(Press-News.org) The subseafloor constitutes one of the largest and most understudied ecosystems on Earth. While it is known that life survives deep down in the fluids, rocks, and sediments that make up the seafloor, scientists know very little about the conditions and energy needed to sustain that life.
An interdisciplinary research team, led from ASU and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), sought to learn more about this ecosystem and the microbes that exist in the subseafloor. The results of their findings were recently published in Science Advances, with ASU School of Earth and Space Exploration assistant professor and geobiologist Elizabeth Trembath-Reichert as lead author.
To study this type of remote ecosystem, and the microbes that inhabit it, the team chose a location called North Pond on the western flank of the mid-Atlantic Ridge, a plate boundary located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean.
North Pond, at a depth of over 14,500 feet (4,500 meters) has served as an important site for deep-sea scientists for decades. It was most recently drilled hundreds of feet through the sediment and crust by the International Ocean Discovery Program in 2010 to create access points for studying life and chemistry beneath the seafloor.
With support from the National Science Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, and the Center for Dark Energy Biosphere Investigations, the team sampled the crustal fluid samples from the borehole seafloor observatories with the deep sea remotely operated vehicle Jason II on the research vessel Atlantis.
These unique samples from the pristine, cool basaltic seafloor were then brought back to the lab and analyzed using a Nanoscale secondary ion mass spectrometer (NanoSIMS), which was used to measure their elemental and isotopic composition.
"Our experiments use specialized tracers that can only be observed if a microorganism eats something on the buffet of options we provide," explains Trembath-Reichert. "If we see these tracers in the microbes, then we know they must have been active and eating during our experiments and we get an idea of what food sources they can use to survive."
Through these analyses, the team discovered that the subseafloor microbial community is active and poised to eat, despite an environment with low biomass and low-carbon conditions.
"The microbes we studied are extremely adaptable and are able to make a living in what seems like a really harsh environment to surface dwellers, like ourselves," says Trembath-Reichert.
One of the most surprising discoveries was how the microorganisms use carbon dioxide. Trembath-Reichert and her team expected the microorganisms to use widely available carbon dioxide the way plants do, by 'fixing' it into other forms of organic carbon that they can then use to grow on. But the findings suggest the microbes in this isolated environment with low nutrients were being more crafty.
"Our theory is that these microbes are being resourceful and using the carbon dioxide directly as a building block without having to convert it into a food source first," says Trembath-Reichert. "And this could have major implications for the deep ocean carbon cycle."
"This work highlights how little we know about the lifestyle of microbes within oceanic crust and the importance of carrying out experiments with sensitive detection limits, such as NanoSIMS," adds senior author Julie Huber of WHOI.
The next steps for Trembath-Reichert and her team are to design experiments to better understand the full diversity of ways carbon dioxide can be used by microbes. As a more readily available food source for microorganisms, they will be looking into the ways carbon dioxide can be used for survival and growth in the Earth's largest aquifer beneath the seafloor.
INFORMATION:
To conduct this research, Trembath-Reichert was supported by fellowships from the NASA Postdoctoral Program and The L'Oréal For Women in Science Program.
Additional authors on this study include Sunita Shah Walter of the University of Delaware, Marc Fontánez Ortiz of ASU's School of Life Sciences, Patrick Carter of the University of Massachusetts, and Peter Girguis of Harvard University.
Organ development in plants mostly occurs through combinatorial activity of so-called meristems. Meristems are plant cells or tissues that give rise to new organs, similar to stem cells in human - including spikelets. Spikelets are components of the spike and form florets (flowers) themselves, which in turn produce grains after fertilisation.
Inflorescence morphogenesis in grasses (Poaceae) is complex and based on a specialised floral meristem, the spikelet meristem, from which all other floral organs arise and which also gives rise to the grain. The fate of the spikelet thus determines not only reproductive success, ...
DETROIT (April 28, 2021) - The results of a large, national heart attack study show that patients with a deadly complication known as cardiogenic shock survived at a significantly higher rate when treated with a protocol developed by cardiologists at Henry Ford Hospital in END ...
