Gene therapy in alzheimer's disease mouse model preserves learning and memory
2021-05-04
(Press-News.org) Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues elsewhere, have used gene therapy to prevent learning and memory loss in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a key step toward eventually testing the approach in humans with the neurodegenerative disease.
The findings are published online in advance of the June 11, 2021 issue of Molecular Therapy-Methods & Clinical Development.
AD is characterized by the accumulation of clumps of misfolded proteins called amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tau tangles, both of which impair cell signaling and promote neuronal death. Current AD treatments targeting plaques and tangles address only symptoms, which the study's authors say suggests a reversal and cure of AD will likely require a combination of interventional approaches that both decrease aggregating toxins and promote neuronal and synaptic plasticity.
Gene therapy is based on the premise that introducing a therapeutic compound to a precisely targeted region of the brain may restore or protect normal neural function and/or reverse neurodegenerative processes. In this case, researchers used a harmless adeno-associated viral vector to introduce synapsin-Caveolin-1 cDNA (AAV-SynCav1) into the hippocampus region of three-month-old transgenic AD mice.
The mice had been genetically modified to exhibit learning and memory deficits at 9 and 11 months, respectively. These deficits are associated with decreased expression of Caveolin-1, a scaffolding protein that builds the membranes housing cellular signaling tools, such as neurotrophin receptors that receive the critical extracellular signals, which govern all cellular life and function. With decay and destruction of these membranes, cell dysfunction and neurodegeneration follow.
"Our goal was to test whether SynCav1 gene therapy in these AD mouse models might preserve neuronal and synaptic plasticity in targeted parts of the membrane, and improve higher brain function," said senior author Brian P. Head, PhD, adjunct professor in the Department of Anesthesiology at UC San Diego School of Medicine and research health scientist at the VA San Diego Healthcare System.
And, in fact, that's what happened after mice received a single injection of AAV-SynCav1 to their hippocampus, which is a complex region deep within the brain that plays a major role in learning and memory. In AD, the hippocampus is among the first areas of the brain to be impaired.
At 9- and 11-months, said Head, hippocampal learning and memory in the mice were preserved. Moreover, researchers found that critical membrane structures and associated neurotrophin receptors also remained intact. Furthermore, these neuroprotective effects from SynCav1 gene delivery occurred independent of reducing amyloid plaque depositions.
"These results suggest SynCav1 gene therapy is an attractive approach to restore brain plasticity and improve brain function in AD and potentially in other forms of neurodegeneration caused by unknown etiology," wrote the authors.
Head's laboratory is currently testing SynCav1 gene delivery in other AD models at symptomatic stages as well as in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig's disease). He hopes to advance this work to human clinical trials soon.
INFORMATION:
The SynCav1 gene therapy is patented through UC San Diego and the Department of Veterans Affairs.
Co-authors include: Shanshan Wang, Joseph S. Leem, Natalia Kleschevnikov, Mehul Dhanani, Kimberly Zhou, Atsushi Miyanohara, David M. Roth, Hemal H. Patel and Piyush M. Patel, VA San Diego Healthcare System and UC San Diego; Paul Savchenko, Isabella C. Kelly, Sonia Podvin, Vivian Hook, Phuong Nguyen, Alexander Kleschevnikov and Steve L. Wagner, UC San Diego; Tong Zhang, Ohio State University; and John Q. Trojanowski, University of Pennsylvania.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-04
Polarization-sensitive photodetectors, based on anisotropic semiconductors, have exhibited wide advantages in specialized applications, such as astronomy, remote sensing, and polarization-division multiplexing. For the active layer of polarization-sensitive photodetectors, recent researches focus on two-dimensional (2D) organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites, where inorganic slabs and organic spacers are alternatively arranged in parallel layered structures. Compared with inorganic 2D materials, importantly, the solution accessibility of hybrid perovskites makes it possible to obtain their large crystals at low cost, offering exciting opportunities to incorporate crystal out-of-plane anisotropy for polarization-sensitive photodetection. However, limited by ...
2021-05-04
During the next 10 years, an estimated half-million individuals in the U.S. with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are expected to transition from adolescence to adulthood, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That means thousands of these young adults will likely fall into a widening and potentially devastating gap in a variety of services--because they're too old for high school, but may not qualify for Medicaid-funded services, social work researchers at Case Western Reserve University predict in a new study.
The team of researchers from the Jack, Joseph and Morton Mandel School of Applied Social Sciences interviewed 174 families from Northeast Ohio to examine the use of health, medical and social services for youth with autism--from 16 to 30 years old--and ...
2021-05-04
HOUSTON - (May 4, 2021) - Private equity investment in hospitals has grown substantially in the 21st century, and it accelerated in the years leading up the COVID-19 pandemic. Now a new study of short-term acute care hospitals acquired by private equity firms finds they not only have higher markups and profit margins, they're also slower to expand their staffs.
