Observation of antichiral edge states in a circuit lattice
2021-05-04
(Press-News.org) Originally formulated in the context of condensed matter physics, the Haldane model is an influential model of a two-dimensional topological insulator. It has also been realized in classical-wave metamaterial analogues of topological insulator, such as photonic crystals, acoustic crystals, and electric LC circuits.
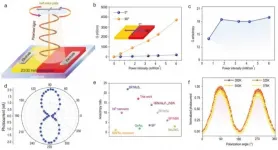
Recently, theorists have shown that a modification to the Haldane model exhibits the novel phenomenon of antichiral edge sates, according to E. Colomés and M. Franz, scholars at Department of Physics and Astronomy and Quantum Matter Institute, University of British Columbia. Unlike the chiral edge states associated with the standard Haldane model, antichiral edge states possess the same propagation direction on opposite edges of a sample; the current carried by the edge states is compensated by counter-propagating bulk states. However, the modified Haldane model has thus far never been realized in any experimental setting. In condensed matter, it is extremely challenging to achieve since it requires an unusual configuration of magnetic vector potentials within each crystalline unit cell.
An article coauthored by Profs. ZhiHong Hang and Yidong Chong, from Soochow University and Nanyang Technological University respectively, provided the first experimental realization of a modified Haldane model, consisting of electrical circuit lattices. This study entitled "Observation of antichiral edge states in a circuit lattice", was published in SCIENCE CHINA Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy. These researchers provide direct experimental evidence that the circuit lattice exhibits edge states, and that their propagation is antichiral. Their experimental results are in good agreement not only with theory, but also with numerical circuit simulations. "It opens the door to further experimental explorations of the properties of antichiral edge states in a real physical system", these researchers stated.
"This work demonstrates the flexibility of electrical circuit lattices as an experimental platform for realizing lattice models with effective magnetic vector potentials", they explained. Previous researchers had shown how to use circuits to implement a very well-studied topological phase (the Chern insulator, i.e. the simplest two-dimensional topological insulator), whereas in their study they implemented a very novel and nontrivial model (the modified Haldane model).
This experiments also point to the intriguing possibility of using circuit lattices to explore models with Möbius strip geometries and other exotic configurations, which may be a rich avenue of future research.
INFORMATION:
See the article:
Y. Yang, D. Zhu, Z. H. Hang, and Y. D. Chong, Observation of antichiral edge states in a circuit lattice, Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 64(5), 257011 (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-021-1675-0
https://www.sciengine.com/publisher/scp/journal/SCPMA/64/5/10.1007/s11433-021-1675-0?slug=fulltext
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-04
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues elsewhere, have used gene therapy to prevent learning and memory loss in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a key step toward eventually testing the approach in humans with the neurodegenerative disease.
The findings are published online in advance of the June 11, 2021 issue of Molecular Therapy-Methods & Clinical Development.
AD is characterized by the accumulation of clumps of misfolded proteins called amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tau tangles, both of which impair cell signaling and promote neuronal death. Current AD treatments targeting plaques and tangles address ...
2021-05-04
Polarization-sensitive photodetectors, based on anisotropic semiconductors, have exhibited wide advantages in specialized applications, such as astronomy, remote sensing, and polarization-division multiplexing. For the active layer of polarization-sensitive photodetectors, recent researches focus on two-dimensional (2D) organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites, where inorganic slabs and organic spacers are alternatively arranged in parallel layered structures. Compared with inorganic 2D materials, importantly, the solution accessibility of hybrid perovskites makes it possible to obtain their large crystals at low cost, offering exciting opportunities to incorporate crystal out-of-plane anisotropy for polarization-sensitive photodetection. However, limited by ...
2021-05-04
During the next 10 years, an estimated half-million individuals in the U.S. with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are expected to transition from adolescence to adulthood, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That means thousands of these young adults will likely fall into a widening and potentially devastating gap in a variety of services--because they're too old for high school, but may not qualify for Medicaid-funded services, social work researchers at Case Western Reserve University predict in a new study.
The team of researchers from the Jack, Joseph and Morton Mandel School of Applied Social Sciences interviewed 174 families from Northeast Ohio to examine the use of health, medical and social services for youth with autism--from 16 to 30 years old--and ...
