(Press-News.org) DALLAS (May 3, 2021) - Researchers from the Center for BrainHealth® at The University of Texas at Dallas are investigating a potential new early indicator of the decline toward Alzheimer's disease: measuring the energy metabolism of the living human brain using cutting-edge imaging techniques.
The scientists devised a unique way to illustrate energy consumption and reserves in the brain with phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy using an ultra-high-field 7 Tesla MRI scanner. Their results suggest that neurological energy metabolism might be compromised in mild cognitive impairment (MCI), the stage of decline between healthy aging and more serious disease states like dementia and Alzheimer's.
Dr. Namrata Das, PhD'20, a program specialist and research neuroscientist in the END
7T brain scans reveal potential early indicator of Alzheimer's
Novel research approach holds promise for early detection and treatment
2021-05-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New class of drug gives hope to some ovarian cancer patients
2021-05-04
A study published today in Nature Communications shows that the drug rucaparib has been effective in treating certain types of ovarian cancers if used early in treatment, after a diagnosis, and before the cancer cells build up a resistance to chemotherapy.
Rucaparib is in a relatively new class of drugs - Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase or PARP inhibitors - which have been approved for therapy in ovarian cancers. This study provides insights into both how the cancers resist treatments, and which patients may respond favorably to the drug, said lead author Dr. Elizabeth Swisher, a UW Medicine ...
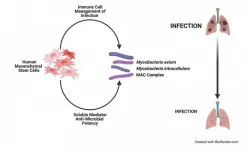
Human mesenchymal stem cells show promise in treating chronic lung infections
2021-05-04
Durham, NC - A study released today in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine offers hope for those suffering from a chronic, difficult to treat condition called non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) lung infection. The study describes how researchers at Case Western University developed a new model of NTM lung infection and then used it to show how effective human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) are in treating this condition - and even which donor cells might be best for doing so.
"The potential to use human mesenchymal stem cells to treat difficult lung infections is promising," said Anthony Atala, M.D., Editor-in-Chief of STEM ...
Researchers advance 3D printing to aid tissue replacement
2021-05-04
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Professor Arda Gozen looks to a future someday in which doctors can hit a button to print out a scaffold on their 3-D printers and create custom-made replacement skin, cartilage, or other tissue for their patients.
Gozen, George and Joan Berry associate professor in the Washington State University School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, and a team of researchers have developed a unique scaffolding material for engineered tissues that can be fine-tuned for the tricky business of growing natural tissue. They report on their research in the journal, Bioprinting. The team also includes researchers from WSU's ...
Poor grasp of dating violence in college perpetuates 'boys will be boys' views
2021-05-04
Dating violence - physical, sexual, psychological or emotional within a relationship, including stalking - is pervasive on college campuses with far-reaching health implications. One in five women experience a sexual assault in college and students living in sorority houses are three times more likely to experience rape. College students are vulnerable to dating violence because of the influence of their social and living environments.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University's College of Education in collaboration with Sacred Heart University conducted a study to understand the dating violence experience and perpetration of college-age women, ...
UBCO researcher uses geology to help astronomers find habitable planets
2021-05-04
Astronomers have identified more than 4,000, and counting, confirmed exoplanets -- planets orbiting stars other than the sun -- but only a fraction have the potential to sustain life.
Now, new research from UBC's Okanagan campus is using the geology of early planet formation to help identify those that may be capable of supporting life.
"The discovery of any planet is pretty exciting, but almost everyone wants to know if there are smaller Earth-like planets with iron cores," says Dr. Brendan Dyck, assistant professor of geology in the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Science and lead author on the study.
"We typically hope to find these planets in the so-called 'goldilocks' or habitable ...
Mobile gaming app enhances HIV care
2021-05-04
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and Duke University improved HIV care by gamifying it with a mobile gaming application.
Gaming features - like those used to drive airline loyalty and track daily steps --- helped young men living with HIV achieve viral suppression and doubled their chances for reaching near perfect adherence to medication plans, according to a study in AIDS and Behavior.
Gamification can inspire changes in behavior when a doctor's advice or a patient's good intentions are not enough. In this case, motivating those living with HIV to stick to ...
Powering Discovery: A new expert panel report from the CCA
2021-05-04
Research funding agencies around the world are testing creative approaches to address urgent needs while laying the foundation for discoveries that will meet the unpredictable demands of the future. According to a new expert panel report from the Council of Canadian Academies (CCA), Canada can bolster its research capacity by reducing administrative burdens, experimenting with funding approaches, and cultivating a robust, resilient, and diverse scientific workforce.
"In the past year we have seen the power and promise of transformative research and the ability of researchers and funding organizations to pivot in times of crisis," said Shirley M. Tilghman, PhD, O.C., FRS, Chair of the Expert Panel. "But the pandemic has also exacerbated existing inequalities ...
Partners of people with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder have often a mental disorder
2021-05-04
Almost half of the parents who have children together with a parent with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, are themselves burdened by psychological issues. This can affect family life and the children. This is shown in the research result from the major Danish psychiatry project iPSYCH.
We typically choose a partner who resembles us in relation to social status, education and, to some extent, also income. Research has previously established this. A new study now shows that almost half of the parents who have children with a partner who suffers from schizophrenia or bipolar disorder themselves meet the criteria for a mental disorder. By comparison, this is 18 percent for parents in the control group.
The results stem from The Danish High-Risk and Resilience ...
Chronic attack on the aging nervous system
2021-05-04
Aging is the biggest risk factor for perturbation of the nervous system, even in the absence of distinct disease or trauma. For yet unknown reasons, the impulse conducting, myelinated projections and synaptic connections between nerve cells are especially vulnerable to aging-related degeneration. These pathological alterations often manifest as cognitive, sensory, and motor decline in older adults and represent a serious socio-economic challenge.
Malactivation leads to damage
Scientists have long assumed that inflammation plays an important role in this process. Mal- or overactivation of distinct cells belonging to the innate immune system - the microglia - appears to promote damage of nerve fibers and synapses ...
Complex shapes of photons to boost future quantum technologies
2021-05-04
As the digital revolution has now become mainstream, quantum computing and quantum communication are rising in the consciousness of the field. The enhanced measurement technologies enabled by quantum phenomena, and the possibility of scientific progress using new methods, are of particular interest to researchers around the world.
Recently two researchers at Tampere University, Assistant Professor Robert Fickler and Doctoral Researcher Markus Hiekkamäki, demonstrated that two-photon interference can be controlled in a near-perfect way using ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
[Press-News.org] 7T brain scans reveal potential early indicator of Alzheimer'sNovel research approach holds promise for early detection and treatment