(Press-News.org) May 14, 2021 - Two years ago, the Veterans Affairs healthcare system (VA) began rolling out a new benefit, enabling Veterans to receive urgent care from a network of community providers - rather than visiting a VA emergency department or clinic. Progress toward expanding community care services for Veterans is the focus of a special supplement to the May issue of Medical Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The urgent care benefit "provides a new way to deliver unscheduled, low-acuity acute care to Veterans," according to the new research by Anita Vashi, MD, MPH, MHS, of VA Palo Alto Health Care System and colleagues. The study is one of 12 research papers and commentaries on "Innovations in Community Care Programs, Policies, and Research" - focusing on Veterans' use of healthcare services in the community, and how VA centers interact with community care providers.
What's the best balance of VA and community care? That's the 'billion-dollar question'
Dr. Vashi and colleagues analyzed initial data on how Veterans are using the community urgent care benefit, which was implemented starting in June 2019. Eligible Veterans were able to receive urgent care from providers in VA's community network, without prior authorization. Focusing on minor illnesses and injuries that might otherwise lead to emergency department (ED) visits, the program was part of VA's "Maintaining Internal Systems and Strengthening Integrated Outside Networks" (MISSION) Act, designed to increase Veterans' access to health care in VA facilities and the community.
Through the first nine months of the program, 138,305 Veterans made a total of 175,821 urgent care visits to VA community network providers. That accounted for 2.4 percent of a cohort of 5.9 million potentially eligible Veterans. By comparison, 7.3 percent of Veterans visited a VA ED or clinic for lower-acuity (non-emergency) conditions during the same period.
Dr. Vashi and colleagues examined trends in community urgent care use, including factors associated with urgent care rather than ED visits. Urgent care visits generally increased over time and varied between regions. Most Veterans using urgent care lived in urban areas - more than 80 percent lived within 30 minutes of a VA primary care site. Most had no copays for urgent care visits.
Upper respiratory infections, back pain, and bronchitis were the most frequent reasons for community urgent care visits. Common procedures and treatments included chest x-rays, influenza or strep testing, and urinalysis. Average cost to VA for urgent care visits was $132, with total costs of about $23 million.
On analysis adjusting for other factors, women and younger Veterans were more likely to take advantage of the urgent care benefit. Driving time was a key factor: Veterans who lived more than 60 minutes from a VA ED or VA urgent care center were twice as likely to choose community urgent care services.
The study provides key information on how "early adopters" are taking advantage of the urgent care benefit. "As the program continues to expand and evolve, impacts on care coordination, medication safety, outcomes, and shifts in utilization of VA primary and emergency services must be evaluated," Dr. Vashi and coauthors write.
While most care is still provided at VA Medical Centers and outpatient sites, initiatives including the MISSION Act have greatly expanded Veterans' ability to seek care at private health care providers, clinics, and hospitals in the community. The papers in the new open-access supplement offer "a broad examination of the first two years of MISSION Act implementation, and highlights areas where additional research is needed to understand Veterans' perceptions, satisfaction and use of VA Community Care," according to an introductory guest editorial by Kristin Mattocks, PhD, of VA Central Western Massachusetts and colleagues.
The supplement papers are an important step toward providing the best experience for Veterans in choosing among their healthcare options. Dr. Mattocks and coauthors conclude: "The enduring challenge for VA - literally the 'billion dollar question' - is to determine what balance of in-person VA care, virtual VA care, and care in the community offers the optimal balance of timely, patient-centered and high-quality care."
INFORMATION:
Click here to read the VA Community Care Supplement.
About Medical Care
Rated as one of the top ten journals in health care administration, Medical Care is devoted to all aspects of the administration and delivery of health care. This scholarly journal publishes original, peer-reviewed papers documenting the most current developments in the rapidly changing field of health care. Medical Care provides timely reports on the findings of original investigations into issues related to the research, planning, organization, financing, provision, and evaluation of health services. In addition, numerous special supplementary issues that focus on specialized topics are produced with each volume. Medical Care is the official journal of the Medical Care Section of the American Public Health Association.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the clinicians, nurses, accountants, lawyers, and tax, finance, audit, risk, compliance, and regulatory sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with advanced technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2020 annual revenues of €4.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 19,200 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
For more information, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
A team led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Children's National Hospital has developed a unique pre-clinical model that enables the study of long-term HIV infection, and the testing of new therapies aimed at curing the disease.
