(Press-News.org) Students who have been exposed to interpersonal trauma — physical assault, sexual assault or unwanted sexual experiences — prior to college are more likely to engage in risky alcohol use. But romantic relationships mitigate these effects of trauma on a student’s drinking behavior, according to a new study led by Virginia Commonwealth University researchers.
The study investigates whether romantic relationships might play a role in mitigating or exacerbating the effects of trauma exposure on alcohol use among college students. It found that students who experienced interpersonal trauma during college consumed more alcohol than those without interpersonal trauma exposure, and that their drinking was more pronounced for those in a relationship with a partner with higher levels of alcohol use. It also found that a student’s satisfaction in their romantic relationship did not change the association between interpersonal trauma and alcohol use.
Previous research has found that college students who have been exposed to interpersonal trauma are more likely to engage in risky alcohol use. Yet not everyone who experiences interpersonal trauma goes on to misuse alcohol, raising questions about what factors might play a role in the interaction of trauma and drinking.
The study, “A Longitudinal Study of the Moderating Effects of Romantic Relationships on the Associations Between Alcohol Use and Trauma in College Students,” will be published in a forthcoming issue of the journal Addiction. It explores whether three aspects of romantic relationships — relationship status, relationship satisfaction and partner alcohol use — change the associations between interpersonal trauma and alcohol use.
“These findings are important because they help elucidate the ways that romantic relationships can improve or undermine health habits, particularly concerning alcohol consumption,” said lead author Rebecca Smith, a doctoral student in the Department of Psychology in the College of Humanities and Sciences. “A better understanding of the ways that social relationships can influence health behaviors might encourage people to carefully consider the people with whom they spend time. Moreover, these findings help us better understand alcohol use risk and protective factors across the lifespan, which can be used to inform prevention and treatment programs.”
Jessica Salvatore, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the Department of Psychology and the senior author on the study, said the findings “underscore the double-edged role that relationships and partners have on health behaviors in college.”
“On the one hand, we found that involvement in a committed relationship buffered the effects of interpersonal trauma exposure on students’ alcohol use,” she said. “On the other, we found that involvement with a heavier drinking partner amplified the association between exposure and alcohol use.”
Smith said she was surprised that relationship satisfaction was not a significant moderator of the associations between interpersonal trauma and alcohol use.
“Based on previous research suggesting that involvement in satisfying relationships is protective against stress and problematic drinking, we had hypothesized that high relationship satisfaction would buffer against the effects of interpersonal trauma on alcohol use,” she said.
The study relied on data collected through Spit for Science, a universitywide project at VCU in which student volunteers provide information on alcohol, substance use, emotional health and more, and contribute DNA samples that provide insight into the role of genetics. The study involved nearly 9,000 students who participated in Spit for Science between 2011 and 2014.
Participants completed baseline assessments during the fall of their freshman year and were invited to complete follow-up assessments every spring thereafter. Participants were included in the study if they completed surveys at baseline and at least one follow-up assessment.
“Each year, participants answered questions about stressful life events they may have experienced, their quantity and frequency of alcohol consumption, and their romantic relationships,” Smith said. “This allowed us to look at the interplay between interpersonal trauma, alcohol use and romantic relationship characteristics over time.”
The study’s findings could be valuable for efforts to increase awareness and education for college students about the ways in which our social ties can promote or undermine health behaviors, like alcohol use, Smith said.
Additionally, she said, the findings could be applied as part of treatment to reduce unsafe drinking.
“We know from previous research that exposure to interpersonal trauma is associated with risky alcohol use, so romantic partners can be included in treatment planning and aftercare to help trauma survivors cope with traumatic events in healthier ways and reduce engagement in risky drinking behaviors,” she said.
In addition to Smith and Salvatore, the study’s co-authors include Danielle Dick, Ph.D., Distinguished Commonwealth Professor in the Departments of Psychology and Human and Molecular Genetics at VCU; Ananda Amstadter, Ph.D., associate professor in the Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics at VCU; Nathaniel Thomas, a doctoral student in the Department of Psychology; and the Spit for Science Working Group.
Romantic relationships mitigate effects of trauma on alcohol use among college students
2021-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sapped: Exploring potential connections between devitalizing anemia and insomnia
2021-04-22
A good night's sleep is essential for a healthy body and mind, for when we sleep is when the body resets, repairs, and refreshes itself. A lot of people, however, have trouble falling or staying asleep, a condition known as insomnia that affects up to 30% of the population. It is usually caused by an underlying psychiatric or clinical condition and is associated with a poorer quality of life. Recent genome wide analyses have revealed that a gene MEIS1 is linked with insomnia. Interestingly, this gene has also been implicated in restless leg syndrome and iron-deficiency anemia (IDA), the latter ...
Climate-smart ag strategies may cut nitrous oxide emissions from corn production
2021-04-22
For corn, using dairy manure and legume cover crops in crop rotations can reduce the need for inorganic nitrogen fertilizer and protect water quality, but these practices also can contribute to emissions of nitrous oxide -- a potent greenhouse gas.
That is the conclusion of Penn State researchers, who measured nitrous oxide emissions from the corn phases of two crop rotations -- a corn-soybean rotation and a dairy forage rotation -- under three different management regimens. The results of the study offer clues about how dairy farmers might reduce the amount of nitrogen fertilizer they apply to corn crops, saving money and contributing less to climate change.
