Researchers develop new metal-free, recyclable polypeptide battery that degrades on demand
This could result in battery production moving away from strategic elements like cobalt
2021-05-06
(Press-News.org) The introduction of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries has revolutionized technology as a whole, leading to major advances in consumer goods across nearly all sectors. Battery-powered devices have become ubiquitous across the world. While the availability of technology is generally a good thing, the rapid growth has led directly to several key ethical and environmental issues surrounding the use of Li-ion batteries.
Current Li-ion batteries utilize significant amounts of cobalt, which in several well-documented international cases is mined using child labor in dangerous working environments. Additionally, only a very small percentage of Li-ion batteries are recycled, increasing the demand for cobalt and other strategic elements.
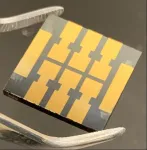
A multidisciplinary team of researchers from Texas A&M University has made a breakthrough that could lead to battery production moving away from cobalt. In an article published in the May issue of Nature, Dr. Jodie Lutkenhaus, Axalta Coating Systems Chair and professor in the Artie McFerrin Department of Chemical Engineering, and Dr. Karen Wooley, distinguished professor in the Department of Chemistry and holder of the W.T. Doherty-Welch Chair in Chemistry in the College of Science, outline their research into a new battery technology platform that is completely metal free. This new battery technology platform utilizes a polypeptide organic radical construction.
"By moving away from lithium and working with these polypeptides, which are components of proteins, it really takes us into this realm of not only avoiding the need for mining precious metals, but opening opportunities to power wearable or implantable electronic devices and also to easily recycle the new batteries," said Wooley, recently honored as the 2021 SEC Professor of the Year. "They [polypeptide batteries] are degradable, they are recyclable, they are non-toxic and they are safer across the board."
The all-polypeptide organic radical battery composed of redox-active amino-acid macromolecules also solves the problem of recyclability. The components of the new battery platform can be degraded on demand in acidic conditions to generate amino acids, other building blocks and degradation products -- one of the major breakthroughs in this research, according to Lutkenhaus.
"The big problem with lithium-ion batteries right now is that they're not recycled to the degree that we are going to need for the future electrified transportation economy," Lutkenhaus added. "The rate of recycling lithium-ion batteries right now is in the single digits. There is valuable material in the lithium-ion battery, but it's very difficult and energy intensive to recover."
The development of a metal-free, all-polypeptide organic radical battery composed of redox-active amino-acid macromolecules that degrade on demand marks significant progress toward sustainable, recyclable batteries that minimize dependence on strategic metals. As a next step, Wooley and Lutkenhaus have begun working in collaboration with Dr. Daniel Tabor, assistant professor in the Department of Chemistry, through a 2020 Texas A&M Triads for Transformation (T3) grant that aims to utilize machine learning to optimize the materials and structure of the battery platform.
INFORMATION:
The lead authors on the paper are Tan Nguyen, a current postdoctoral associate at the University of Michigan and former doctoral student from the Texas A&M Department of Chemistry, and Alexandra Easley, a doctoral student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Texas A&M.
This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation, the Welch Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-06
The idea of creating quantum computers has long captured the minds of researchers and experts of IT corporations. They are the most powerful computers operating according to the laws of the quantum world and capable of solving many problems more efficiently than the most productive classical supercomputers. Similar developments are underway, for example, at Google and IBM. However, many such projects require the use of cryostats. These are vessels with liquid nitrogen or compressed helium, inside which quantum processors are cooled to temperatures below -270°C. Such a low temperature is required to maintain the superconductivity effect, which is necessary for the operation ...
2021-05-06
Today's 10,000 species of birds live in virtually every habitat on Earth, but only a handful have adaptations enabling them to hunt active prey in the dark of night. Scientists have long wondered whether theropod dinosaurs - the group that gave rise to modern birds - had similar sensory adaptations.
A new study led by University of the Witwatersrand scientist, Professor Jonah Choiniere, sought to investigate how vision and hearing abilities of dinosaurs and birds compared. The international team of researchers used CT scanning and detailed measurements to collect information ...
2021-05-06
New Haven, Conn. -- If paleontologists had a wish list, it would almost certainly include insights into two particular phenomena: how dinosaurs interacted with each other and how they began to fly.
