(Press-News.org) Western Australia's wheatbelt is a biodiversity desert, but the remaining wildlife - surviving in 'wheatbelt oases' - may offer insights for better conservation everywhere, according to researchers.
University of Queensland researcher Dr Graham Fulton and local John Lawson have been reviewing the biodiversity in the woodland oasis of Dryandra, in WA's south west.
"It's hard to witness the devastating loss of wilderness in Western Australia's wheatbelt," Dr Fulton said.
"Ninety-seven per cent of the best native vegetation has been taken - around 14 million hectares - it's an area greater in size than England.
"And the animals have gone with it, it's little wonder Australia has the highest mammal extinction rate in the world.
"Despite this harrowing loss, we're determined to help protect the area's remaining species, learning how best to protect animals in similar threatened habitats the world over."
In this vastly diminished environment, this remaining pocket of native Western Australian woodland - old growth woodland - is a last refuge for the birds.
The researchers counted birds at 70 points through three woodland types: powderbark wandoo (Eucalyptus accedens), wandoo (Eucalyptus wandoo) and brown mallet (Eucalyptus astringens).
Overall 2397 birds, of 52 species were detected by the pair, with evidence suggesting more oases need to be created.
"These birds can only survive thanks to these small islands of woodland scattered through this vast sea of wheat," Dr Fulton said.
"Habitat islands like this are common all around the world, where human development has significantly broken up natural habitats.
"It's time to push government planners globally to take a look at the big picture, building havens for disappearing and under-threat wildlife wherever possible."
The research revealed that diversity of habitat type was critical for protecting remaining species.
"By protecting a wide array of habitat types - not just tokenistic, monocultural protected sites - we can offer species like these birds access to the range of habitat they need to survive and thrive.
"And it's not just birds - even the iconic, and endangered, Australian numbat survives thanks to Dryandra.
"If we're serious about reducing our extinction rate, and protecting species that mean so much to so many, it's time to look at expanding our habitat oases and managing those habitats effectively."
INFORMATION:
The research has been published in the Australian Journal of Zoology (DOI: 10.1071/ZO20095).
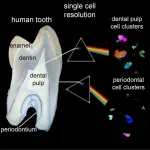
During the last 30 years, medical and dental research has attracted a large number of scientists and practitioners working on aspects of high medical relevance that involve a combination of genetic and tissue regeneration approaches. These developments in stem cell and tissue engineering have provided medical and dental researchers with new insights and given rise to new ideas as to how everyday clinical practice can be improved. Many research groups are dealing with questions like: How can we help injured tissues and organs heal? Can lost tissue be regenerated? How can we create solid protocols that apply across all stem cell therapies?
Advanced single-cell sequencing technology used
A team of researchers led by Thimios ...
In light of declining natural forests, tree plantations may seem like a good way to replace forest habitats. But what are the possible benefits of these plantations for biological diversity? A team of researchers led by led by the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), Friedrich Schiller University Jena (FSU) and Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) investigated this question using the example of beetles. Beetles account for 27% of all insect species worldwide and are often used as indicators for the effects of climate change and habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. In forest, they serve important functions - for example, they contribute to the decomposition of plant and animal biomass, making the nutrients stored ...
A recent study by the University of Eastern Finland shows that loneliness among middle-aged men is associated with an increased risk of cancer. According to the researchers, taking account of loneliness and social relationships should thus be an important part of comprehensive health care and disease prevention. The findings were published in Psychiatry Research.
"It has been estimated, on the basis of studies carried out in recent years, that loneliness could be as significant a health risk as smoking or overweight. Our findings support the idea that attention should be paid to this issue," Project Researcher Siiri-Liisi Kraav from the University of Eastern Finland says.
The study was ...