The results are important because although nitrous ...
XYZeq: A better map of cell diversity
2021-04-22
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--April 21, 2021--Not all cancer cells within a tumor are created equal; nor do all immune cells (or all liver or brain cells) in your body have the same job. Much of their function depends on their location. Now, researchers at Gladstone Institutes, UC San Francisco (UCSF), and UC Berkeley have developed a more efficient method than ever before to simultaneously map the specialized diversity and spatial location of individual cells within a tissue or a tumor.
The technique, called XYZeq, was described online this week in the journal Science Advances. It involves segmenting a tissue into a microscopic grid before analyzing RNA from intact cells in each square of the grid, in order to gain a clear understanding of how each particular cell is functioning within ...
Study of 'breakthrough' cases suggests COVID testing may be here to stay
2021-04-22
In rare cases, people who have been fully vaccinated against COVID and are immune to the virus can nevertheless develop the disease. New findings from The Rockefeller University now suggest that these so-called breakthrough cases may be driven by rapid evolution of the virus, and that ongoing testing of immunized individuals will be important to help mitigate future outbreaks.
The research, published this week in the New England Journal of Medicine, reports results from ongoing monitoring within the Rockefeller University community where two fully vaccinated individuals tested positive for the coronavirus. Both had received two doses of either the Moderna or the Pfizer vaccine, with the second dose occurring more than two weeks before the positive test. One person was initially ...
How we know whether and when to pay attention
2021-04-22
Fast reactions to future events are crucial. A boxer, for example, needs to respond to her opponent in fractions of a second in order to anticipate and block the next attack. Such rapid responses are based on estimates of whether and when events will occur. Now, scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics (MPIEA) and New York University (NYU) have identified the cognitive computations underlying this complex predictive behavior.
How does the brain know when to pay attention? Every future event carries two distinct kinds of uncertainty: ...
Using exoplanets as dark matter detectors
2021-04-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio - In the continuing search for dark matter in our universe, scientists believe they have found a unique and powerful detector: exoplanets.
In a new paper, two astrophysicists suggest dark matter could be detected by measuring the effect it has on the temperature of exoplanets, which are planets outside our solar system.
This could provide new insights into dark matter, the mysterious substance that can't be directly observed, but which makes up roughly 80% of the mass of the universe.
"We believe there should be about 300 billion exoplanets that are waiting to be discovered," said Juri Smirnov, a fellow at The Ohio ...
Fighting harmful bacteria with nanoparticles
2021-04-22
In the arms race "mankind against bacteria", bacteria are currently ahead of us. Our former miracle weapons, antibiotics, are failing more and more frequently when germs use tricky maneuvers to protect themselves from the effects of these drugs. Some species even retreat into the inside of human cells, where they remain "invisible" to the immune system. These particularly dreaded pathogens include multi-resistant staphylococci (MRSA), which can cause life-threatening diseases such as sepsis or pneumonia.
In order to track down the germs in their hidouts and eliminate them, a team of researchers from Empa and ETH Zurich is now developing nanoparticles that use a completely different mode ...
Sculpting radiation beam spares lung cancer patients from severe, disabling complication
2021-04-22
BOSTON - For many patients with localized lung cancer (non-small-cell lung carcinoma and small cell lung carcinoma), high-dose radiation with concurrent chemotherapy is a potential cure. Yet this treatment can cause severe, acute inflammation of the esophagus (esophagitis) in about one in five patients, requiring hospitalization and placement of a feeding tube.
A team of radiation oncologists at Mass General Cancer Center demonstrate in an early clinical trial that the radiation beam can be carefully "sculpted" to deliver the majority of a radiation dose directly to the tumor while effectively sparing tissues in the side of the ...
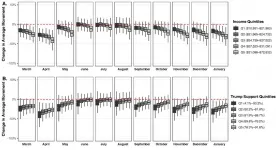
Individuals in lower-income US counties or high support for former President Trump continue to be less likely to socially distance
2021-04-22
Ann Arbor, April 22, 2021 - Using nearly a year of anonymous geolocation data from 15-17 million cell phone users in 3,037 United States counties, investigators have found that individuals with lower income per capita or greater Republican orientation were associated with significantly reduced social distancing throughout the study period from March 2020 through January 2021. Their findings are reported in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier.
The associations persisted after adjusting for a variety of county-level demographic and socioeconomic characteristics. Other county-level characteristics, such as the share of Black and Hispanic residents, were also associated ...
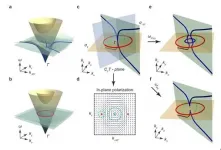
Intrinsic in-plane nodal chain and generalized quaternion charge protected nodal link in photonics
2021-04-22
Topological photonics has attracted a lot of attention recently. The application of topological band theory to photonics not only opens the door to novel devices, but also stimulates the exploration of new topological phases. In the photonic regime, symmetries that are unique to electromagnetic (EM) waves can intrinsically protect the band degeneracies in the momentum space. Topological systems realized using such symmetries are uniquely "photonic", having no counterparts in electronic or phononic systems.
Among various topological features in momentum space, nodal chain is a special ...