Firearms laws curb rates of gun violence across United States
Number of firearm laws significantly predicted suicide and homicide rates, Rutgers study finds
2021-04-22
(Press-News.org) States with stricter firearms laws reported lower suicide and homicide rates, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, conducted by the New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center, the Rutgers School of Public Health, the Rutgers University-Newark Department of Psychology, the Rutgers School of Criminal Justice, the Rutgers New Jersey Medical School and the Rutgers-Newark Department of Social Work, was published in the Journal of Public Health and examined the association between firearm laws and suicide and homicide rates.
Firearm violence is a major public health concern in the United States, with firearm suicide and homicide accounting for the majority of gun deaths. In 2017, 66,683 people died by suicide and homicide with a majority of the deaths resulting from a firearm: 48 percent for suicide and 74 percent for homicide.
Using the State Firearm Law Database, the Rutgers researchers compared suicide and homicide rates across the United States from 1991 to 2017 with the number of firearm laws in each state. The study found that even with several factors, such as unemployment and overall gun ownership rates, taken into account, the total number of firearm laws in a state was a significant predictor of suicide and homicide rates.
"As states' strictness increased, their suicide and homicide rates decreased," said lead author John F. Gunn III, a postdoctoral researcher at the Rutgers School of Public Health and New Jersey Gun Violence Research Center.
The researchers, who were the first to focus on the impact of the total number of firearms regulations in each state, utilized a general index of states' overall approach to firearms regulation by aggregating the total number of gun laws. This index broadly defined states as restrictive or lenient towards firearms.
"With close to 40, 000 deaths annually from firearm violence, regulations that can limit access to firearms appear to reduce state-level mortality," says senior study author Bernadette Hohl, an assistant professor at Rutgers School of Public Health. "Evidence-based implementation of firearm regulations across the whole of the United States has the potential to significantly reduce the toll of firearm violence."
Previous research supports associations between state suicide and homicide rates and specific gun laws, such as waiting periods and universal background checks, with most work finding that the presence of specific firearm laws is associated with reductions in gun mortality.
Future research is required to continue to holistically examine the relationship between firearm laws and suicide and homicide rates. "Assessing the implications of law changes, regulation enforcement and if there is a correlation with violent crime decline will be necessary," Gunn said.
INFORMATION:
Link to study: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-22
Irvine, Calif., April 22, 2021 -- California's wildfire problem, fueled by a concurrence of climate change and a heightened risk of human-caused ignitions in once uninhabited areas, has been getting worse with each passing year of the 21st century.
Researchers in the Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering at the University of California, Irvine have conducted a thorough analysis of California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection wildfire statistics from 2000 to 2019, comparing them with data from 1920 to 1999. They learned that the annual burn season has lengthened in the past two decades and that the yearly peak has shifted from August to July. The team's findings are the subject of a study published today in the ...
2021-04-22
A minimally invasive retinal reattachment procedure that can be done in an ophthalmologist's office leads to better long-term integrity and structure of the retina's photoreceptors - cells that allow us to see - compared with more invasive operating room procedures, according to new research published April 22.
The study, published in JAMA Ophthalmology and led by researchers at St. Michael's Hospital of Unity Health Toronto, contributes to a growing body of evidence pointing towards pneumatic retinopexy (PnR) as the better first-line retinal reattachment technique to achieve the best visual outcomes.
Retinal detachment is the most common surgical ocular emergency, progressing to loss of vision within hours ...
2021-04-22
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (4/22/2021) - Confirming anecdotal evidence that the spread of the coronavirus has strained Americans' mental health, Boston College researchers found reports of anxiety increased to 50 percent and depression to 44 percent by November, 2020 - rates six times higher than 2019 - according to a new report in the journal Translational Behavioral Medicine.
Among U.S. adults aged 18-29, the impact on mental health was even more severe. Rates of anxiety and depression increased to 65 percent and 61 percent, respectively, of the respondents in that age group, according to the report.
Use of prescription medication, counseling services, and unmet need for mental health services also rose significantly, according to the co-authors of the new study, Boston ...
