Being around children makes adults more generous
2021-05-05
(Press-News.org) Adults are more compassionate and are up to twice as likely to donate to charity when children are present, according to a new study from psychologists.
The research, conducted by social psychologists at the University of Bath and Cardiff University and funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC), examined how the presence of children influences adults' compassionate motivations and behaviours.
Across eight experiments and more than 2,000 participants, the researchers asked adults to describe what typical children are like. After focusing on children in this way, participants subsequently indicated higher motivations towards compassionate values, such as helpfulness and social justice, and they reported greater empathy with the plight of other adults.
In a field study, which built on these findings, the researchers found that adult passers-by on a shopping street in Bath were more likely to donate to charity when more children were around relative to adults.
When no children were present and all passers-by were adults, a student research team from the University of Bath observed roughly one donation every ten minutes. But when children and adults were equally present on the shopping street, adult passers-by made two donations every ten minutes.
These effects could not be accounted for by higher footfall during busy times or whether donors were accompanied by a child or not. Instead, they suggest that the presence of children can nudge adults to behave more generously and donate more often. The on-street donations were made to 'Bath Marrow', a charity which supports people with blood cancer.
Interestingly, these findings point to a widely applicable effect. The researchers observed that the 'child salience effect' was evident among both parents and non-parents, men and women, younger and older participants, and even among those who had relatively negative attitudes towards children. The researchers involved suggest these effects could also have widespread implications.
Lead researcher Dr Lukas Wolf from the Department of Psychology at Bath explains: "While previous evidence has shown that we are typically more helpful and empathetic towards children, no research has been done to date to examine whether the presence of children alone encourages us to be more pro-social towards others in general. Our research addresses this gap by showing that the presence of children elicits broad pro-social motivation and donation behaviour towards causes not directly related to children."
Dr Wolf says that this potential for widespread effect is important because it indicates society needs to consider new ways to involve children more directly in various aspects of life.
"Our findings showing the importance of children for compassionate behaviour in society provides a glimpse of a much bigger impact," he says.
"Children are indirectly dependent on how adults behave towards each other and towards the planet. Yet, children are also separated from many adult environments, such as workplaces and from political bodies where important decisions affect their futures."
He adds: "The finding that the presence of children motivates adults to be more compassionate towards others calls for more integration of children in contexts where adults make important long-term decisions, such as on climate change."
Various initiatives over recent years have been established to increase the prominence of young voices, for example Children's Parliaments. Future work from the researchers involved in this study will look in more detail at the nature of the child salience effect and its ramifications for society and the planet.
INFORMATION:
Their results are published in the journal Social Psychological and Personality Science.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-04
A hot topic symposia session during the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2021 Virtual Meeting will discuss a multipronged approach to addressing childhood adversity and promoting resilience - at the clinical, systems, community and educational levels.
The effect of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) on health outcomes across the lifespan is well recognized among pediatric practitioners. Increasing the ability of healthcare providers to recognize and respond to ACEs can buffer the long-term negative physical and mental health impacts of adversity and increase patient-centered care.
"In the era of COVID-19, ...
2021-05-04
Biological organisms (such as elephant trunks, octopus tentacles, and human tongues) show remarkable dexterity and self-adaptation in unstructured environments, relying on the multiple-mode actuations of the skeleton-free muscular hydrostats. In general, muscular hydrostats mainly consist of well-ranged active 3D muscle-fiber arrays bundled by passive connective tissues (Fig. 1A). By selectively actuating the active 3D muscle-fiber arrays, muscular hydrostats can generate elongation, bending, contraction and twisting. Producing such multiple-mode actuation of muscular hydrostats is an interesting but long-lasting challenge in the field of robotics.
During past decades, many artificial muscles (such ...
2021-05-04
A Pediatric Policy Council state of the art plenary session during the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2021 Virtual Meeting explored the role of public health research in iterative policymaking to reduce gun violence in America.
The toll of gun violence on young people represents one of the most significant public health challenges facing contemporary America. In recent years, firearm-related injury and death has made headlines routinely, including mass shootings at schools, public festivals, and places of worship, while daily occurrences of gun violence affect local communities.
Gun ...
