(Press-News.org) The process designed to harvest on Earth the fusion energy that powers the sun and stars can sometimes be tricked. Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics laboratory have derived and demonstrated a bit of slight-of-hand called "quasi-symmetry" that could accelerate the development of fusion energy as a safe, clean and virtually limitless source of power for generating electricity.
Fusion reactions combine light elements in the form of plasma -- the hot, charged state of matter composed of free electrons and atomic nuclei that makes up 99 percent of the visible universe -- to generate massive amounts of energy. Scientists around the world are seeking to reproduce the process in doughnut-shaped fusion facilities called tokamaks that heat the plasma to million-degree temperatures and confine it in symmetrical magnetic fields produced by coils to create fusion reactions.
Crucial issue
A crucial issue for these efforts is maintaining the fast rotation of the doughnut-shaped plasma that swirls within a tokamak. However, small magnetic field distortions, or ripples, caused by misalignment of the magnetic field coils can slow the plasma motion, making it more unstable. The coil misalignments and resulting field ripples are tiny, as small as 1 part in 10,000 parts of the field, but they can have a significant impact.
Maintaining stability in future tokamaks such as ITER, the international facility going up in France to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion energy, will be essential to harvesting the energy to generate electricity. One way to minimize the impact of the field ripples is to add additional magnets to cancel out, or heal, the effect of magnetic field errors. However, field ripples can never be completely cancelled and there has been no optimal method for mitigating their effects until now.
The newly discovered method calls for fooling the swirling plasma particles by canceling out the magnetic field errors along the path they travel. "A way to preserve rotation while providing stability is to change the shape of the magnetic field so that the particles are fooled into thinking that they are not moving in a rippled magnetic field," said PPPL physicist Jong-Kyu Park, lead author of a END
Fooling fusion fuel: How to discipline unruly plasma
2021-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
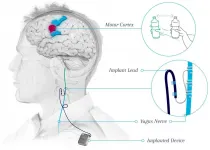
Surgical procedure may help restore hand and arm function after stroke
2021-04-26
LOS ANGELES -- Every year, more than 795,000 people in the United States have a stroke. Of these, approximately 80% lose arm function and as many as 50-60% of this population still experience problems six months later.
Traditionally, stroke patients try to regain motor function through physical rehabilitation, where patients re-learn pre-stroke skills, such as eating motions and grasping. However, most patients eventually plateau and stop improving over time.
Now, results of a clinical trial published in The Lancet gives patients new hope in their recovery.
Patients who received a novel treatment that combines vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) and rehabilitation showed ...
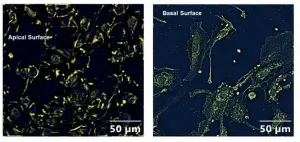
Cell study suggests pesticide exposure may increase COVID-19 susceptibility
2021-04-26
A new study performed in human lung airway cells is one of the first to show a potential link between exposure to organophosphate pesticides and increased susceptibility to COVID-19 infection. The findings could have implications for veterans, many of whom were exposed to organophosphate pesticides during wartime.
Exposure to organophosphate pesticides is thought to be one of the possible causes of Gulf War Illness, a cluster of medically unexplained chronic symptoms that can include fatigue, headaches, joint pain, indigestion, insomnia, dizziness, respiratory disorders and memory problems. More than 25% of Gulf War veterans are estimated to experience this condition.
"We have identified a basic mechanism linked with inflammation that could increase susceptibility to COVID-19 infection ...
Could heart medications increase COVID-19 risk?
2021-04-26
During infection, SARS-CoV-2 binds to a cellular receptor known as angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) before entering a cell and replicating. Because it is not well established whether common blood pressure medications can increase the levels of ACE2, there has been some concern that patients taking these medications might be more susceptible to COVID-19.
In a new study, researchers led by Hans Ackerman, MD, DPhil, in the Laboratory of Malaria and Vector Research (LMVR) at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, found that mice treated with an ACE inhibitor blood pressure medication showed increased levels of ACE2. However, mice that received both an ACE inhibitor and a different blood pressure medicine known as an angiotensin ...
