(Press-News.org) Thursday, 22 April 2021 - New research has found that childhood adversity, such as parental conflict, death of a close family member or serious injury, before the age of nine was associated with mental health problems in late adolescence.
However, the research also shows that improving the relationship between parents and children could prevent subsequent mental health problems, even in children who have experienced severe adversities. The research also indicated that improving a child's self-esteem and increasing their levels of physical activity can help to reduce the risk of developing mental health problems.
The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is recently published in END
Adversity in early life linked to higher risk of mental health problems
Risk can be reduced by improving parent-child relationship and increasing child self-esteem and physical activity
2021-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nanofiltration membranes to treat industrial wastewater from heavy metals
2021-04-22
NUST MISIS scientists together with Indian colleagues from Jain University and Sri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara College presented innovative membranes for the complete removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. The special nanostructure of zinc-modified aluminum oxide made it possible to remove arsenic and lead from water with an efficiency of 87% and 98%, respectively. The results of the work were published in the Chemosphere journal.
Industrialization is the main cause of water pollution due to the ingress of industrial waste. In particular, heavy metals -- arsenic, lead and cadmium -- can cause metabolic disorders and multiple critical effects to the body, ...
Properties of chromium tribromide show path to innovative electronic devices
2021-04-22
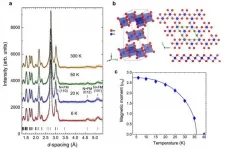
Two-dimensional (2D) materials with a single-layer thickness retaining magnetic order in atomically thin limit began to increase their scientific and technological significance after the successful synthesis of graphene and later investigations of van der Waals materials. CrBr3 has been known since the 60s as a van der Waals ferromagnet. Hansen, Tsubokawa, and Dillon have pioneered the work on magnetism in this compound. However, it has only recently been established that CrBr3 exhibits ferromagnetism when exfoliating to several layers and monolayers while ...
IU researchers tackled the challenges of conducting intrastate policy surveillance
2021-04-22
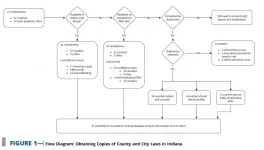
The design, interpretation, and enforcement of county and municipal laws significantly affect local public health. But accessing those laws can be difficult.
A study by Indiana University researchers found that unlike Indiana state laws, which are collected, catalogued by topic, and kept regularly updated in centralized, publicly available electronic databases, laws in about half of all Indiana counties were not online, or if they were online, they weren't necessarily up to date. This means that in Indiana, there is no comprehensive, up-to-date central source that can be used to study how different local governments respond to similar health-related ...
Mutations can reduce effect of hormonal treatment in early breast cancer
2021-04-22
A small proportion of women who receive anti-estrogen treatment after breast cancer surgery have worse outcomes. This is associated with mutations in the estrogen receptor gene, according to a study from Lund University now published in JNCI Cancer Spectrum.
"If our results are confirmed in further studies, it would be relevant to screen for these resistance mutations already at diagnosis, and then consider other treatment options that could work better for patients with mutated tumors," says Lao Saal, who led the study, the largest of its kind on resistance mutations in the estrogen receptor in primary breast cancer.
Breast cancer is the most common ...
Inspired by nature, the research to develop a new load-bearing material
2021-04-22
Inspired by nature, the researchers developing a new load-bearing material
Engineers have developed a new material that mimics human cartilage - the body's shock absorbing and lubrication system, and it could herald the development of a new generation of lightweight bearings.
Cartilage is a soft fibrous tissue found around joints which provides protection from the compressive loading generated by walking, running or lifting. It also provides a protective, lubricating layer allowing bones to pass over one another in a frictionless way. For years, scientists have been trying to create a synthetic material with the properties of cartilage. ...
Updated results on coronavirus vaccination effectiveness
2021-04-22
Several weeks following the publication of the large real-world Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness study by the Clalit Research Institute in Collaboration with Harvard University in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), additional results focusing on vaccine effectiveness in specific sub-populations have now been published.
While the original publication demonstrated the effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine in the general population, outstanding questions remained regarding vaccine effectiveness in specific sub-populations of interest, including the elderly, multi-morbid ...
Researchers design micro-sized capsules for targeted drug delivery -- inspired by Russian pelmeni
2021-04-22
An international team led by a Skoltech researcher has developed a method of fabrication for biodegradable polymer microcapsules, made more efficient by turning to an unusual source of inspiration - traditional Russian dumpling, or pelmeni, making. The two papers were published in Materials and Design and ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces.
Micro-sized capsules, which can be tailored to a variety of purposes, have proven very useful in targeted delivery of drugs and other bioactive compounds. To ensure optimal functioning, these have to be designed and manufactured with precision and in particular shapes, as non-spherical capsules turned out to be more efficient and effective than spherical ones.
"Non-spherical capsules could have side directed release ...
Romantic relationships mitigate effects of trauma on alcohol use among college students
2021-04-22
Students who have been exposed to interpersonal trauma — physical assault, sexual assault or unwanted sexual experiences — prior to college are more likely to engage in risky alcohol use. But romantic relationships mitigate these effects of trauma on a student’s drinking behavior, according to a new study led by Virginia Commonwealth University researchers.
The study investigates whether romantic relationships might play a role in mitigating or exacerbating the effects of trauma exposure on alcohol use among college students. It found that students who experienced interpersonal trauma during college consumed more alcohol than those without interpersonal trauma exposure, and that their drinking was more pronounced for those in a relationship with a partner with ...
Sapped: Exploring potential connections between devitalizing anemia and insomnia
2021-04-22
A good night's sleep is essential for a healthy body and mind, for when we sleep is when the body resets, repairs, and refreshes itself. A lot of people, however, have trouble falling or staying asleep, a condition known as insomnia that affects up to 30% of the population. It is usually caused by an underlying psychiatric or clinical condition and is associated with a poorer quality of life. Recent genome wide analyses have revealed that a gene MEIS1 is linked with insomnia. Interestingly, this gene has also been implicated in restless leg syndrome and iron-deficiency anemia (IDA), the latter ...
Climate-smart ag strategies may cut nitrous oxide emissions from corn production
2021-04-22
For corn, using dairy manure and legume cover crops in crop rotations can reduce the need for inorganic nitrogen fertilizer and protect water quality, but these practices also can contribute to emissions of nitrous oxide -- a potent greenhouse gas.
That is the conclusion of Penn State researchers, who measured nitrous oxide emissions from the corn phases of two crop rotations -- a corn-soybean rotation and a dairy forage rotation -- under three different management regimens. The results of the study offer clues about how dairy farmers might reduce the amount of nitrogen fertilizer they apply to corn crops, saving money and contributing less to climate change.
The results are important because although nitrous ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Adversity in early life linked to higher risk of mental health problemsRisk can be reduced by improving parent-child relationship and increasing child self-esteem and physical activity