Each year, between 2 to 3 million lives are saved by immunisation against diseases like diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, influenza or measles [1]. However, several vaccines such as the one against measles can only reach their full potential--protecting not just those who are immunised, but also those who might not be eligible for vaccination--if the vaccination coverage in a population is high enough [2].
Looking at immunisation programmes' successes and remaining challenges, this week's issue of Eurosurveillance is published on the occasion of European Immunization Week (EIW), from 26 April to 2 May 2021. The campaign, observed annually in the last week of April, was established by the World Health Organization (WHO) Regional Office for Europe in 2005 and aims to highlight the benefits of routine immunisation and to support national immunisation systems.
This year's EIW slogan, 'Vaccines bring us closer', embraces coronavirus disease (COVID-19) vaccines as an integral part of the response to end the ongoing pandemic and ease the physical distancing measures that have been implemented to help control it [3].
Thanks to routine vaccination--which has helped to eradicate for example smallpox and to protect against other diseases with potentially serious health consequences [4]--we know that vaccines work. Yet, WHO estimates that around 20 million children worldwide do not receive the vaccines they need or miss out on vaccination later in life [5].
Vaccines are most often administered to infants and children as part of routine national vaccination schedules. But immunisation protection reaches further than childhood and is important for people in all stages of life, from teenagers to adults and elderly people. Providing such lifelong protection poses further challenges for vaccination programmes, including ensuring equitable access to vaccines [6].
The editorial in this Eurosurveillance issue outlines the lessons learnt since the outset of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, with regards to rapid vaccine development, authorisation, procurement, distribution and administration in large vaccination campaigns. It looks at the key considerations for national vaccine decision-making--during a pandemic or otherwise--and the role that National Immunisation Technical Advisory Groups (NITAGs) or equivalent bodies play when they advise their governments on how to best use new vaccines or design national immunisation programmes.
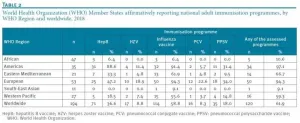
Also in this issue, Williams et al. documented and quantified immunisation programmes for adults across 194 WHO Member States in order to assess existing infrastructures' suitability for COVID-19 vaccine deployment. Looking at five vaccines licensed for adult immunisation (hepatitis B, herpes zoster, influenza, pneumococcal conjugate and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines), the authors found that of the 194 WHO Member States, 120 (62%) reported having at least one adult vaccination programme in 2018, and that 59% of countries had adult vaccination programmes for influenza.
High- or upper-middle-income countries were found to be significantly more likely to report adult immunisation programmes, with country income serving as the most strongly associated factor overall in a multivariable analysis. Other significantly associated factors in a bivariable analysis included meeting National Immunisation Technical Advisory Group (NITAG) basic functional indicators, having introduced new or underused vaccines and having achieved paediatric vaccine coverage goals.
Based on their assessment, Williams et al. conclude that almost 40% of the assessed countries have no infrastructure for adult immunisation and that even the presence of a national adult vaccination programme does not guarantee extensive use of vaccines in the adult population [7].
One target group for adult vaccination is healthcare workers, given that they are exposed to vaccine-preventable diseases like measles, mumps, pertussis and varicella at work and can also transmit these to patients.
In their article, von Linstow et al. detected immunity gaps mainly among young healthcare workers. In addition, considerable proportions of healthcare workers in the study reported that they were unsure about their vaccination status (22-32%, depending on the disease) and possible previous infections (11% for varicella and 41% for pertussis). According to the authors, this demonstrates the need for more targeted measures like screening and a vaccine strategy to address these gaps in healthcare workers [8].
Specifically for measles and its related elimination goal, coverage and uptake of routine childhood immunisation programmes have to improve in many European countries in the same way that immunity gaps in adolescents and adults need to be addressed [9].
In their paper, Rohleder et al. examine a possible relationship between socioeconomic deprivation and measles incidence in Germany, taking into account demographic, spatial and temporal factors [10]. They conclude that the risks for measles infections are higher and more concentrated in areas with the highest socioeconomic status.
In a study of 6,423 healthcare workers in Italy who received the Comirnaty vaccine (BNT162b2, BioNTech/Pfizer, Mainz, Germany/New York, United States), Fabiani et al. found that the effectiveness of preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection was 84% (95% confidence interval (CI): 40-96) 14-21 days after receiving the first dose and 95% (95% CI: 62-99) at least 7 days after the second dose. According to the authors, these results could support the ongoing COVID-19 vaccination campaigns with evidence for targeted communication [11].
Vaccination may be receiving more attention than usual right now, as many adults worldwide are currently being vaccinated or awaiting their opportunity to receive protection against COVID-19. Topics around vaccine safety and efficacy, ethical and equity considerations, as well as logistics are being discussed more widely and more intensely. In this context, EIW serves to highlight the ongoing need to increase efforts to achieve better vaccination coverage for all vaccine-preventable diseases, in order to prevent disease and protect individuals beyond the COVID-19 pandemic.
INFORMATION:
References
1. World Health Organization (WHO). Vaccines and Immunization. Geneva: WHO; 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/health-topics/vaccines-and-immunization#tab=tab_1
2. European Vaccination Information Portal (EVIP). Benefits of vaccination for the community. Stockholm: European Commission, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, European Medicines Agency; 2021. Available from: https://vaccination-info.eu/en/vaccination/benefits-vaccination-community
3. World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe (WHO/Europe). European Immunization Week. Copenhagen: WHO/Europe; 2021. Available from: https://www.euro.who.int/en/media-centre/events/events/2021/04/european-immunization-week
4. European Vaccination Information Portal (EVIP). Benefits of vaccination for individuals. Stockholm: European Commission, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, European Medicines Agency; 2021. Available from: https://vaccination-info.eu/en/vaccination/benefits-vaccination-individuals
5. World Health Organization (WHO). World Immunization Week 2021 - Vaccines bring us closer. Geneva: WHO: 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2021/04/24/default-calendar/world-immunization-week-2021
6. World Health Organization (WHO). Immunization Agenda 2030: A Global Strategy to Leave No One Behind. Geneva: WHO; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/teams/immunization-vaccines-and-biologicals/strategies/ia2030
7. Williams S, Driscoll A, LeBuhn H, Chen W, Neuzil K, Ortiz J. National Routine Adult Immunization Programs among World Health Organization Member States: an assessment of health systems to deploy future SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Euro Surveill. 2021; 26(17). https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.17.2001195
8. von Linstow M-L, Yde Nielsen A, Kirkby N, Eltvedt A, Nordmann Winther T, Bybeck Nielsen A, Bang D, Poulsen A. Immunity to vaccine-preventable diseases among paediatric healthcare workers in Denmark, 2019. Euro Surveill. 2021; 26(17). https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.17.2001167
9. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Who is at risk for measles in the EU/EEA? Identifying susceptible groups to close immunity gaps towards measles elimination. Stockholm: ECDC; 2019. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/risk-assessment-measles-eu-eea-2019
10. Rohleder S, Stock C, Bozorgmehr K. Socioeconomic deprivation is inversely associated with measles incidence: a longitudinal small-area analysis in Germany, 2001-2017. Euro Surveill. 2021; 26(17). https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.17.1900755
11. Fabiani M, Ramigni M, Gobbetto V, Mateo-Urdiales A, Pezzotti P, Piovesan C. Effectiveness of the Comirnaty (BNT162b2, BioNTech/Pfizer) vaccine in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers, Treviso province, Veneto region, Italy, 27 December 2020 to 24 March 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021; 26(17). https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.17.2100420