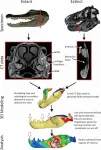
How did dinosaurs deliver bone-crushing bites? By keeping a stiff lower jaw.
2021-04-26
Tyrannosaurus rex dinosaurs chomped through bone by keeping a joint in their lower jaw steady like an alligator, rather than flexible like a snake, according to a study being presented at the END ...
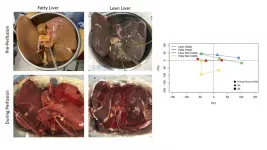
Researchers work to increase number of transplantable livers
2021-04-26
Thousands of livers donated for transplantation are discarded or turned down every year due to concerns about organ quality and function. New insights into why these organs are considered unusable and how they function during external perfusion could help save lives by greatly increasing the number of livers that are transplantable.
After a liver is removed from a donor's body, it undergoes a process known as perfusion which flows blood or a blood replacement though the organ's blood vessels to keep them open and active before the transplantation surgery.
"Our new findings will allow us to design therapies that could be used during external perfusion to improve the quality of organs so that these livers can be transplanted instead of being discarded," ...
Taking vitamin D could lower heart disease risk for people with dark skin
2021-04-26
New research suggests a simple step could help millions of people reduce their risk of heart disease: make sure to get enough vitamin D. Elucidating linkages between skin pigmentation, vitamin D and indicators of cardiovascular health, the new study, combined with evidence from previous research, suggests vitamin D deficiency could contribute to the high rate of heart disease among African Americans.
"More darkly-pigmented individuals may be at greater risk of vitamin D deficiency, particularly in areas of relatively low sun exposure or high seasonality of sun exposure," said S. Tony Wolf, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Pennsylvania State University and the study's lead author. "These ...
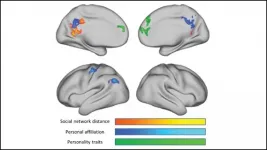
How the brain encodes social network structure
2021-04-26
The brain encodes information about our relationships and the relationships between our friends using areas involved in spatial processing, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Humans maintain hundreds of social relationships, requiring the brain to catalogue countless details about each person and their connections to other people. But it is not known how exactly the brain stores all of this information.
To uncover how the brain encodes social network structure, Peer et al. used Facebook data to map out participants' social connections. Then the researchers measured their brain activity with fMRI as they thought about people from their network. Thinking about a connection generated ...
Research result reporting set for boost under new system
2021-04-26
A new guideline for reporting research results has been developed to improve reproducibility, replication, and transparency in life sciences.
The new Research Materials, Design, Analysis and Reporting (MDAR) Framework will harmonise the recording of outcomes across several major journals, its developers say.
Existing guidelines address specific parts of biomedical research, such as ARRIVE - which relates to animal research - and CONSORT, associated with clinical trial reporting.
The MDAR Framework - developed by a team from the University of Edinburgh, the Centre for Open Science and six major journal publishers - complements these by establishing basic minimum reporting requirements and best practice recommendations.
The Framework ...
Spike in severe pediatric type 2 diabetes complication during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-04-26
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), children generally appear to be less severely impacted by COVID-19 than adults. But a new study from Children's Hospital Los Angeles shows that the pandemic could be affecting children's health in unexpected ways. The study reveals a surge of patients presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis, a severe complication of type 2 diabetes. Published today in Diabetes Care, these data offer additional insights into how the pandemic may be impacting the nation's children.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA, is life-threatening. "DKA happens when insulin levels in the blood drop too low for too long," says Lily Chao, MD, MS, ...
Supervisors focused on others' needs get 'benefit of the doubt' from employees
2021-04-26
Like beauty, fairness is in the eye of the beholder.
In the workplace, whether or not we believe that a supervisor has treated us fairly depends on a number of factors, including motive, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame.
Employees evaluate the fairness of an interaction with an authority figure based on what researcher Cindy Muir (Zapata), associate professor of management at Notre Dame's Mendoza College of Business, describes as justice criteria or rules. These include relying on decision-making processes that grant employees voice and are consistent among employees, ethical and free of bias; treating team members with dignity, respect and ...