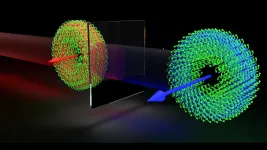
New algorithm uses a hologram to control trapped ions
2021-05-05
(Press-News.org) Researchers have discovered the most precise way to control individual ions using holographic optical engineering technology.
The new technology uses the first known holographic optical engineering device to control trapped ion qubits. This technology promises to help create more precise controls of qubits that will aid the development of quantum industry-specific hardware to further new quantum simulation experiments and potentially quantum error correction processes for trapped ion qubits.
"Our algorithm calculates the hologram's profile and removes any aberrations from the light, which lets us develop a highly precise technique for programming ions," says lead author Chung-You Shih, a PhD student at the University of Waterloo's Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC).
Kazi Rajibul Islam, a faculty member at IQC and in physics and astronomy at Waterloo is the lead investigator on this work. His team has been trapping ions used in quantum simulation in the Laboratory for Quantum Information since 2019 but needed a precise way to control them.
A laser aimed at an ion can "talk" to it and change the quantum state of the ion, forming the building blocks of quantum information processing. However, laser beams have aberrations and distortions that can result in a messy, wide focus spot, which is a problem because the distance between trapped ions is a few micrometers - much narrower than a human hair.
The laser beam profiles the team wanted to stimulate the ions would need to be precisely engineered. To achieve this they took a laser, blew its light up to 1cm wide and then sent it through a digital micromirror device (DMD), which is programable and functions as a movie projector. The DMD chip has two-million micron-scale mirrors on it that are individually controlled using electric voltage. Using an algorithm that Shih developed, the DMD chip is programmed to display a hologram pattern. The light produced from the DMD hologram can have its intensity and phase exactly controlled.
In testing, the team has been able to manipulate each ion with the holographic light. Previous research has struggled with cross talk, which means that if a laser focuses on one ion, the light leaks on the surrounding ions. With this device, the team successfully characterizes the aberrations using an ion as a sensor. They can then cancel the aberrations by adjusting the hologram and obtain the lowest cross talk in the world.
"There is a challenge in using commercially available DMD technology," Shih says. "Its controller is made for projectors and UV lithography, not quantum experiments. Our next step is to develop our own hardware for quantum computation experiments."
INFORMATION:
The study, Reprogrammable and high-precision holographic optical addressing of trapped ions for scalable quantum control, details the researchers' work published in the journal npj Quantum Information.
This research was supported in part by the Canada First Research Excellence Fund through Transformative Quantum Technologies.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-05
A computer science engineer at Michigan State University has a word of advice for the millions of bitcoin owners who use smartphone apps to manage their cryptocurrency: don't. Or at least, be careful. Researchers from MSU are developing a mobile app to act as a safeguard for popular but vulnerable "wallet" applications used to manage cryptocurrency.
"More and more people are using bitcoin wallet apps on their smartphones," said Guan-Hua Tu, an assistant professor in MSU's College of Engineering who works in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering. "But these applications have vulnerabilities." ...
2021-05-05
A new USC study suggests that certain neighborhoods - particularly those characterized by poverty and unemployment - may pose an environmental risk to the developing brains of children, impacting neurocognitive performance and even brain size.
The research was published May 3 in the journal JAMA Pediatrics.
These findings highlight the importance of neighborhood environments for child and adolescent brain development, the researchers said, and suggest that policies, programs and investments that help improve local neighborhood conditions and empower communities could support children's neurodevelopment and long-term health.
"This is the first large, national study ...
2021-05-05
Using a bit of machine learning magic, astrophysicists can now simulate vast, complex universes in a thousandth of the time it takes with conventional methods. The new approach will help usher in a new era in high-resolution cosmological simulations, its creators report in a study END ...
2021-05-05
Many miles of streams and rivers in the United States and elsewhere are polluted by toxic metals in acidic runoff draining from abandoned mining sites, and major investments have been made to clean up acid mine drainage at some sites. A new study based on long-term monitoring data from four sites in the western United States shows that cleanup efforts can allow affected streams to recover to near natural conditions within 10 to 15 years after the start of abatement work.
The four mining-impacted watersheds--located in mountain mining regions of California, Colorado, Idaho, and Montana--were all designated as Superfund sites under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), which helps ...
2021-05-05
A universe evolves over billions upon billions of years, but researchers have developed a way to create a complex simulated universe in less than a day. The technique, published in this week's Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, brings together machine learning, high-performance computing and astrophysics and will help to usher in a new era of high-resolution cosmology simulations.
Cosmological simulations are an essential part of teasing out the many mysteries of the universe, including those of dark matter and dark energy. But until now, researchers faced the common conundrum of not being ...
2021-05-05
As pandemic lockdowns went into effect in March 2020 and millions of Americans began working from home rather than commuting to offices, heavy traffic in America's most congested urban centers--like Boston--suddenly ceased to exist. Soon afterwards, the air was noticeably cleaner. But that wasn't the only effect. A team of Boston University biologists who study how human-related sounds impact natural environments seized the opportunity to learn how the reduced movement of people would impact local ecosystems. They found--surprisingly--that sound levels increased in some nature conservation areas, a result of cars driving faster on roads no longer choked by traffic.
BU ecologist Richard Primack and Carina Terry, an undergraduate student working in Primack's ...
2021-05-05
Spinning or rotating objects are commonplace, from toy tops, fidget spinners, and figure skaters to water circling a drain, tornadoes, and hurricanes.
In physics, there are two kinds of rotational motion: spin and orbital. Earth's motion in our solar system illustrates these; the daily 360-degree rotation of Earth around its own axis is spin rotation, while Earth's yearly trip around the sun is orbital rotation.
The quantity in physics defined to describe such motion is angular momentum (AM). AM is a conserved quantity: given an initial amount of it, it can be broken up and redistributed among particles such as atoms and photons, ...
2021-05-05
BOSTON -- Immunity often calls to mind the adaptive immune response, made up of antibodies and T cells that learn to fight specific pathogens after infection or vaccination. But the immune system also has an innate immune response, which uses a set number of techniques to provide a swift, non-specialized response against pathogens or support the adaptive immune response.
In the past few years, however, scientists have found that certain parts of the innate immune response can, in some instances, also be trained in response to infectious pathogens, such as HIV. Xu Yu, MD, a Core Member of the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard, and colleagues ...
2021-05-05
Adults are more compassionate and are up to twice as likely to donate to charity when children are present, according to a new study from psychologists.
The research, conducted by social psychologists at the University of Bath and Cardiff University and funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC), examined how the presence of children influences adults' compassionate motivations and behaviours.
Across eight experiments and more than 2,000 participants, the researchers asked adults to describe what typical children are like. After focusing on children in this way, participants ...
2021-05-04
A hot topic symposia session during the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) 2021 Virtual Meeting will discuss a multipronged approach to addressing childhood adversity and promoting resilience - at the clinical, systems, community and educational levels.
The effect of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) on health outcomes across the lifespan is well recognized among pediatric practitioners. Increasing the ability of healthcare providers to recognize and respond to ACEs can buffer the long-term negative physical and mental health impacts of adversity and increase patient-centered care.
"In the era of COVID-19, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New algorithm uses a hologram to control trapped ions