(Press-News.org) A new Dartmouth-led study, published this week in the journal Pediatrics, has found that the disproportionate use of premiums within child-targeted TV advertising for children's fast-food meals is deceptive. The researchers examined thousands of advertisements from 11 fast-food restaurants, but one company--McDonald's--accounted for nearly all the airtime and, as a result, the findings.
The researchers report that these ads often overemphasize premiums such as toy giveaways and games relative to the primary product being sold, the fast food itself. This marketing practice violates the industry's own guidelines--put in place to ensure that the use of premiums in ads is not deceptive or unfair--as young children lack the cognitive ability to understand advertising.
The practice also works against childhood obesity prevention efforts. Previous studies have shown that childhood obesity is common in the U.S. About 26 percent of children ages 2-5 are overweight or obese, putting them at risk for major health consequences as they get older. Still, fast food is heavily promoted and regularly consumed by kids--nearly one-third of U.S. children eat fast-food on any given day.
"In the past, we've looked at the prevalence of child-directed food marketing and how it negatively impacts kids' diets, behaviors, and even weight status, but this is the first time we've examined if these companies are adhering to their own guidelines, in relationship to the content they can present to children," explains first author Jennifer Emond, PhD, MS, an assistant professor of biomedical data science and of pediatrics at Dartmouth's Geisel School of Medicine.
In the study, the investigators analyzed content of all child-directed fast-food TV advertisements on four popular national networks--Disney XD, Nickelodeon, Nicktoons, and Cartoon Network--aired from February 1, 2019 through January 31, 2020.
The team quantified the percent of the audio transcript (word count) and visual airtime (seconds) that included premiums or food, as well as the onscreen size of the toys or giveaways. During the study period, which included 142 hours of total airtime, more than 20,000 child-directed ads from 11 fast-food restaurants were aired on the four TV networks.
Of the 28 unique child-directed advertisements for children's fast-food meals during the study year, 27 were for McDonald's Happy Meals, accounting for nearly all (99.8 percent) of the total airtime. On average, premiums (vs. food) accounted for 53 percent (vs. 16 percent) of words in the audio transcript and 59.2 percent (vs. 54.3 percent) of the visual airtime.
Industry guidelines, which are managed through the Children's Advertising Review Unit and are administered by the BBB National Programs (formerly the Better Business Bureau), clearly state that premiums within child-directed advertising must be secondary to the advertised product to avoid undue influence.
"I find it very interesting that these are self-regulatory guidelines or pledges that the companies have signed on to as part of an industry initiative," says Emond. "But they're not even adhering to their own pledges. We need to hold them accountable--through stronger oversight of child-directed marketing in the U.S., from an independent review body or regulatory agency."
INFORMATION:
To see a video about this research and co-author Hannah Utter D'21, a student intern at the C. Everett Koop Institute at Dartmouth, go to: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w0kM-HFH1qs.
Other co-authors of the study include James Sargent, MD, the Scott M. and Lisa G. Stuart Professor in Pediatric Oncology, Vincent Chang D'21, Alec Eschholz D'19, and Mark Gottlieb, JD, from Northeastern University School of Law.
This study was supported by funding from the C. Everett Koop Institute at Dartmouth College and a mentored research scientist training award from the National Institute of Health (5K01DK117971).
Founded in 1797, the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth strives to improve the lives of the communities it serves through excellence in learning, discovery, and healing. The Geisel School of Medicine is renowned for its leadership in medical education, healthcare policy and delivery science, biomedical research, global health, and in creating innovations that improve lives worldwide. As one of America's leading medical schools, Dartmouth's Geisel School of Medicine is committed to training new generations of diverse leaders who will help solve our most vexing challenges in healthcare.
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this review the authors Yuheng Bao, Jifan Chen, Pintong Huang and Weijun Tong from Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China discuss the synergistic effects of acoustics-based therapy and immunotherapy in cancer treatment.
Cancer immunotherapy to enhance the autogenous immune response to cancer tissue is reported to be a promising method for cancer treatment. After the release of damage-associated molecular patterns, dendritic cells mature and recruit activated T cells to induce immune response.
To trigger the release of cancer associated antigens, cancer acoustics-based therapy has various prominent advantages and has been reported in various research. ...
In a retrospective study of trauma patients over 65 years of age attended by KSS, it was found that, although a number of these patients had sustained a minor injury through seemingly innocuous mechanisms, a high proportion of this group required advanced clinical interventions and subsequent tertiary level care at a major trauma centre.
