(Press-News.org) In a newly published paper, Virginia Tech geoscientists have found that shallow wastewater injection -- not deep wastewater injections -- can drive widespread deep earthquake activity in unconventional oil and gas production fields.
Brine is a toxic wastewater byproduct of oil and gas production. Well drillers dispose of large quantities of brine by injecting it into subsurface formations, where its injection can cause earthquakes, according to Guang Zhai, a postdoctoral research scientist in the Department of Geosciences, part of the Virginia Tech College of Science, and a visiting assistant researcher at the University of California, Berkeley.
The findings appear in the May 10 edition of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Joining Zhai on the paper are END
Geoscientists find that shallow wastewater injection drives deep earthquakes in Texas
2021-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
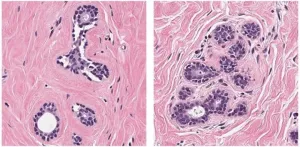
Grand Challenge research harnesses AI to fight breast cancer
2021-05-10
Breast cancer has recently overtaken lung cancer to become the most common cancer globally, END ...
New theory may revolutionize treatment of endometriosis
2021-05-10
Endometriosis, a disease found in up to 10 per cent of women, has been enigmatic since it was first described. A new theory developed by researchers at Simon Fraser University suggests a previously overlooked hormone -- testosterone -- has a critical role in its development. The research could have direct impacts on diagnosis and treatment of the disease, signaling hope for women with endometriosis worldwide.
The disease is caused by endometrial tissue growing outside of the uterus, usually in the pelvic area, where it contributes to pain, inflammation, and infertility. But why some women get it, and others do not, has remained unclear.
The new research is based on recent findings that women with endometriosis developed, as fetuses in their mother's womb, under conditions of relatively ...
Does driving wear you out? You might be experiencing 'accelerousal'
2021-05-10
Admit it: Daily commutes - those stops, the starts, all that stress - gets on your last nerve.
Or is that just me?
It might be, according to a new study from the University of Houston's Computational Physiology Lab. UH Professor Ioannis Pavlidis and his team of researchers took a look at why some drivers can stay cool behind the wheel while others keep getting more irked.
"We call the phenomenon 'accelerousal.' Arousal being a psychology term that describes stress. Accelarousal is what we identify as stress provoked by acceleration events, even small ones," said Pavlidis, ...
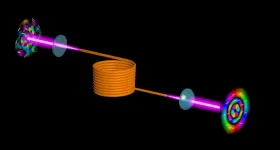
'Flipping' optical wavefront eliminates distortions in multimode fibers
2021-05-10
The use of multimode optical fibers to boost the information capacity of the Internet is severely hampered by distortions that occur during the transmission of images because of a phenomenon called modal crosstalk.
However, University of Rochester researchers at the Institute of Optics have devised a novel technique, described in a paper in Nature Communications, to "flip" the optical wavefront of an image for both polarizations simultaneously, so that it can be transmitted through a multimode fiber without distortion. Researchers at the University of South Florida and at the University of Southern California collaborated ...
Stanford researchers map how people in cities get a health boost from nature
2021-05-10
Your local city park may be improving your health, according to a new paper led by Stanford University researchers. The research, published in END ...
Even when they include them, gifted programs aren't serving Black or low-income kids
2021-05-10
After years of criticism for their lack of diversity, programs for high achievers may not be adequately serving their Black and low-income students, a new study shows.
"The potential benefits aren't equally distributed," said lead author and University of Florida College of Education professor Christopher Redding, Ph.D., who evaluated data from gifted programs in elementary schools nationwide. "The conversation up to this point has been about access, with less emphasis on how students perform once in gifted programs."
While academic achievement gains for students overall were modest -- going from ...
Top educational apps for children might not be as beneficial as promised
2021-05-10
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Log on to any app store, and parents will find hundreds of options for children that claim to be educational. But new research suggests these apps might not be as beneficial to children as they seem.
A new study analyzed some of the most downloaded educational apps for kids using a set of four criteria designed to evaluate whether an app provides a high-quality educational experience for children. The researchers found that most of the apps scored low, with free apps scoring even lower than their paid counterparts on some criteria.
Jennifer Zosh, associate professor of human development ...
CDK inhibitors may improve immune therapy effectiveness for recurrent breast cancer
2021-05-10
Recurrent, metastatic breast cancer resists treatment and is usually fatal.
These tumors often have low numbers of immune cells in them, which renders immune therapies less effective for the disease.
This preclinical study suggests that drugs called CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitors may make immune-cell therapies an effective option for treating recurrent ER-positive metastatic breast cancer.
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A class of drugs that inhibits breast cancer progression when used with hormonal therapy might also boost the effectiveness of immune therapy in cases of recurrent, metastatic breast cancer, according to a new study led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center - Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital ...
The next generation of hunters could look different
2021-05-10
A new survey led by researchers from North Carolina State University found that the future of hunting in the United States might look different than it has in the past.
In The Journal of Wildlife Management, researchers reported findings from a nationwide survey of college students' interest and participation in hunting. They found current, active hunters were more likely to be white, male and from rural areas, and to have family members who hunted. But they also found a group of potential hunters - with no hunting experience but an interest in trying it - who were more diverse in terms of gender, ...
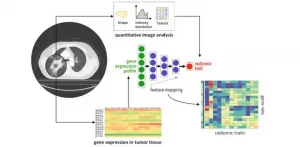
Integrating medical imaging and cancer biology with deep neural networks
2021-05-10
Despite our remarkable advances in medicine and healthcare, the cure to cancer continues to elude us. On the bright side, we have made considerable progress in detecting several cancers in earlier stages, allowing doctors to provide treatments that increase long-term survival. The credit for this is due to "integrated diagnosis," an approach to patient care that combines molecular information and medical imaging data to diagnose the cancer type and, eventually, predict treatment outcomes.
There are, however, several intricacies involved. The correlation of molecular patterns, such as gene expression and mutation, with image features (e.g., how a tumor appears in a CT scan), is ...