The problem is, using fossils to deduce such behavior is a tricky business. But a new, Yale-led study offers a promising entry point -- the inner ear of an ancient reptile.
According to the study, the shape of the inner ear offers reliable signs as to whether an animal soared gracefully through the air, flew only fitfully, walked on the ground, or sometimes went swimming. In some cases, the inner ear even indicates whether ...
2021-05-06
The findings, published in the journal Science today, demonstrate how integrating vertical descent and horizontal gene transfer can be used to infer the root of the bacterial tree and the nature of the last bacterial common ancestor.
Bacteria comprise a very diverse domain of single-celled organisms that can be found almost everywhere on Earth. All Bacteria are related and derive from a common ancestral Bacterial cell. Until now, the shape of the bacterial tree of life and the placement of its root has been contested, but is necessary to shed light on the early evolution of life on our ...
2021-05-06
The uncertainty principle, first introduced by Werner Heisenberg in the late 1920's, is a fundamental concept of quantum mechanics. In the quantum world, particles like the electrons that power all electrical product can also behave like waves. As a result, particles cannot have a well-defined position and momentum simultaneously. For instance, measuring the momentum of a particle leads to a disturbance of position, and therefore the position cannot be precisely defined.
In recent research, published in Science, a team led by Prof. Mika Sillanpää at Aalto University in Finland has shown that there is a way to get around ...
2021-05-06
In the 150 years since Charles Darwin speculated that humans originated in Africa, the number of species in the human family tree has exploded, but so has the level of dispute concerning early human evolution. Fossil apes are often at the center of the debate, with some scientists dismissing their importance to the origins of the human lineage (the "hominins"), and others conferring them starring evolutionary roles. A new review out on May 7 in the journal Science looks at the major discoveries in hominin origins since Darwin's works and argues that fossil apes can inform us about essential aspects of ape and human evolution, including the nature ...
2021-05-06
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- A research team from Brown University has made a major step toward improving the long-term reliability of perovskite solar cells, an emerging clean energy technology. In a study to be published on Friday, May 7 in the journal Science, the team demonstrates a "molecular glue" that keeps a key interface inside cells from degrading. The treatment dramatically increases cells' stability and reliability over time, while also improving the efficiency with which they convert sunlight into electricity.
"There have been great strides ...
2021-05-06
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researchers added to the understanding of the protective immune response against the SARS-CoV-2 virus in a study published in April in iScience. The team found that approximately 3% of the population is asymptomatic, which means that their bodies can get rid of the virus without developing signs of illness.
The researchers screened more than 60,000 blood samples from symptomless individuals in the Southeastern U.S., including Georgia, South Carolina and North Carolina, for the IgG antibody to the viral spike protein.
What began as a highly collaborative statewide effort to detect SARS-CoV-2 accurately, ...
2021-05-06
Recently published research from the University of Arizona Health Sciences shows that advanced-stage kidney cancer is more common in Hispanic Americans and Native Americans than in non-Hispanic whites, and that both Hispanic Americans and Native Americans in Arizona have an increased risk of mortality from the disease.
"We knew from our past research that Hispanic Americans and Native Americans have a heavier burden of kidney cancer than non-Hispanic whites," said Ken Batai, PhD, a Cancer Prevention and Control Program research member at the UArizona Cancer Center and research assistant professor of urology in the College of Medicine - Tucson. "But we also know that around 90% of the Hispanic population in Arizona is Mexican American - either U.S.-born or Mexican-born ...
2021-05-06
The air in the United States and Western Europe is much cleaner than even a decade ago. Low-sulfur gasoline standards and regulations on power plants have successfully cut sulfate concentrations in the air, reducing the fine particulate matter that harms human health and cleaning up the environmental hazard of acid rain.
Despite these successes, sulfate levels in the atmosphere have declined more slowly than sulfur dioxide emissions, especially in wintertime. This unexpected phenomenon suggests sulfur dioxide emission reductions are less efficient than expected for cutting sulfate aerosols. A new study led by Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Hokkaido University and the University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers develop new metal-free, recyclable polypeptide battery that degrades on demand
This could result in battery production moving away from strategic elements like cobalt