Ordinary mice cannot be infected with HIV, so previous HIV mouse models have used mice that carry human stem cells or CD4 T cells, a type of immune cell that can be infected with HIV. But these models tend to have limited utility because the human cells soon perceive the tissues of their mouse hosts as "foreign," ...
The question of why we dream is a divisive topic within the scientific community: it's hard to prove concretely why dreams occur and the neuroscience field is saturated with hypotheses. Inspired by techniques used to train deep neural networks, Erik Hoel (@erikphoel), a research assistant professor of neuroscience at Tufts University, argues for a new theory of dreams: the overfitted brain hypothesis. The hypothesis, described May 14 in a review in the journal Patterns, suggests that the strangeness of our dreams serves to help our brains better generalize our day-to-day experiences.
"There's obviously an incredible number of theories of why we dream," says Hoel. "But I wanted to bring to ...
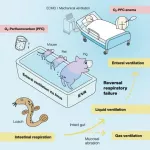
Rodents and pigs share with certain aquatic organisms the ability to use their intestines for respiration, finds a study publishing May 14th in the journal Med. The researchers demonstrated that the delivery of oxygen gas or oxygenated liquid through the rectum provided vital rescue to two mammalian models of respiratory failure.
"Artificial respiratory support plays a vital role in the clinical management of respiratory failure due to severe illnesses such as pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome," says senior study author Takanori Takebe (@TakebeLab) of the Tokyo Medical and Dental University and the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center. "Although the side effects and safety need to be thoroughly ...
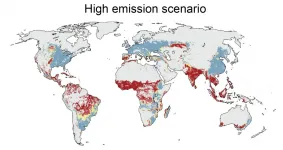
Climate change is known to negatively affect agriculture and livestock, but there has been little scientific knowledge on which regions of the planet would be touched or what the biggest risks may be. New research led by Aalto University assesses just how global food production will be affected if greenhouse gas emissions are left uncut. The study is published in the prestigious journal One Earth on Friday 14 May.
'Our research shows that rapid, out-of-control growth of greenhouse gas emissions may, by the end of the century, lead to more than a third of current global food production falling into conditions in which no food is produced today - that is, out of safe climatic space,' explains Matti Kummu, professor of global water and food issues at Aalto University.
According ...
What The Study Did: Researchers analyzed changes in filled prescriptions for naloxone (medication to reverse opioid overdoses) during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States and compared them with changes in opioid prescriptions and overall prescriptions.
Authors: Ashley L. O'Donoghue, Ph.D., of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.0393)
Editor's Note: The ...
What The Study Did: Associations of staffing and testing interventions with COVID-19 transmission in nursing homes are examined in this decision analytical modeling study.
Authors: Rebecca Kahn, Ph.D., of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10071)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
What The Study Did: This is a qualitative study that evaluates a crowdsourcing open call to gather community input for engaging the university community in COVID-19 safety strategies.
Authors: Suzanne Day, Ph.D., of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10090)
Editor's Note: This article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
What The Study Did: Researchers evaluated the compliance of hospitals with a Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ruling mandating that a list of charges for services, procedures and items be publicly available and in a machine-readable file.
Authors: David Hsiehchen, M.D., of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10109)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Tokyo, Japan - Oxygen is crucial to many forms of life. Its delivery to the organs and tissues of the body through the process of respiration is vital for most biological processes. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have shown that oxygen can be delivered through the wall of the intestine to compensate for the reduced availability of oxygen within the body that occurs in lung diseases that cause respiratory failure.
To breathe is to live; for higher animals, respiration involves absorbing oxygen and excreting carbon dioxide at gills or in the lungs. However, some animals have evolved alternative ventilatory mechanisms: loaches, catfish, sea cucumbers and orb-weaving spiders can absorb oxygen through their hindgut to ...
Scientists have uncovered the exact mechanism that causes new solar cells to break down, and suggest a potential solution.
Solar cells harness energy from the Sun and provide an alternative to non-renewable energy sources like fossil fuels. However, they face challenges from costly manufacturing processes and poor efficiency - the amount of sunlight converted to useable energy.
Perovskites are materials developed for next-generation solar cells. Although perovskites are more flexible cheaper to make than traditional silicon-based solar panels and deliver similar efficiency, perovskites ...