(Press-News.org) If you are reading this, chances are you have several other tabs open in your browser that you mean to get to eventually.
Internet browser tabs are a major source of friction on the internet. People love them. People hate them. For some users, tabs bring order and efficiency to their web browsing. For others, they spiral out of control, shrinking at the top of the screen as their numbers expand.
A research team at Carnegie Mellon University recently completed the first in-depth study of browser tabs in more than a decade. They found that many people struggle with tab overload, an underlying reason being that while tabs serve a variety of functions, they often do so poorly.
"Browser tabs are sort of the most basic tools that you use on the internet," said Joseph Chee Chang, a postdoctoral fellow in the School of Computer Science's Human Computer Interaction Institute (HCII) and a member of the research team. "Despite being so ubiquitous, we noticed that people were having all sorts of issues with them."
The team will present their paper, "When the Tab Comes Due: Challenges in the Cost Structure of Browser Tab Usage," at the Association for Computing Machinery's Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 2021), May 8-13.
For the study, the team conducted surveys and interviews with people about their tab use. The study details why people kept tabs open, including using them as reminders or fearing they would have to search for the information again. It also looked at why people closed tabs, knowing that tab overload can strain a person's attention and computer resources. About 25% of the participants in one aspect of the study reported that their browser or computer crashed because they had too many tabs open.
The researchers found that people felt invested in the tabs they had open, making it difficult for them to close the tabs even as they started to feel overwhelmed or ashamed by how many they had open.
Tabs first showed up in web browsers in 2001 and haven't changed much since. The internet, however, has. There is about a billion times more information on the web now than there was 20 years ago. Today, one tab could house an email inbox. Another could be used for a music or video player. Articles stashed away to read later could be in other tabs, as could restaurant reviews or information for an upcoming trip. Add in social media sites, news or other pages used for work or play, and it is easy to have a dozen or more tabs or windows open at any given time.
Tabs, it turns out, aren't the best tool for assisting with complex work and life tasks that people perform on the internet. Their simple list structure makes it difficult for users to jump between sets of tasks throughout the day. And despite people using tabs as an external form of memory, they do not capture the rich structure of their thoughts. Researchers found that while users complained about being overwhelmed by the number of tabs they queued up to work on later, they also didn't want to move them out of sight, as they worried about never going back to them.
"People feared that as soon as something went out of sight, it was gone," said Aniket Kittur, a professor in the HCII and head of the research team. "Fear of this black hole effect was so strong that it compelled people to keep tabs open even as the number became unmanageable."
Tab overload also arises from sense-making and decision tasks that require a person to absorb information from many sources, stitch it together and come to a conclusion. For instance, if someone is researching what camera to buy, that person may search several different reviews, how-to guides and shopping sites to compare models.
"Managing this sort of task is really one of the most important aspects of productivity in our lives," Kittur said. "And the number one tool that everyone uses for it is tabs, even though they don't do a good job."
The team believes that today's browsers do not offer a good tool for managing all the information and tasks people head to the internet for. To fix this, they created Skeema, an extension for the Google Chrome browser that reimagines tabs as tasks.
The extension helps users group their tabs into tasks and then organize, prioritize and switch between them. Skeema uses machine learning to make suggestions for grouping open tabs into tasks and supports nested tasks and complex decision-making.
Users of an early version of the tool significantly reduced the number of tabs and windows they kept open, reported much less stress connected to tabs, and remained more focused on the task at hand. Many of the early beta testers started using the tool daily to manage the tabs and tasks in their lives.
"Our task-centric approach allowed users to manage their browser tabs more efficiently, enabling them to better switch between tasks, reduce tab clutter and create task structures that better reflected their mental models," Chang said. "As our online tasks become increasingly complex, new interfaces and interactions that can merge tab management and task management in a browser will become increasingly important. After 20 years of little innovation, Skeema is a first step toward making tabs work better for users."
INFORMATION:
ITHACA, N.Y. - An 18.5 million-year-old fossil found in Panama provides evidence of a new species and is the oldest reliable example of a climbing woody vine known as a liana from the soapberry family. The discovery sheds light on the evolution of climbing plants.
The new species, named Ampelorhiza heteroxylon, belongs to a diverse group of tropical lianas called Paullinieae, within the soapberry family (Sapindaceae). More than 475 species of Paullinieae live in the tropics today.
Researchers identified the species from fossilized roots that revealed features known to be unique to the wood of modern climbing vines, adaptations that allow them to twist, grow and climb.
The study, "Climbing ...
