INFORMATION:
About the Smithsonian Migratory Bird Center
The Smithsonian Migratory Bird Center (SMBC) is dedicated to understanding, conserving and championing the grand phenomenon of bird migration. Founded in 1991, and part of the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute (SCBI), SMBC scientists work to conserve migratory species through research and public education that foster a better understanding of migratory birds and the need to protect diverse habitats across the Western Hemisphere. SCBI plays a leading role in the Smithsonian's global efforts to save wildlife species from extinction and train future generations of conservationists, spearhead research programs at its headquarters in Front Royal, Virginia, the Smithsonian's National Zoo in Washington, D.C., and at field research stations and training sites worldwide.
Bornean rajah scops owl rediscovered after 125 years
First-ever photographs of what may be a distinct species
2021-05-03
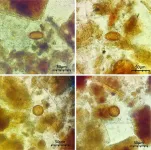
(Press-News.org) The Bornean subspecies of Rajah scops owl (Otus brookii brookii), documented in the wild for the first time since 1892, may be its own unique species and deserving of a conservation designation. Published April 28 in The Wilson Journal of Ornithology, Smithsonian Migratory Bird Center ecologist Andy Boyce reported the rediscovery and photographed this elusive subspecies in the mountainous forests of Mount Kinabalu in Sabah, Malaysia.
"It was a pretty rapid progression of emotions when I first saw the owl--absolute shock and excitement that we'd found this mythical bird, then pure anxiety that I had to document it as fast as I could," Boyce said. "Based on size, eye color and habitat, I knew it was the Bornean Rajah scops owl. What's more, taking into account this bird's specific plumage characters, known speciation patterns within the Otus genus and phylogeographic patterns of montane birds in Borneo and Sumatra, O. b. brookii is likely its own unique species and further study is needed."
Scops owls weigh approximately 100 grams (about 4 ounces), equivalent to four AA batteries. Both subspecies of Rajah scops owl are native to southeast Asia--Otus brookii brookii on the island of Borneo and Otus brookii solokensis on Sumatra. Small owls in the genus Otus often show rapid divergence following isolation in this region. In fact, the Indonesian archipelago is composed of islands that facilitate species divergence, and Borneo and Sumatra have been particularly prone to speciation events.
The serendipitous discovery occurred in May 2016 as part of a 10-year study of avian life-history evolution at Mount Kinabalu in seven study plots at elevations from 1,500-1,900 meters (about 5,000-6,200 feet). The project was led by T.E. Martin, assistant unit leader and research wildlife biologist with the Montana Cooperative Wildlife Research Unit at the University of Montana. While nest-searching in May 2016, technician Keegan Tranquillo notified Boyce, then a doctoral student at the University of Montana, after spotting a roosting scops owl larger and with different plumage than the regularly encountered Mountain scops owl (O. spilocephalus luciae).
"Unfortunately, we are only good at conserving what we know and what we name," Boyce said. "If this rare bird is endemic only to Borneo and is its own species, conservation action is more likely. Our sole sighting during this intensive study confirms this owl lives in mature montane forests, likely above or below the survey area. Those elevations are already threatened by habitat loss due to climate change, deforestation and palm oil development. To protect this bird, we need a firm understanding of its habitat and ecology."
Almost all data on this species is of the Sumatran subspecies. O. b. brookii's vocalizations, distribution, breeding biology and population size are totally unknown. Despite the lack of information on the species and subspecies, and the apparent rarity of the Bornean taxa, the Rajah scops owl was designated a species of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
Properly resolving the ecology, distribution and taxonomic standing of O. b. brookii could have important conservation implications toward both subspecies of owls given each would be an island-endemic species. Researchers recommend nocturnal surveys in specific elevations to study habitat, record vocalizations and collect blood or feather samples to resolve the taxonomic relationship between O. brookii subspecies.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Social cognition plays a key role in everyday lives of people with multiple sclerosis
2021-05-03
East Hanover, NJ. May 3, 2021. An international team of multiple sclerosis (MS) researchers showed that longitudinal changes in social cognition are associated with psychological outcomes of daily living, suggesting that social cognition may exert a central role in people with MS. The article, "Social Cognition in Multiple Sclerosis: A 3-Year Follow-Up MRI and Behavioral Study" (doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11030484) was published on March 9, 2021, in Diagnostics. It is available open access at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8001246/.
The authors are Helen M. Genova, PhD, of Kessler Foundation's Center for Neuropsychology ...
Low doses of radiation may improve quality of life for those with severe Alzheimer's
2021-05-03
Individuals living with severe Alzheimer's disease showed remarkable improvements in behaviour and cognition within days of receiving an innovative new treatment that delivered low doses of radiation, a recent Baycrest-Sunnybrook pilot study found.
"The primary goal of a therapy for Alzheimer's disease should be to improve the patient's quality of life. We want to optimize their well-being and restore communication with family and friends to avoid social isolation, loneliness and under-stimulation. Although the study was a small pilot and should be interpreted with caution, our results suggest that low-dose radiation therapy may successfully achieve this," says Dr. Morris Freedman, scientist at Baycrest's Rotman Research ...