In a study published in Health Affairs, a multi-institutional team of investigators led by Dr. Anaeze C. Offodile II, a nonresident scholar in the Center for Health and Biosciences at Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy, the Gilbert Omenn Fellow at the National Academy of Medicine and an assistant professor of plastic and reconstructive surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, examined ...
2021-05-04
ORLANDO, Fla. (May 3, 2021) - Researchers have identified a gene expressed in children with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) that could serve as a new immunotherapy treatment target, according to a new study published today in Blood Advances, a journal of the American Society of Hematology. The study, co-authored by researchers with Nemours Children's Health System, outlines the process and potential path for new immunotherapy drugs that improve survival and reduce treatment-related toxicity in children with AML.
Leukemia is the most common cancer in children and teens, and AML accounts for nearly one-fourth of those cases. AML is a fast-growing cancer that typically starts in immature bone marrow cells.
"Using ...
2021-05-04
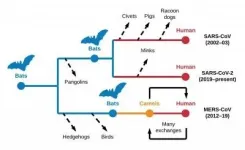
Coronavirus (CoVs) infection in animals and humans is not new. The earliest papers in the scientific literature of coronavirus infection date to 1966. However, prior to SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2, very little attention had been paid to coronaviruses.
Suddenly, coronaviruses changed everything we know about personal and public health, and societal and economic well-being. The change led to rushed analyses to understand the origins of coronaviruses in humans. This rush has led to a thus far fruitless search for intermediate hosts (e.g., civet in SARS-CoV and pangolin in SARS-CoV-2) rather than focusing on the important work, which has always been surveillance of ...
2021-05-04
When was the last time you repainted your car? Redesigned your coffee mug collection? Gave your shoes a colorful facelift?
You likely answered: never, never, and never. You might consider these arduous tasks not worth the effort. But a new color-shifting "programmable matter" system could change that with a zap of light.
MIT researchers have developed a way to rapidly update imagery on object surfaces. The system, dubbed "ChromoUpdate" pairs an ultraviolet (UV) light projector with items coated in light-activated dye. The projected light alters the reflective properties of the dye, creating colorful new images in just a few minutes. The advance could accelerate product development, enabling product designers to churn through ...
2021-05-04
Since it was first introduced in 2016, transparent wood has been developed by researchers at KTH Royal Institute of Technology as an innovative structural material for building construction. It lets natural light through and can even store thermal energy.
The key to making wood into a transparent composite material is to strip out its lignin, the major light-absorbing component in wood. But the empty pores left behind by the absence of lignin need to be filled with something that restores the wood's strength and allows light to permeate.
In earlier versions of the composite, researchers at KTH's Wallenberg Wood Science Centre used fossil-based polymers. Now, the researchers have successfully tested an eco-friendly alternative: limonene acrylate, a monomer made ...
2021-05-04
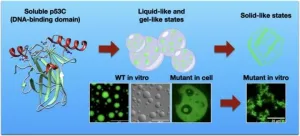
Cancer has been recently shown to be affected by protein clusters, particularly by the aggregation of mutant variants of the tumor suppressor protein p53, which are present in more than half of malignant tumors. However, how the aggregates are formed is not yet fully understood. The understanding of this process is expected to provide new therapeutic tools able to prevent proteins to clump and cancer progression.
In Brazil, researchers at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro have identified a key mechanism behind the mutant p53 aggregation process, linked to cancer pathology, opening new paths for the development of novels ...
2021-05-04
BAR HARBOR, MAINE — Our kidneys are charged with the extraordinary task of filtering about 53 gallons of fluid a day, a process that depends on podocytes, tiny, highly specialized cells in the cluster of blood vessels in the kidney where waste is filtered that are highly vulnerable to damage.
In research at the MDI Biological Laboratory in Bar Harbor, Maine, a team led by Iain Drummond, Ph.D., director of the Kathryn W. Davis Center for Regenerative Biology and Aging, has identified the signaling mechanisms underlying podocyte formation, or morphogenesis. The discovery opens the door to ...
2021-05-04
A team of University of Alberta researchers has discovered a way to use 3-D bioprinting technology to create custom-shaped cartilage for use in surgical procedures. The work aims to make it easier for surgeons to safely restore the features of skin cancer patients living with nasal cartilage defects after surgery.
The researchers used a specially designed hydrogel--a material similar to Jell-O--that could be mixed with cells harvested from a patient and then printed in a specific shape captured through 3-D imaging. Over a matter of weeks, the material is cultured in a lab to become functional cartilage.
"It takes a lifetime to make cartilage in an individual, while this method takes about four weeks. So you still expect ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Gene therapy in alzheimer's disease mouse model preserves learning and memory