cell Reports Physical Science, Dahlhauser et al.: "Efficient Molecular Encoding in Multifunctional Self-Immolative Urethanes" https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-physical-science/fulltext/S2666-3864(21)00083-7
Cell Reports Physical Science (@CellRepPhysSci), published by Cell Press, is a new broad-scope, open access journal that publishes cutting-edge research across the spectrum of the physical sciences, including chemistry, physics, materials science, energy science, engineering, and related interdisciplinary work. Visit: https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-physical-science/home. To receive Cell Press media alerts, please contact press@cell.com.
Biodegradable plastics have been advertised as one solution to the plastic pollution problem bedeviling the world, but today's "compostable" plastic bags, utensils and cup lids don't break down during typical composting and contaminate other recyclable plastics, creating headaches for recyclers. Most compostable plastics, made primarily of the polyester known as polylactic acid, or PLA, end up in landfills and last as long as forever plastics.
University of California, Berkeley, scientists have now invented a way to make these compostable plastics break down more easily, with just heat and water, within a few weeks, solving a problem that has flummoxed the plastics industry and environmentalists.
"People are now prepared to move into biodegradable polymers for single-use ...
It isn't only myriads of currently unknown species that await discovery in the Amazon rainforests. As a new study by German scientists at the Ruhr-University (Bochum) and the Bavarian State Collection of Zoology (Munich), published in the open-access peer-reviewed scientific Journal of Orthoptera Research, concludes, it seems that so do plenty of unusual behaviours.
"When I saw the maggot-like structures peeking out from the back of the praying mantis and then withdrew, I immediately thought of parasites that eat the animal from the inside, because that is not really uncommon in insects," says Frank Glaw, a reptile and amphibian expert from the Bavarian State Collection of Zoology, who discovered ...
Categorization is the brain's tool to organize nearly everything we encounter in our daily lives. Grouping information into categories simplifies our complex world and helps us to react quickly and effectively to new experiences. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology have now shown that also mice categorize surprisingly well. The researchers identified neurons encoding learned categories and thereby demonstrated how abstract information is represented at the neuronal level.
A toddler is looking at a new picture book. Suddenly it points to an illustration and shouts 'chair'. The kid made the right call, but that does not seem particularly noteworthy to us. We recognize all kinds of chairs as 'chair' without any difficulty. ...
Central Africa is home to the world's second-largest area of dense tropical rainforest. This major reservoir of biodiversity stretches out over five main countries: Cameroon, Gabon, the Republic of Congo, the Democratic Republic of Congo and the Central African Republic. It provides numerous ecosystem services, such as regulating exchange cycles between the earth and the atmosphere, and helps to ensure food supply for local populations. Due to the threats from climate change and demographic pressure expected in Africa by the end of the 21st century, the protection and sustainable management of these forests is a challenge for policy ...
The disastrous consequences of climate "tipping points" could be averted if global warming was reversed quickly enough, new research suggests.
Once triggered, tipping points may lead to abrupt changes such as the dieback of the Amazon rainforest or melting of major ice sheets.
Until now, crossing these thresholds has been assumed to be a point of no return, but the new study - published in the journal Nature - concludes that thresholds could be "temporarily exceeded" without prompting permanent shifts.
The research team, from the University of Exeter and the UK Centre for Ecology and Hydrology (UKCEH), say the time available to act would depend on the level ...
Scientists have provided the first evidence to show that eradicating rats from tropical islands effects not just the biodiversity on the islands, but also the fragile coral seas that surround them.
The new study led by scientists at Lancaster University and published in the journal Current Biology shows that critical cycles of seabird nutrients flowing to coral reefs are re-established within relatively short time periods after rats are removed - even around islands that have been infested for hundreds of years.
The findings offer encouragement that rat eradication can benefit coral ...
What The Study Did: Researchers looked at whether short-term exposure to air pollution from a 2018 California wildfire was associated with changes in the number of clinic visits for eczema or itch and medications prescribed for eczema.
Authors: Maria L. Wei, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0179)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
Wildfire smoke can trigger a host of respiratory and cardiovascular symptoms, ranging from runny nose and cough to a potentially life-threatening heart attack or stroke. A new study suggests that the dangers posed by wildfire smoke may also extend to the largest organ in the human body, and our first line of defense against outside threat: the skin.
During the two weeks in November 2018 when wildfire smoke from the Camp Fire choked the San Francisco Bay Area, health clinics in San Francisco saw an uptick in the number of patients visiting with concerns of eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, and general itch, compared to the same time of the year ...
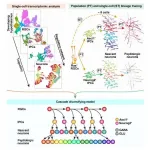
A mechanistic understanding of brain development requires a systematic survey of neural progenitor cell types, their lineage specification and maturation of postmitotic neurons. Cumulative evidences based on single-cell transcriptomic analysis have revealed the heterogeneity of cortical neural progenitors, their temporal patterning and the developmental trajectories of excitatory and inhibitory neurons in the developing neocortex. Nevertheless, the developmental hierarchy of the hypothalamus, which contains an astounding diversity of neurons that regulate endocrine, autonomic and behavioral functions, has not been well understood.
Recently, however, Prof. WU Qingfeng's ...
WHO Peter Libby, MD, cardiovascular medicine specialist at Brigham and Women's Hospital and the Mallinckrodt Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School; author of a new review paper published in Nature.
WHAT Atherosclerosis -- hardening of the arteries -- is now involved in the majority of deaths worldwide, and advances in our understanding of the biology of the disease are changing traditional views and opening up new avenues for treatment.
The picture of who may be at risk for a heart attack has evolved considerably in recent decades. At one time, a heart attack might have conjured up the image of a middle-aged white man with high cholesterol and high blood pressure who smoked cigarettes. Today, traditional concepts of what contributes to risk have changed. These ...