Anyone researching the global carbon cycle has to deal with unimaginably large numbers. The Southern Ocean - the world's largest ocean sink region for human-made CO2 - is projected to absorb a total of about 244 billion tons of human-made carbon from the atmosphere over the period from 1850 to 2100 under a high CO2 emissions scenario. But the uptake could possibly be only 204 or up to 309 billion tons. That's how much the projections of the current generation of climate models vary. The reason for this large uncertainty is the complex circulation of the Southern Ocean, which ...
A protein variant common in malignant bladder tumor cells may serve as a new avenue for treating bladder cancer. A multi-institution study led by END ...
Veterinarians, pet owners and breeders often have preconceived notions about each other, but by investigating these biases, experts at the University of Arizona College of Veterinary Medicine hope to improve both human communication and animal care.
"Veterinary medicine may require us to treat the patient, but we are unable to improve pet patient outcomes without human client consent and trust. Communication is an essential component of veterinary practice," said Ryane Englar, an associate professor and the director of veterinary skills development for the college. "As an anecdotal example, vets and breeders don't always get along, but there was no research on these subjects. I wondered, what do the groups want and need? If ...
Washington, D.C. - April 28, 2021 - As of April 2021, more than 3 million people worldwide have died of COVID-19. Early in the pandemic, researchers developed accurate diagnostic tests and identified health conditions that correlated with worse outcomes. However, a clinical predictor of who faces the highest risk of being hospitalized, put on a ventilator or dying from the disease has remained largely out of reach.
This week in mSphere, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, researchers describe a two-step prognostic test that can help predict a patient's response to infection with SARS-CoV-2. The test combines a disease risk factor score with a test ...
LAWRENCE -- College students across the country struggle with a vicious cycle: Test anxiety triggers poor sleep, which in turn reduces performance on the tests that caused the anxiety in the first place.
New research from the University of Kansas just published in the International Journal of Behavioral Medicine is shedding light on this biopsychosocial process that can lead to poor grades, withdrawal from classes and even students who drop out. Indeed, about 40% of freshman don't return to their universities for a second year in the United States.
"We were interested ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Socially just policies aimed at limiting the Earth's human population hold tremendous potential for advancing equity while simultaneously helping to mitigate the effects of climate change, Oregon State University researchers say.
In a paper published this week in Sustainability Science, William Ripple and Christopher Wolf of the OSU College of Forestry also note that fertility rates are a dramatically understudied and overlooked aspect of the climate emergency. That's especially true relative to the attention devoted to other climate-related topics including energy, short-lived pollutants and ...
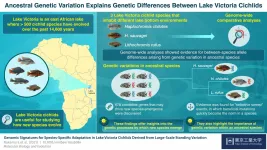
Biologists use the term adaptive radiation to describe a phenomenon in which new species rapidly evolve from an ancestral species, often in response to changes in the local environment that lead to new biological niches becoming available. To understand this process, biologists often turn to the cichlids of Lake Victoria, in which over 500 species of the fish have evolved over the past 14,600 years. As Professor Masato Nikaido of Tokyo Tech explains, "The level of genetic differentiation among species is considered very low due to the short period of time after these different species began evolving, and this limited genetic differentiation provides us with a great opportunity to find candidate genes that have contributed to adaptive ...
Predatory bacteria--bacteria that eat other bacteria--grow faster and consume more resources than non-predators in the same soil, according to a new study out this week from Northern Arizona University. These active predators, which use wolfpack-like behavior, enzymes, and cytoskeletal 'fangs' to hunt and feast on other bacteria, wield important power in determining where soil nutrients go. The results of the study, published in the journal mBio this week, show predation is an important dynamic in the wild microbial realm, and suggest that these predators play an outsized role in how elements are stored in or released from soil.
Like every other life form on earth, bacteria belong to intricate food webs in which organisms are connected ...