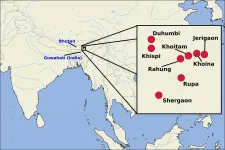
For a long time, historical linguists have been using the comparative method to reconstruct earlier states of languages that are not attested in written sources. The method consists of the detailed comparison of words in the related descendant languages and allows linguists to infer the ancient pronunciation of words which were never recorded in any form in great detail. That the method can also be used to infer how an undocumented word in a certain language would sound, provided that at least some information on that language, as well as information on related languages is available, has been known for a long time, but so far never explicitly tested.
Two researchers from SOAS University of London and the Max Planck Institute for the Science ...
Scientific studies rarely focus on long non-coding RNA molecules (lncRNAs), even though they potentially regulate several diseases. The role of several lncRNAs in anti-viral inflammatory response regulation has recently been reported. Considering their significant regulatory function in immune response, researchers from the Azrieli Faculty of Medicine of Bar-Ilan University sought to identify lncRNAs co-expressed with human genes involved in immune-related processes during severe SARS-CoV-2 infection in the lungs.
Recent studies demonstrated that ...
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses powerful chemicals to kill fast-growing cancer cells in the body. It is a systemic treatment where drugs travel throughout the body and destroy cancer cells that have spread (metastasized) to parts of the body far away from the original (primary) tumour. As such, chemotherapy remains the main treatment against various cancers. Thus, when cancer cells resist chemotherapeutic drugs, treatment failure results.
The resistance of cancer cells to chemotherapy is marked by changes and increased output of certain proteins. These altered proteins can help doctors to identify patients who will not respond well to chemotherapy and paves the way for the development of therapeutic intervention to "re-sensitise" their cancer cells to treatment.
In a Nature ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A new treatment is among the first known to reduce the severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by the flu in animals, according to a new study.
Tests in mice infected with high doses of influenza showed that the treatment could improve lung function in very sick mice and prevent progression of disease in mice that were pre-emptively treated after being exposed to the flu.
The hope is that it may also help humans infected with the flu, and potentially other causes of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) such as SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Specific cells in mice are less able to ...
An international collaboration of astronomers led by a researcher from the Astrobiology Center and Queen's University Belfast, and including researchers from Trinity College Dublin, has detected a new chemical signature in the atmosphere of an extrasolar planet (a planet that orbits a star other than our Sun).
The hydroxyl radical (OH) was found on the dayside of the exoplanet WASP-33b. This planet is a so-called 'ultra-hot Jupiter', a gas-giant planet orbiting its host star much closer than Mercury orbits the Sun and therefore reaching atmospheric temperatures of more than 2,500° C (hot enough to melt most metals).
The lead researcher based at the Astrobiology Center and Queen's University Belfast, ...
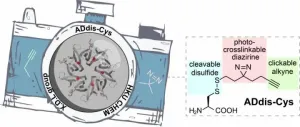
A research group led by Professor Xiang David LI from the Research Division for Chemistry and the Department of Chemistry, The University of Hong Kong, has developed a novel chemical tool for elucidating protein interaction networks in cells. This tool not only facilitates the identification of a protein's interacting partners in the complex cellular context, but also simultaneously allows the 'visualisation' of these protein-protein interactions. The findings were recently published in the prestigious scientific journal Molecular Cell.
In the human body, proteins interact with each other to cooperatively regulate essentially every biological process ranging from gene expression and signal transduction, to immune response. As a result, dysregulated ...
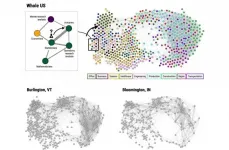
The researchers in this study reached this conclusion by drawing on network modelling research and mapped the job landscapes in cities across the United States during economic crises.
Knowing and understanding which factors contribute to the health of job markets is interesting as it can help promote faster recovery after a crisis, such as a major economic recession or the current COVID pandemic. Traditional studies perceive the worker as someone linked to a specific job in a sector. However, in the real-world professionals often end up working in other sectors that require similar skills. In this sense, researchers consider job markets as being something similar to ecosystems, where organisms are linked in a complex network of interactions.
In this context, an effective job market depends ...