2021-05-04
Originally formulated in the context of condensed matter physics, the Haldane model is an influential model of a two-dimensional topological insulator. It has also been realized in classical-wave metamaterial analogues of topological insulator, such as photonic crystals, acoustic crystals, and electric LC circuits.
Recently, theorists have shown that a modification to the Haldane model exhibits the novel phenomenon of antichiral edge sates, according to E. Colomés and M. Franz, scholars at Department of Physics and Astronomy and Quantum Matter Institute, University of British Columbia. Unlike the chiral edge states associated with the standard Haldane model, antichiral edge states possess the same propagation direction on opposite edges of a sample; the current carried by the edge ...
2021-05-04
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues elsewhere, have used gene therapy to prevent learning and memory loss in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a key step toward eventually testing the approach in humans with the neurodegenerative disease.
The findings are published online in advance of the June 11, 2021 issue of Molecular Therapy-Methods & Clinical Development.
AD is characterized by the accumulation of clumps of misfolded proteins called amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tau tangles, both of which impair cell signaling and promote neuronal death. Current AD treatments targeting plaques and tangles address ...
2021-05-04
Polarization-sensitive photodetectors, based on anisotropic semiconductors, have exhibited wide advantages in specialized applications, such as astronomy, remote sensing, and polarization-division multiplexing. For the active layer of polarization-sensitive photodetectors, recent researches focus on two-dimensional (2D) organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites, where inorganic slabs and organic spacers are alternatively arranged in parallel layered structures. Compared with inorganic 2D materials, importantly, the solution accessibility of hybrid perovskites makes it possible to obtain their large crystals at low cost, offering exciting opportunities to incorporate crystal out-of-plane anisotropy for polarization-sensitive photodetection. However, limited by ...
2021-05-04
During the next 10 years, an estimated half-million individuals in the U.S. with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are expected to transition from adolescence to adulthood, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That means thousands of these young adults will likely fall into a widening and potentially devastating gap in a variety of services--because they're too old for high school, but may not qualify for Medicaid-funded services, social work researchers at Case Western Reserve University predict in a new study.
The team of researchers from the Jack, Joseph and Morton Mandel School of Applied Social Sciences interviewed 174 families from Northeast Ohio to examine the use of health, medical and social services for youth with autism--from 16 to 30 years old--and ...
2021-05-04
HOUSTON - (May 4, 2021) - Private equity investment in hospitals has grown substantially in the 21st century, and it accelerated in the years leading up the COVID-19 pandemic. Now a new study of short-term acute care hospitals acquired by private equity firms finds they not only have higher markups and profit margins, they're also slower to expand their staffs.
In a study published in Health Affairs, a multi-institutional team of investigators led by Dr. Anaeze C. Offodile II, a nonresident scholar in the Center for Health and Biosciences at Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy, the Gilbert Omenn Fellow at the National Academy of Medicine and an assistant professor of plastic and reconstructive surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, examined ...
2021-05-04
ORLANDO, Fla. (May 3, 2021) - Researchers have identified a gene expressed in children with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) that could serve as a new immunotherapy treatment target, according to a new study published today in Blood Advances, a journal of the American Society of Hematology. The study, co-authored by researchers with Nemours Children's Health System, outlines the process and potential path for new immunotherapy drugs that improve survival and reduce treatment-related toxicity in children with AML.
Leukemia is the most common cancer in children and teens, and AML accounts for nearly one-fourth of those cases. AML is a fast-growing cancer that typically starts in immature bone marrow cells.
"Using ...
2021-05-04
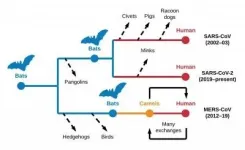
Coronavirus (CoVs) infection in animals and humans is not new. The earliest papers in the scientific literature of coronavirus infection date to 1966. However, prior to SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2, very little attention had been paid to coronaviruses.
Suddenly, coronaviruses changed everything we know about personal and public health, and societal and economic well-being. The change led to rushed analyses to understand the origins of coronaviruses in humans. This rush has led to a thus far fruitless search for intermediate hosts (e.g., civet in SARS-CoV and pangolin in SARS-CoV-2) rather than focusing on the important work, which has always been surveillance of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Being around children makes adults more generous