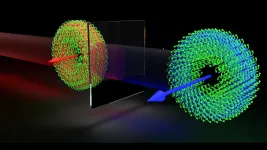
New application of AI just removed one of the biggest roadblocks in astrophysics
Using neural networks, Flatiron Institute research fellow Yin Li and his colleagues simulated vast, complex universes in a fraction of the time it takes with conventional methods
2021-05-05
(Press-News.org) Using a bit of machine learning magic, astrophysicists can now simulate vast, complex universes in a thousandth of the time it takes with conventional methods. The new approach will help usher in a new era in high-resolution cosmological simulations, its creators report in a study END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Long-term monitoring shows successful restoration of mining-polluted streams
2021-05-05
Many miles of streams and rivers in the United States and elsewhere are polluted by toxic metals in acidic runoff draining from abandoned mining sites, and major investments have been made to clean up acid mine drainage at some sites. A new study based on long-term monitoring data from four sites in the western United States shows that cleanup efforts can allow affected streams to recover to near natural conditions within 10 to 15 years after the start of abatement work.
The four mining-impacted watersheds--located in mountain mining regions of California, Colorado, Idaho, and Montana--were all designated as Superfund sites under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), which helps ...
Machine learning accelerates cosmological simulations
2021-05-05
A universe evolves over billions upon billions of years, but researchers have developed a way to create a complex simulated universe in less than a day. The technique, published in this week's Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, brings together machine learning, high-performance computing and astrophysics and will help to usher in a new era of high-resolution cosmology simulations.
Cosmological simulations are an essential part of teasing out the many mysteries of the universe, including those of dark matter and dark energy. But until now, researchers faced the common conundrum of not being ...
Without commuter traffic, pandemic-era drivers are speeding up, increasing noise pollution
2021-05-05
As pandemic lockdowns went into effect in March 2020 and millions of Americans began working from home rather than commuting to offices, heavy traffic in America's most congested urban centers--like Boston--suddenly ceased to exist. Soon afterwards, the air was noticeably cleaner. But that wasn't the only effect. A team of Boston University biologists who study how human-related sounds impact natural environments seized the opportunity to learn how the reduced movement of people would impact local ecosystems. They found--surprisingly--that sound levels increased in some nature conservation areas, a result of cars driving faster on roads no longer choked by traffic.
BU ecologist Richard Primack and Carina Terry, an undergraduate student working in Primack's ...
UMD team demonstrates swarm of photons that somersault in lockstep
2021-05-05
Spinning or rotating objects are commonplace, from toy tops, fidget spinners, and figure skaters to water circling a drain, tornadoes, and hurricanes.
In physics, there are two kinds of rotational motion: spin and orbital. Earth's motion in our solar system illustrates these; the daily 360-degree rotation of Earth around its own axis is spin rotation, while Earth's yearly trip around the sun is orbital rotation.
The quantity in physics defined to describe such motion is angular momentum (AM). AM is a conserved quantity: given an initial amount of it, it can be broken up and redistributed among particles such as atoms and photons, ...
A trait of the rare few whose bodies naturally control HIV: "trained" immune cells
2021-05-05
BOSTON -- Immunity often calls to mind the adaptive immune response, made up of antibodies and T cells that learn to fight specific pathogens after infection or vaccination. But the immune system also has an innate immune response, which uses a set number of techniques to provide a swift, non-specialized response against pathogens or support the adaptive immune response.
In the past few years, however, scientists have found that certain parts of the innate immune response can, in some instances, also be trained in response to infectious pathogens, such as HIV. Xu Yu, MD, a Core Member of the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard, and colleagues ...
Being around children makes adults more generous
2021-05-05
Adults are more compassionate and are up to twice as likely to donate to charity when children are present, according to a new study from psychologists.
The research, conducted by social psychologists at the University of Bath and Cardiff University and funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC), examined how the presence of children influences adults' compassionate motivations and behaviours.
Across eight experiments and more than 2,000 participants, the researchers asked adults to describe what typical children are like. After focusing on children in this way, participants ...
A multipronged approach to addressing childhood adversity and promoting resilience
2021-05-04
A hot topic symposia session during the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2021 Virtual Meeting will discuss a multipronged approach to addressing childhood adversity and promoting resilience - at the clinical, systems, community and educational levels.
The effect of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) on health outcomes across the lifespan is well recognized among pediatric practitioners. Increasing the ability of healthcare providers to recognize and respond to ACEs can buffer the long-term negative physical and mental health impacts of adversity and increase patient-centered care.
"In the era of COVID-19, ...
Muscle-fiber inspired pneumatic artificial muscles for multiple-mode actuations
2021-05-04
Biological organisms (such as elephant trunks, octopus tentacles, and human tongues) show remarkable dexterity and self-adaptation in unstructured environments, relying on the multiple-mode actuations of the skeleton-free muscular hydrostats. In general, muscular hydrostats mainly consist of well-ranged active 3D muscle-fiber arrays bundled by passive connective tissues (Fig. 1A). By selectively actuating the active 3D muscle-fiber arrays, muscular hydrostats can generate elongation, bending, contraction and twisting. Producing such multiple-mode actuation of muscular hydrostats is an interesting but long-lasting challenge in the field of robotics.
During past decades, many artificial muscles (such ...
A pediatric policy council plenary: The role of research in reducing gun violence
2021-05-04
A Pediatric Policy Council state of the art plenary session during the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2021 Virtual Meeting explored the role of public health research in iterative policymaking to reduce gun violence in America.
The toll of gun violence on young people represents one of the most significant public health challenges facing contemporary America. In recent years, firearm-related injury and death has made headlines routinely, including mass shootings at schools, public festivals, and places of worship, while daily occurrences of gun violence affect local communities.
Gun ...
Observation of antichiral edge states in a circuit lattice
2021-05-04
Originally formulated in the context of condensed matter physics, the Haldane model is an influential model of a two-dimensional topological insulator. It has also been realized in classical-wave metamaterial analogues of topological insulator, such as photonic crystals, acoustic crystals, and electric LC circuits.
Recently, theorists have shown that a modification to the Haldane model exhibits the novel phenomenon of antichiral edge sates, according to E. Colomés and M. Franz, scholars at Department of Physics and Astronomy and Quantum Matter Institute, University of British Columbia. Unlike the chiral edge states associated with the standard Haldane model, antichiral edge states possess the same propagation direction on opposite edges of a sample; the current carried by the edge ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
[Press-News.org] New application of AI just removed one of the biggest roadblocks in astrophysicsUsing neural networks, Flatiron Institute research fellow Yin Li and his colleagues simulated vast, complex universes in a fraction of the time it takes with conventional methods