200-year-old poop shows rural elites in New England had parasitic infections
2021-05-03
In the early 19th century in North America, parasitic infections were quite common in urban areas due in part to population growth and urbanization. Prior research has found that poor sanitation, unsanitary privy (outhouse) conditions, and increased contact with domestic animals, contributed to the prevalence of parasitic disease in urban areas. A new study examining fecal samples from a privy on Dartmouth's campus illustrates how rural wealthy elites in New England also had intestinal parasitic infections. The findings are published in the Journal of Archeological Science: Reports.
"Our study is one of the first to demonstrate evidence of parasitic infection in an affluent rural household in the Northeast," says co-author Theresa Gildner, who was ...
Glandular fever increases the risk of depression
2021-05-03
New research shows that patients who have had contact with the hospital due to serious glandular disease have a greater risk of subsequently developing depression. The study from iPSYCH is the largest yet to show a correlation between glandular fever and depression.
The vast majority of Danes have had glandular fever - also called mononucleosis - before adulthood. And for the vast majority of them, the disease can be cured at home with throat lozenges and a little extra care. But for some, the disease is so serious that they need to visit the hospital.
A new research result now shows that precisely those patients who have been in contact with the hospital in connection with their illness, have a greater risk of suffering a depression later.
"Our study ...
Blockchain as 'TechQuity': How tech solutions have the power to help the homeless
2021-05-03
AUSTIN, Texas -- For people experiencing homelessness, missing proof of identity can be a major barrier to receiving critical services, from housing to food assistance to health care. Physical documents such as driver's licenses are highly susceptible to loss, theft or damage. However, researchers from Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin say new technology solutions such as blockchain can be used to keep important health care information secure and portable.
"Health care institutions and social services are so fragmented and siloed they're unable to accurately collect, share or verify basic identity information about a person experiencing homelessness," said Tim Mercer, M.D., MPH, director ...
Dogs' aggressive behavior towards humans is often caused by fear
2021-05-03
A study encompassing some 9,000 dogs conducted at the University of Helsinki demonstrated that fearfulness, age, breed, the company of other members of the same species and the owner's previous experience of dogs were associated with aggressive behaviour towards humans. The findings can potentially provide tools for understanding and preventing aggressive behaviour.
Aggressive behaviour in dogs can include growling, barking, snapping and biting. These gestures are part of normal canine communication, and they also occur in non-aggressive situations, such as during play. However, aggressive behaviour ...
An animal able to regenerate all of its organs even when it is dissected into three parts
2021-05-03
An extraordinary discovery in the Gulf of Eilat: Researchers from Tel Aviv University have discovered a species of ascidian, a marine animal commonly found in the Gulf of Eilat, capable of regenerating all of its organs - even if it is dissected into three fragments. The study was led by Prof. Noa Shenkar, Prof. Dorothee Huchon-Pupko, and Tal Gordon of Tel Aviv University's School of Zoology at the George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences and the Steinhardt Museum of Natural History. The findings of this surprising discovery were published in the leading journal Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
"It is an astounding discovery, as this is an animal that belongs to the Phylum Chordata - animals with a dorsal cord - which also includes us humans," explains Prof. Noa ...
Less precipitation means less plant diversity
2021-05-03
Water is a scarce resource in many of the Earth's ecosystems. This scarcity is likely to increase in the course of climate change. This, in turn, might lead to a considerable decline in plant diversity. Using experimental data from all over the world, scientists from the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ), the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), and the Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) have demonstrated for the first time that plant biodiversity in drylands is particularly sensitive to changes in precipitation. In an article published in Nature Communications, the team warns that this can also have consequences for the people living in the ...
Empowering citizens for successful energy transitions
2021-05-03
The terms "co-creation" and "co-production", which denote the possibility for laypeople to participate in decision-making processes that affect their lives, have been gaining popularity. A new IIASA-led study explored options for empowering citizens as a driver for moving from awareness about the need to transform energy systems to action and participation.
The European Union's climate and energy policies for 2020-2030 require decarbonization of the energy sector. To this end, EU member countries are working on a number of key goals including greater energy efficiency, greater use of renewable energy, and increased energy security across the EU. The successful ...
The level of satisfaction with life in Spain is marked by household financial capacity
2021-05-03
In recent decades, Spain has undergone rapid social changes in terms of gender equality, despite, as a result of the Franco dictatorship, starting from a more backward position than most European countries. This process is hampered by the economic downturn that began in 2008, underlining the importance of the economic context in the development of gender inequality levels. Little attention has been paid in academia to how this gender revolution is associated with factors related to individual wellbeing.
A study by Jordi Gumà, a researcher at the Department of Political and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Bornean rajah scops owl rediscovered after 125 yearsFirst-ever photographs of what may be a distinct species