Online learning doesn't improve student sleep habits, research suggests
Students working/studying from home sleep later but not longer, according to a new study from Simon Fraser University researchers
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) New research from Simon Fraser University suggests that students learning remotely become night owls but do not sleep more despite the time saved commuting, working or attending social events.
The study, led by psychology professor Ralph Mistlberger, Andrea Smit and Myriam Juda, at SFU's Circadian Rhythms and Sleep Lab, compared self-reported data on sleep habits from 80 students enrolled in a 2020 summer session course at SFU with data collected from 450 students enrolled in the same course during previous summer semesters. The study results were recently published in the journal PLOS ONE.
"There is a widespread belief among sleep researchers that many people, especially young adults, regularly obtain insufficient sleep due to work, school, and social activities," says Mistlberger. "The move toward remote work and school during COVID-19 has provided a novel opportunity to test this belief."
The student participants kept daily sleep diaries over a period of two-to-eight weeks, completed questionnaires and provided written reports. Fitbit sleep tracker data was collected from a subsample of participants.
The team found that students learning remotely in the summer 2020 session went to bed an average of 30 minutes later than pre-pandemic students. They slept less efficiently, less at night and more during the day, but did not sleep more overall despite having no early classes and 44 per cent fewer work days compared to students in previous semesters.
"One very consistent finding is a collective delay of sleep timing - people go to bed and wake up later," says Mistlberger. "Not surprisingly, there is also a marked reduction in natural light exposure, especially early in the day. The lack of change in sleep duration was a bit of a surprise, as it goes against the assumption that young adults would sleep more if they had the time."
Self-described night owls were more likely to report a greater positive impact on their sleep, getting to sleep in, instead of waking up early for that morning class, while morning types were more likely to report a negative response to sleeping later than usual.
Sleep plays an important role in immune functioning and mental health, which is why good sleep habits are crucial.
"My advice for students and anybody working from home is to try to get outside and be active early in the day because the morning light helps stabilize your circadian sleep-wake cycle - this should improve your sleep, and allow you to feel more rested and energized during the day," says Mistlberger.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
In a study published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers show that although two doses of a vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 -- the virus that causes COVID 19 -- confers some protection for people who have received solid organ transplants, it's still not enough to enable them to dispense with masks, physical distancing and other safety measures.
This is a follow-up study to an earlier one published in March in JAMA, in which the researchers reported that only 17% of the participating transplant recipients produced sufficient antibodies after just one dose of a two-dose COVID-19 vaccine regimen.
"While there was an ...
2021-05-06
Loneliness and social isolation have been significant problems for the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic, but for cancer patients these issues were particularly acute, likely due to isolation and social distancing, according to a new UCSF study.
The study, which is the first to evaluate loneliness, anxiety, depression, fatigue and other symptoms in a single group of patients, is published in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
"We found that oncology patients were experiencing a deep sense of loneliness," ...
2021-05-06
Researchers at North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina Greensboro made a surprising finding while examining areas where sand flies rear their young: a new species of bacteria that is highly attractive to pregnant, or gravid, sand flies. The findings could advance the production of ecologically safe baits or traps to reduce sand fly populations.
Sand flies are vectors for important parasitic diseases affecting people in tropical and subtropical regions in Asia, Africa and the Middle East. One of those diseases is Leishmaniasis, which generally causes ...
2021-05-06
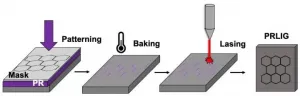
HOUSTON - (May 6, 2021) - A Rice University laboratory has adapted its laser-induced graphene technique to make high-resolution, micron-scale patterns of the conductive material for consumer electronics and other applications.
Laser-induced graphene (LIG), introduced in 2014 by Rice chemist James Tour, involves burning away everything that isn't carbon from polymers or other materials, leaving the carbon atoms to reconfigure themselves into films of characteristic hexagonal graphene.
The process employs a commercial laser that "writes" graphene patterns into surfaces that to date have included wood, paper and even food.
The new iteration writes fine patterns of graphene into photoresist polymers, light-sensitive materials used in photolithography and ...
2021-05-06
As the human body's largest organ, the skin is responsible for protecting against a wide range of possible infections on all fleshy surfaces, from head to toe. So how exactly does the skin organize its defenses against such an array of threats?
A new Yale study shows that the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, is comprised of an army of immune cells that station themselves at regular intervals across the skin's vast expanse to resist infection. When necessary, the researchers found, these immune system soldiers are able to reposition themselves to protect vulnerable areas.
The study, published in the journal Nature Cell Biology, was conducted by the lab of Valentina ...
2021-05-06
The introduction of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries has revolutionized technology as a whole, leading to major advances in consumer goods across nearly all sectors. Battery-powered devices have become ubiquitous across the world. While the availability of technology is generally a good thing, the rapid growth has led directly to several key ethical and environmental issues surrounding the use of Li-ion batteries.
Current Li-ion batteries utilize significant amounts of cobalt, which in several well-documented international cases is mined using child labor in dangerous working ...
2021-05-06
The idea of creating quantum computers has long captured the minds of researchers and experts of IT corporations. They are the most powerful computers operating according to the laws of the quantum world and capable of solving many problems more efficiently than the most productive classical supercomputers. Similar developments are underway, for example, at Google and IBM. However, many such projects require the use of cryostats. These are vessels with liquid nitrogen or compressed helium, inside which quantum processors are cooled to temperatures below -270°C. Such a low temperature is required to maintain the superconductivity effect, which is necessary for the operation ...
2021-05-06
Today's 10,000 species of birds live in virtually every habitat on Earth, but only a handful have adaptations enabling them to hunt active prey in the dark of night. Scientists have long wondered whether theropod dinosaurs - the group that gave rise to modern birds - had similar sensory adaptations.
A new study led by University of the Witwatersrand scientist, Professor Jonah Choiniere, sought to investigate how vision and hearing abilities of dinosaurs and birds compared. The international team of researchers used CT scanning and detailed measurements to collect information ...
2021-05-06
New Haven, Conn. -- If paleontologists had a wish list, it would almost certainly include insights into two particular phenomena: how dinosaurs interacted with each other and how they began to fly.
The problem is, using fossils to deduce such behavior is a tricky business. But a new, Yale-led study offers a promising entry point -- the inner ear of an ancient reptile.
According to the study, the shape of the inner ear offers reliable signs as to whether an animal soared gracefully through the air, flew only fitfully, walked on the ground, or sometimes went swimming. In some cases, the inner ear even indicates whether ...
2021-05-06
The findings, published in the journal Science today, demonstrate how integrating vertical descent and horizontal gene transfer can be used to infer the root of the bacterial tree and the nature of the last bacterial common ancestor.
Bacteria comprise a very diverse domain of single-celled organisms that can be found almost everywhere on Earth. All Bacteria are related and derive from a common ancestral Bacterial cell. Until now, the shape of the bacterial tree of life and the placement of its root has been contested, but is necessary to shed light on the early evolution of life on our ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Online learning doesn't improve student sleep habits, research suggests
Students working/studying from home sleep later but not longer, according to a new study from Simon Fraser University researchers