2021-04-22
As the COVID-19 pandemic has progressed, it has become clear that many survivors -- even those who had mild cases -- continue to manage a variety of health problems long after the initial infection should have resolved. In what is believed to be the largest comprehensive study of long COVID-19 to date, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis showed that COVID-19 survivors -- including those not sick enough to be hospitalized -- have an increased risk of death in the six months following diagnosis with the virus.
The researchers also have catalogued the numerous diseases associated ...
2021-04-22
Skoltech scientists in collaboration with researchers from the University of Arizona and the Los Alamos National Laboratory have developed an approach that allows power grids to return to stability fast after demand response perturbation. Their research at the crossroads of demand response, smart grids, and power grid control was published in the journal Applied Energy.
Power grids are complex systems that manage the generation, transmission and distribution of electrical power to consumers, also called loads. As it is not possible to store electrical energy along the transmission lines, grid operators must ensure, ideally at all times, the balance between production and consumption of electrical energy, ...
2021-04-22
A test which uses artificial intelligence (AI) to measure proteins present in some patients with advanced bowel cancer could hold the key to more targeted treatment, according to research published today.
A team at the University of Leeds collaborated with researchers at Roche Diagnostics to develop the technique, which will help doctors and patients to decide on the best treatment options.
They used samples from a previous trial funded by Cancer Research UK to look at the levels of two proteins, known as AREG and EREG, which are produced by some colorectal cancers.
Algorithms driven by AI enabled the researchers to show that patients with higher levels of these proteins received significant benefit from a treatment which inhibits a different protein involved ...
2021-04-22
Key takeaways
Tourniquet use has been consistently increasing in Los Angeles County since 2015 and is significantly associated with improved patient survival.
Tourniquet use is safe and does not lead to increased risk of amputation with proper surgical care after arriving at the hospital.
Findings are specific to Los Angeles County, where patients who had a tourniquet placed were able to be transported quickly to a trauma center for further life-saving care.
CHICAGO (April 22, 2021): Uncontrolled bleeding continues to be one of the most common causes of preventable ...
2021-04-22
Insect decline is one of the greatest challenges facing our society. As a result of the destruction of many natural habitats, bees, bumblebees, butterflies, beetles and the like find less and less food. As a consequence, they are barely able to fulfil their role as pollinators of wild and cultivated plants. This trend is increasingly noticeable in agricultural regions in particular.
Researchers at the University of Münster have now taken a more detailed look at how the choice of seeds in restoration measures - i.e. the restoration of natural habitats at degraded land - affects how insects benefit from these measures. Here, not only the plant ...
2021-04-22
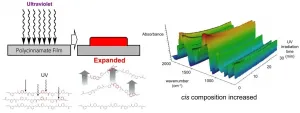
A phenomenon of "photoexpansion" in hard plastic films with a high glass transition temperature in the dry state was established, which was essentially different from very soft actuators, such as elastomers or gels. The photoexpanding hard actuators were expected to apply in the wide fields because they do not contain vaporable matters such as solvents and were much more thermoresistant than conventional ones.
Ishikawa, April 22, 2021 - Polymers that exhibit their functions by light have been studied for a few decades because they enable device miniaturization, energy saving, and precise signal control. Polymers based on azobenzene, diarylethene, etc. are the pioneers, ...
2021-04-22
Patients with chronic kidney dysfunction frequently develop thickening of the heart muscle, so-called left ventricular hypertrophy. This is particularly pronounced in patients who are in the late stage of renal dysfunction, that is to say those requiring renal replacement therapy such as haemodialysis. The danger of this cardiac hypertrophy lies in the considerable associated increase in risk of acute cardiovascular disease, such as sudden cardiac death, for example. Haemodialysis patients have a number of risk factors for developing this form of cardiac hypertrophy. One of those is elevated levels of the protein Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23), ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Firearms laws curb rates of gun violence across United States
Number of firearm laws significantly predicted suicide and homicide rates, Rutgers study finds