The study also identified that dispatch time to these patients was typically longer, in particular in instances when KSS's critical care was requested by an ambulance crew already in attendance.
With response time often critical to patient outcomes, the ...
Soon after E.L. James's Fifty Shades of Grey appeared in 2015, the book market was inundated with a flood of erotic bestsellers. People from all corners began wondering what this type of novel's secret of success could be. Now, a research team at the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics (MPIEA) in Frankfurt/Main, Germany, has taken a closer look at the readership of erotic novels and investigated the causes of this literary predilection.
In the media as well as the academy, contemporary erotica is typically dismissed as being of low literary value. Critics and scholars tend to classify its readers as having mediocre to poor taste, without, however, examining ...
Twenty dollars a month might not seem like a lot to pay for health insurance. But for people getting by on $15,000 a year, it's enough to make some drop their coverage - especially if they're healthy, a new study of Medicaid expansion participants in Michigan finds.
That could keep them from getting preventive or timely care, and could leave their insurance company with a sicker pool of patients than before, say the researchers from the University of Michigan and University of Illinois Chicago. They have published their findings as a working paper through the National Bureau of Economic Research, ahead of publication in the American Journal of Health Economics.
The study has implications for other states that require ...
DURHAM, N.C. - A potential new vaccine developed by members of the Duke Human Vaccine Institute has proven effective in protecting monkeys and mice from a variety of coronavirus infections -- including SARS-CoV-2 as well as the original SARS-CoV-1 and related bat coronaviruses that could potentially cause the next pandemic.
The new vaccine, called a pan-coronavirus vaccine, triggers neutralizing antibodies via a nanoparticle. The nanoparticle is composed of the coronavirus part that allows it to bind to the body's cell receptors and is formulated with a chemical booster called an adjuvant. ...
A Flinders University researcher has finally fathomed why large numbers of killer whales gather at a single main location off the Western Australian southern coastline every summer.
In a new paper published in Deep Sea Research, physical oceanographer Associate Professor Jochen Kampf describes the conditions which have produced this ecological natural wonder of orcas migrating to the continental slope near Bremer Bay in the western Great Australian Bight from late austral spring to early autumn (January-April).
"The aggregation is connected to the local marine food web that follows from the upwelling of benthic particulate organic matter (POM) ...
A novel approach to immunotherapy design could pave the way for new treatments for people with an aggressive form of brain cancer called glioblastoma.
Using specifically designed receptors, researchers were able to completely clear brain cancer tumours in preclinical models, using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy.
Published today in Clinical & Translational Immunology and led by Associate Professor Misty Jenkins, the research is a crucial step towards developing new immunotherapy treatments for this devastating illness.
More than 1800 Australians are diagnosed with brain cancer every year. ...
A new micro-light-emitting diode (micro-LED) developed at KAUST can efficiently emit pure red light and may help in the quest to develop full-color displays based on just a single semiconductor.
Micro-LEDs are a promising technology for the next generation of displays. They have the advantage of being energy efficient and very small. But each LED can only emit light over a narrow range of colors. A clever solution is to create devices that combine many different LEDs, each emitting a different color. Full-color micro-displays can be created by combining red, green and blue (RGB) micro-LEDs. Now, a KAUST team of Zhe Zhuang, Daisuke Iida and Kazuhiro Ohkawa have worked to develop ...
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (May 10, 2021) -- The Gulf of Guinea islands harbor an abundance of species found nowhere else on Earth. But for over 100 years, scientists have wondered whether or not a population of limbless, burrowing amphibians--known as caecilians--found on one of the islands is a single or multiple species. Now, a team of researchers from the California Academy of Sciences and the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History has contributed the strongest evidence to date that there is not one, but two different species of caecilians on São Tomé ...
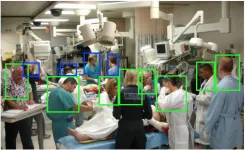
Computer scientists at the University of California San Diego have developed a more accurate navigation system that will allow robots to better negotiate busy clinical environments in general and emergency departments more specifically. The researchers have also developed a dataset of open source videos to help train robotic navigation systems in the future.
The team, led by Professor Laurel Riek and Ph.D. student Angelique Taylor, detail their findings in a paper for the International Conference on Robotics and Automation taking place May 30 to June 5 in Xi'an, China.
The project stemmed from conversations with clinicians over several years. The consensus was that robots would best help physicians, nurses and staff ...