The functions of water-dominated ecosystems can be considerably influenced and changed by hydrological fluctuation. The varying states of redox-active substances are of crucial importance here. Researchers at the University of Bayreuth have discovered this, in cooperation with partners from the Universities of Tübingen and Bristol and the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research, Halle-Leipzig. They present their discovery in the journal Nature Geoscience. The new study enables a more precise understanding of the biogeochemical processes that contribute to the degradation of pollutants and the reduction of greenhouse gas ...
More than ever, patients are using telehealth to ask doctors and nurses about worrying blood-pressure readings, nauseating migraines and stubborn foot ulcers. But for patients with chronic conditions, how frequent should telehealth appointments be? Can that frequency change? Under what conditions?
West Virginia University researcher Jennifer Mallow is trying to answer these questions. In a new project, she and her colleagues completed a systematic review of studies that dealt with telehealth and chronic conditions. They found that--in general--telehealth services benefitted patients more if they ...
A comprehensive review into what we know about COVID-19 and the way it functions suggests the virus has a unique infectious profile, which explains why it can be so hard to treat and why some people experience so-called "long-COVID", struggling with significant health issues months after infection.
There is growing evidence that the virus infects both the upper and lower respiratory tracts - unlike "low pathogenic" human coronavirus sub-species, which typically settle in the upper respiratory tract and cause cold-like symptoms, or "high pathogenic" viruses such as those that cause SARS and ARDS, which typically settle in the lower respiratory tract.
Additionally, more frequent multi-organ impacts, and blood clots, and ...
Which wound cuts deeper: the loss of an only child or loss of a spouse? A new study led by researchers at NYU Rory Meyers College of Nursing and Fudan University suggests that Chinese parents find the loss of an only child to be approximately 1.3 times as psychologically distressing than the loss of a spouse. The findings are published in the journal Aging & Mental Health.
Older adults in China rely heavily on family support, particularly from their adult children. Filial piety--the Confucian idea describing a respect for one's parents and responsibility for adult children to care for ...
Observing how cells stick to surfaces and their motility is vitally important in the study of tissue maintenance, wound healing and even understanding how cancers progress. A new paper published in EPJ Plus, by Raj Kumar Sadhu, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel, takes a step towards a deeper understanding of these processes.
"Cell adhesion is the ability of a cell to stick to another cell or an extracellular matrix. This process is important in order to understand how cells interact and coordinate their behaviour in multicellular organisms," says sadhu. "We theoretically model the adhesion of a cell-like vesicle by describing the cell as a three-dimensional vesicle adhering on a flat substrate with a constant adhesion interaction."
Alongside ...
Neuroblastoma is a childhood cancer, most commonly affecting children aged between 2 -3 and can be fatal. Since the tumour cells resemble certain cells in the adrenal glands, a joint research group from MedUni Vienna's Center for Brain Research and the Swedish Karolinska Institute investigated the cellular origin of these cells and sympathetic neurons during the embryonic development of human adrenal glands. During the course of their investigations, they discovered a previously unknown cell type that might potentially be the origin of the tumour cells.
Treatments for this disease are extremely aggressive and challenging ...
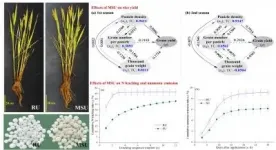
The applied nitrogen in crop production is easily lost through ammonia emission and nitrogen leaching. Therefore, many attempts have been made on the development of novel slow-release fertilizers to reduce nitrogen loss and improve crop production.
A research team led by Prof. WU Yuejin from the Institute of Intelligent Machines of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science developed a novel matrix-based slow-release urea (MSU) recently to improve nitrogen use efficiency in rice production, and they assessed the performances of it.
"MSU is a promising fertilizer for rice production," said WU, "as less nitrogen loss and greater soil nitrogen ...
Physicists at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) have for the first time been able to prove a long-predicted but as yet unconfirmed fundamental effect. In Faraday chiral anisotropy, the propagation characteristics of light waves are changed simultaneously by the natural and magnetic-field induced material properties of the medium through which the light travels. The researchers obtained proof that this is the case by conducting experiments using nickel helices at the nanometre scale. Their findings have now been published in the academic journal 'Physical Review Letters'.
Light is transmitted as sine waves consisting of crossed electric and magnetic fields and interacts with matter. This ...
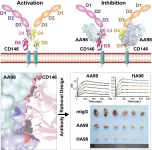
Recently, Prof. XIE Can from the High Magnetic Field Laboratory of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), in a collaboration with Prof. YAN Xiyun's lab from the Institute of Biophysics, reported the structural basis of mAb AA98's inhibition on CD146-mediated endothelial cells (EC) activation and designed higher affinity monoclonal antibody HA98 for cancer treatment.
CD146 is an adhesion molecule that plays important roles in angiogenesis, cancer metastasis, and immune response. Prof. YAN Xiyun's lab has been focused on the function of CD146 and the mechanism ...