2021-05-04
HOUSTON - (May 4, 2021) - Private equity investment in hospitals has grown substantially in the 21st century, and it accelerated in the years leading up the COVID-19 pandemic. Now a new study of short-term acute care hospitals acquired by private equity firms finds they not only have higher markups and profit margins, they're also slower to expand their staffs.
In a study published in Health Affairs, a multi-institutional team of investigators led by Dr. Anaeze C. Offodile II, a nonresident scholar in the Center for Health and Biosciences at Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy, the Gilbert Omenn Fellow at the National Academy of Medicine and an assistant professor of plastic and reconstructive surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, examined ...
2021-05-04
ORLANDO, Fla. (May 3, 2021) - Researchers have identified a gene expressed in children with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) that could serve as a new immunotherapy treatment target, according to a new study published today in Blood Advances, a journal of the American Society of Hematology. The study, co-authored by researchers with Nemours Children's Health System, outlines the process and potential path for new immunotherapy drugs that improve survival and reduce treatment-related toxicity in children with AML.
Leukemia is the most common cancer in children and teens, and AML accounts for nearly one-fourth of those cases. AML is a fast-growing cancer that typically starts in immature bone marrow cells.
"Using ...
2021-05-04
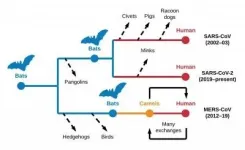
Coronavirus (CoVs) infection in animals and humans is not new. The earliest papers in the scientific literature of coronavirus infection date to 1966. However, prior to SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2, very little attention had been paid to coronaviruses.
Suddenly, coronaviruses changed everything we know about personal and public health, and societal and economic well-being. The change led to rushed analyses to understand the origins of coronaviruses in humans. This rush has led to a thus far fruitless search for intermediate hosts (e.g., civet in SARS-CoV and pangolin in SARS-CoV-2) rather than focusing on the important work, which has always been surveillance of ...
2021-05-04
When was the last time you repainted your car? Redesigned your coffee mug collection? Gave your shoes a colorful facelift?
You likely answered: never, never, and never. You might consider these arduous tasks not worth the effort. But a new color-shifting "programmable matter" system could change that with a zap of light.
MIT researchers have developed a way to rapidly update imagery on object surfaces. The system, dubbed "ChromoUpdate" pairs an ultraviolet (UV) light projector with items coated in light-activated dye. The projected light alters the reflective properties of the dye, creating colorful new images in just a few minutes. The advance could accelerate product development, enabling product designers to churn through ...
2021-05-04
Since it was first introduced in 2016, transparent wood has been developed by researchers at KTH Royal Institute of Technology as an innovative structural material for building construction. It lets natural light through and can even store thermal energy.
The key to making wood into a transparent composite material is to strip out its lignin, the major light-absorbing component in wood. But the empty pores left behind by the absence of lignin need to be filled with something that restores the wood's strength and allows light to permeate.
In earlier versions of the composite, researchers at KTH's Wallenberg Wood Science Centre used fossil-based polymers. Now, the researchers have successfully tested an eco-friendly alternative: limonene acrylate, a monomer made ...
2021-05-04
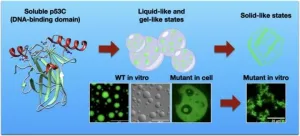
Cancer has been recently shown to be affected by protein clusters, particularly by the aggregation of mutant variants of the tumor suppressor protein p53, which are present in more than half of malignant tumors. However, how the aggregates are formed is not yet fully understood. The understanding of this process is expected to provide new therapeutic tools able to prevent proteins to clump and cancer progression.
In Brazil, researchers at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro have identified a key mechanism behind the mutant p53 aggregation process, linked to cancer pathology, opening new paths for the development of novels ...
2021-05-04
BAR HARBOR, MAINE — Our kidneys are charged with the extraordinary task of filtering about 53 gallons of fluid a day, a process that depends on podocytes, tiny, highly specialized cells in the cluster of blood vessels in the kidney where waste is filtered that are highly vulnerable to damage.
In research at the MDI Biological Laboratory in Bar Harbor, Maine, a team led by Iain Drummond, Ph.D., director of the Kathryn W. Davis Center for Regenerative Biology and Aging, has identified the signaling mechanisms underlying podocyte formation, or morphogenesis. The discovery opens the door to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Observation of antichiral edge states in a circuit lattice