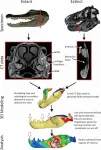
How did dinosaurs deliver bone-crushing bites? By keeping a stiff lower jaw.
New research addresses longstanding mystery on the anatomy of the Tyrannosaurus rex jaw
2021-04-26
(Press-News.org) Tyrannosaurus rex dinosaurs chomped through bone by keeping a joint in their lower jaw steady like an alligator, rather than flexible like a snake, according to a study being presented at the END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
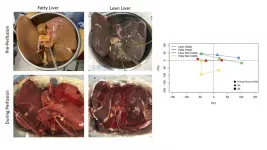
Researchers work to increase number of transplantable livers
2021-04-26
Thousands of livers donated for transplantation are discarded or turned down every year due to concerns about organ quality and function. New insights into why these organs are considered unusable and how they function during external perfusion could help save lives by greatly increasing the number of livers that are transplantable.
After a liver is removed from a donor's body, it undergoes a process known as perfusion which flows blood or a blood replacement though the organ's blood vessels to keep them open and active before the transplantation surgery.
"Our new findings will allow us to design therapies that could be used during external perfusion to improve the quality of organs so that these livers can be transplanted instead of being discarded," ...
Taking vitamin D could lower heart disease risk for people with dark skin
2021-04-26
New research suggests a simple step could help millions of people reduce their risk of heart disease: make sure to get enough vitamin D. Elucidating linkages between skin pigmentation, vitamin D and indicators of cardiovascular health, the new study, combined with evidence from previous research, suggests vitamin D deficiency could contribute to the high rate of heart disease among African Americans.
"More darkly-pigmented individuals may be at greater risk of vitamin D deficiency, particularly in areas of relatively low sun exposure or high seasonality of sun exposure," said S. Tony Wolf, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Pennsylvania State University and the study's lead author. "These ...
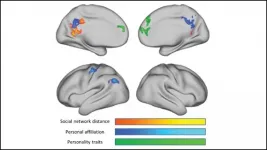
How the brain encodes social network structure
2021-04-26
The brain encodes information about our relationships and the relationships between our friends using areas involved in spatial processing, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Humans maintain hundreds of social relationships, requiring the brain to catalogue countless details about each person and their connections to other people. But it is not known how exactly the brain stores all of this information.
To uncover how the brain encodes social network structure, Peer et al. used Facebook data to map out participants' social connections. Then the researchers measured their brain activity with fMRI as they thought about people from their network. Thinking about a connection generated ...
Research result reporting set for boost under new system
2021-04-26
A new guideline for reporting research results has been developed to improve reproducibility, replication, and transparency in life sciences.
The new Research Materials, Design, Analysis and Reporting (MDAR) Framework will harmonise the recording of outcomes across several major journals, its developers say.
Existing guidelines address specific parts of biomedical research, such as ARRIVE - which relates to animal research - and CONSORT, associated with clinical trial reporting.
The MDAR Framework - developed by a team from the University of Edinburgh, the Centre for Open Science and six major journal publishers - complements these by establishing basic minimum reporting requirements and best practice recommendations.
The Framework ...
Spike in severe pediatric type 2 diabetes complication during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-04-26
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), children generally appear to be less severely impacted by COVID-19 than adults. But a new study from Children's Hospital Los Angeles shows that the pandemic could be affecting children's health in unexpected ways. The study reveals a surge of patients presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis, a severe complication of type 2 diabetes. Published today in Diabetes Care, these data offer additional insights into how the pandemic may be impacting the nation's children.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA, is life-threatening. "DKA happens when insulin levels in the blood drop too low for too long," says Lily Chao, MD, MS, ...
Supervisors focused on others' needs get 'benefit of the doubt' from employees
2021-04-26
Like beauty, fairness is in the eye of the beholder.
In the workplace, whether or not we believe that a supervisor has treated us fairly depends on a number of factors, including motive, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
Employees evaluate the fairness of an interaction with an authority figure based on what researcher Cindy Muir (Zapata), associate professor of management at Notre Dame's Mendoza College of Business, describes as justice criteria or rules. These include relying on decision-making processes that grant employees voice and are consistent among employees, ethical and free of bias; treating team members with dignity, respect and ...
Mayo Clinic researchers question effectiveness of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines for solid organ transplant
2021-04-26
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. -- A small study from Mayo Clinic researchers raises the concern that some transplant patients may have a limited immune response after being vaccinated for COVID-19 with an mRNA vaccine. Their findings are published as a letter to the editor in the American Journal of Transplantation.
The letter covers seven organ transplant recipients diagnosed with COVID-19 at Mayo Clinic in Florida six to 44 days after receiving either of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines that have been authorized for emergency use by the Food and Drug Administration. Two patients had received one dose, and five patients had received both doses.
COVID-19 infection was confirmed in all patients with a polymerase chain reaction nasal swab test. The study team, led by Hani Wadei, M.D., ...
Hydrocracking our way to recycling plastic waste
2021-04-26
Millions of tons of plastic end up in landfills every year. It's a big societal problem and an even larger environmental threat.
In the United States, less than 9% of plastic waste is recycled. Instead, more than 75% of plastics waste ends up in landfills and up to 16% is burned, a process that releases toxic gases into the atmosphere.
Researchers from the University of Delaware's Center for Plastics Innovation (CPI) have developed a direct method to convert single-use plastic waste -- plastic bags, yogurt containers, plastic bottles and bottle caps, packaging and more -- to ready-to-use molecules for jet fuels, diesel and lubricants.
The work, reported in a paper in Science ...
Asteroid that hit Botswana in 2018 likely came from Vesta
2021-04-26
April 23, 2021, Mountain View, CA -- An international team of researchers searched for pieces of a small asteroid tracked in space and then observed to impact Botswana on June 2, 2018. Guided by SETI Institute meteor astronomer Peter Jenniskens, they found 23 meteorites deep inside the Central Kalahari Game Reserve and now have published their findings online in the journal Meteoritics and Planetary Science.
"Combining the observations of the small asteroid in space with information gleaned from the meteorites shows it likely came from Vesta, second largest asteroid in our Solar System and target of NASA's ...
Study finds increased risk of serious opioid events in mothers, regardless of dose
2021-04-26
A new study from Vanderbilt University Medical Center researchers finds that new mothers who receive opioids after uncomplicated vaginal births face an increased risk of serious opioid-related events regardless of the opioid dosage, a finding that could significantly impact care delivery.
Andrew Wiese, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of Health Policy in the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology, authored the paper published online April 15 in Women's Health Issues, with Sarah Osmundson, MD, MPH, associate professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, and other researchers in the departments of Biostatistics and Health Policy.
The study examined roughly 147,000 women enrolled in TennCare -- Tennessee's Medicaid program -- between ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
[Press-News.org] How did dinosaurs deliver bone-crushing bites? By keeping a stiff lower jaw.New research addresses longstanding mystery on the anatomy of the Tyrannosaurus rex jaw