Bacterial DNA can be read either forwards or backwards - new study
2021-05-06
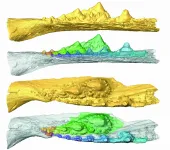
(Press-News.org) Bacteria contain symmetry in their DNA signals that enable them to be read either forwards or backwards, according to new findings at the University of Birmingham which challenge existing knowledge about gene transcription.
In all living organisms, DNA code is divided into sections which provide information about a specific process. These must be read before the information can be used. Cells identify the start of each section using 'signposts', which scientists first identified in the 1960s.
It has always been assumed that these signposts enable genetic sequences to be read in a single direction. The new study, published in Nature Microbiology, however, shows that single-celled organisms have symmetrical DNA signposts. This means that the DNA code can be read in either direction.
Lead author, Professor David Grainger, explains: "Most of the studies on gene signalling overlook the symmetry, but we think this is incredibly significant and represents a whole new level of regulating genes that has not yet been investigated."
The precise reasons for the two-directional reading are not yet clear and will require further investigation. One theory the team is considering is that it helps to avoid reading 'collisions' with other sequences.
Although the current study focuses mainly on bacteria, the team speculate that the signpost symmetry is likely to be found in humans, animals and other organisms too. The next step for the research will be to investigate the phenomenon in yeast cells which more closely resemble human cells.
Professor Grainger adds: "Understanding how genes are read is fundamental to many branches of biotechnology. Lots of medicines, for example, are dependent on being able to control how genes are read, so it's important to fully understand how these signals work, and how we can use that knowledge to improve healthcare."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
The origins of a pretty smile have long been sought in the fearsome jaws of living sharks which have been considered living fossils reflecting the ancestral condition for vertebrate tooth development and inference of its evolution. However, this view ignores real fossils which more accurately reflect the nature of ancient ancestors.
New research led by the University of Bristol and the Naturalis Biodiversity Center published in Nature Ecology and Evolution reveals that the dentitions of living shark relatives are entirely unrepresentative of the last shared ancestor of jawed vertebrates.
The study reveals ...
2021-05-06
What The Study Did: This study estimates the association between Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccination and symptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections among health care workers more than seven days after getting a second vaccine dose.
Authors: Ronen Ben-Ami, M.D., of the Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center in Israel, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.7152)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study ...
2021-05-06
What The Study Did: This study describes an association between the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine and decreased risk of symptomatic and asymptomatic infections with SARS-CoV-2 in hospital employees.
Authors: Li Tang, Ph.D., of the St. Jude Children's Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6564)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
2021-05-06
The bulging, equator-belted midsection of Earth currently teems with a greater diversity of life than anywhere else -- a biodiversity that generally wanes when moving from the tropics to the mid-latitudes and the mid-latitudes to the poles.
As well-accepted as that gradient is, though, ecologists continue to grapple with the primary reasons for it. New research from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Yale University and Stanford University suggests that temperature can largely explain why the greatest variety of aquatic life resides in the tropics -- but also why it has not ...
2021-05-06
A key driver of patients' well-being and clinical trials for Parkinson's disease (PD) is the course the disease takes over time. However, nearly all that is known about the genetics of PD is related to susceptibility -- a person's risk for developing the disease in the future. A new study by investigators from Brigham and Women's Hospital published in Nature Genetics uncovers the genetic architecture of progression and prognosis, identifying five genetic locations (loci) associated with progression. The team also developed the first risk score for predicting ...
2021-05-06
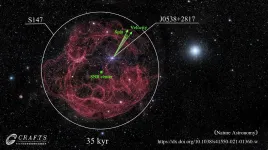
Pulsars - another name for fast-spinning neutron stars - originate from the imploded cores of massive dying stars through supernova explosion.
Now, more than 50 years after the discovery of pulsars and confirmation of their association with supernova explosions, the origin of the initial spin and velocity of pulsars is finally beginning to be understood.
Based on observations from the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), Dr. YAO Jumei, member of a team led by Dr. LI Di from National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC), found the first evidence for three-dimensional (3D) spin-velocity alignment in pulsars.
The study was published in Nature Astronomy on May 6. It also marks the beginning of in-depth pulsar research with FAST.
For decades, ...
2021-05-06
While other medical systems across the country failed to maintain HIV screening volumes throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, the University of Chicago Medicine maintained screening volumes by including universal HIV screening alongside COVID-19 testing in its busy emergency department, according to a new report published April 12 in JAMA Internal Medicine. Through targeted efforts to maintain infrastructure and enthusiasm for HIV screening, the number of HIV tests remained at pre-pandemic levels while the rate of acute HIV diagnoses actually increased.
Widespread screening to diagnose individuals newly infected with HIV is a key part of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's (CDC) plan to ...
2021-05-06
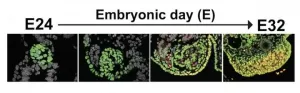
Early in human development, during the first trimester of gestation, a fetus may have XX or XY chromosomes that indicate its sex. Yet at this stage a mass of cells known as the bipotential gonad that ultimately develops into either ovaries or testes has yet to commit to its final destiny.
While researchers had studied the steps that go into the later stages of this process, little has been known about the precursors of the bipotential gonad. In a new study published in Cell Reports and co-led by Kotaro Sasaki of Penn's School of Veterinary Medicine, an international team lays ...
2021-05-06
Although the fairy tale of the wicked stepmother is a tale as old as time, the effects of blending children with their new stepfamilies may not be as grim as once thought.
In fact, new research shows that stepparents are not at a disadvantage compared to their peers from single-parent households and actually experience better outcomes than their halfsiblings -- good news for the more than 113 million Americans that are part of a steprelationship.
Led by East Carolina University anthropologist Ryan Schacht and researchers from the University of Utah, the study, "Was Cinderella just a fairy tale? Survival differences between stepchildren and their half-siblings," is available in the May edition of the Philosophical Transactions ...
2021-05-06
The European Alps is certainly one of the most scrutinized mountain range in the world, as it forms a true open-air laboratory showing how climate change affects biodiversity. Although many studies have independently demonstrated the impact of climate change in the Alps on either the seasonal activity (i.e. phenology) or the migration of plants and animals, no systematic analysis has been carried out on both consequences simultaneously. A European team of ecologists1, including Jonathan Lenoir, CNRS Researcher in the research unit Écologie et Dynamique des Systèmes Anthropisés (CNRS/University of Picardie Jules Verne), has just published a review that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Bacterial DNA can be read either forwards or backwards - new study