INFORMATION:
The research has been published in Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abe4507).
The joint first authors are Dr Natalee Newton from UQ's Watterson lab and Dr Joshua Hardy from Coulibaly lab at the Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute.
Scientists rewrite the genesis of mosquito-borne viruses
Better designed vaccines for insect-spread viruses like dengue and Zika now possible
2021-05-14
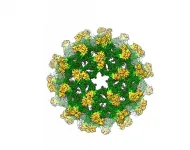
(Press-News.org) Better designed vaccines for insect-spread viruses like dengue and Zika are likely after researchers discovered models of immature flavivirus particles were originally misinterpreted.
Researchers from The University of Queensland and Monash University have now determined the first complete 3D molecular structure of the immature flavivirus, revealing an unexpected organisation.
UQ researcher Associate Professor Daniel Watterson said the team was studying the insect-specific Binjari virus when they made the discovery.
"We were using Australia's safe-to-handle Binjari virus, which we combine with more dangerous viral genes to make safer and more effective vaccines," Dr Watterson said.
"But when analysing Binjari we could clearly see that the molecular structure we've all been working from since 2008 wasn't quite correct.
"Imagine trying to build a house when your blueprints are wrong - that's exactly what it's like when you're attempting to build effective vaccines and treatments and your molecular 'map' is not quite right."
The team used a technique known as cryogenic electron microscopy to image the virus, generating high resolution data from Monash's Ramaciotti Centre for Cryo-Electron Microscopy facility.
With thousands of collected two-dimensional images of the virus, the researchers then combined them using a high-performance computing platform called 'MASSIVE' to construct a high-resolution 3D structure.
Monash's Associate Professor Fasséli Coulibaly, a co-leader of the study, said the revelation could lead to new and better vaccines for flaviviruses, which have a huge disease burden globally.
"Flaviviruses are globally distributed and dengue virus alone infects around 400 million people annually," Dr Coulibaly said.
"They cause a spectrum of potentially severe diseases including hepatitis, vascular shock syndrome, encephalitis, acute flaccid paralysis, congenital abnormalities and foetal death.
"This structure defines the exact wiring of the immature virus before it becomes infectious, and we now have a better understanding of the levers and pulleys involved in viral assembly.
"This is a continuation of fundamental research by us and others and, without this hard-won basic knowledge, we wouldn't have the solid foundation needed to design tomorrow's treatments."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New cyanobacteria species spotlights early life
2021-05-14
ITHACA, NY, May 13, 2021 -- Cyanobacteria are one of the unsung heroes of life on Earth. They first evolved to perform photosynthesis about 2.4 billion years ago, pumping tons of oxygen into the atmosphere - a period known as the Great Oxygenation Event - which enabled the evolution of multicellular life forms.
Led by BTI faculty member END ...
Teachers' gender, sexuality, and age affect perceptions of sexual misconduct of students
2021-05-14
The United States has witnessed a steep rise in reports, arrests, and media coverage of teachers' sexual misconduct with students. A new study investigated the impact of perpetrators' gender, sexuality, and age on perceptions of teacher sexual misconduct. The study found that
responses to teachers' misconduct varied according to certain characteristics, which can influence whether victims report the misconduct.
The study, by researchers at Prairie View A&M University and the University of Nevada, Reno, appears in Feminist Criminology.
"Because sexual abuse of a child or adolescent in any context has substantial psychological, emotional, and physical consequences for the victim, teachers' sexual misconduct is a serious public health ...
You're so vein: Scientists discover faster way to manufacture vascular materials
2021-05-14
Developing self-healing materials is nothing new for Nancy Sottos, lead of the Autonomous Materials Systems Group at the END ...
U-M researchers trace path of light in photosynthesis
2021-05-14
Three billion years ago, light first zipped through chlorophyll within tiny reaction centers, the first step plants and photosynthetic bacteria take to convert light into food.
Heliobacteria, a type of bacteria that uses photosynthesis to generate energy, has reaction centers thought to be similar to those of the common ancestors for all photosynthetic organisms. Now, a University of Michigan team has determined the first steps in converting light into energy for this bacterium.
"Our study highlights the different ways in which nature has made use of the basic reaction ...
Most pediatric spinal fractures related to not wearing seatbelts
2021-05-14
May 14, 2021 - Two thirds of all pediatric spinal fractures, especially in the adolescent population, occur in motor vehicle accidents (MVAs) where seatbelts are not utilized, reports a study in Spine. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Over 60 percent of pediatric spinal fractures occur in children ages 15 to 17, coinciding with the beginning of legal driving," according to the new research by Dr. Vishal Sarwahi, MD, of Cohen Children's Medical Center, New Hyde Park, NY, and colleagues. They emphasize the need for measures to increase seatbelt usage, particularly by younger drivers, and outline the potential trauma that can be avoided through proper seatbelt use.
Seatbelts save lives... and ...
New benefit increases Veterans' access to urgent care in the community
2021-05-14
May 14, 2021 - Two years ago, the Veterans Affairs healthcare system (VA) began rolling out a new benefit, enabling Veterans to receive urgent care from a network of community providers - rather than visiting a VA emergency department or clinic. Progress toward expanding community care services for Veterans is the focus of a special supplement to the May issue of Medical Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The urgent care benefit "provides a new way to deliver unscheduled, low-acuity acute care to Veterans," according to the ...
New pre-clinical model could hold the key to better HIV treatments
2021-05-14
A team led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Children's National Hospital has developed a unique pre-clinical model that enables the study of long-term HIV infection, and the testing of new therapies aimed at curing the disease.
Ordinary mice cannot be infected with HIV, so previous HIV mouse models have used mice that carry human stem cells or CD4 T cells, a type of immune cell that can be infected with HIV. But these models tend to have limited utility because the human cells soon perceive the tissues of their mouse hosts as "foreign," ...
Our dreams' weirdness might be why we have them, argues new AI-inspired theory of dreaming
2021-05-14
The question of why we dream is a divisive topic within the scientific community: it's hard to prove concretely why dreams occur and the neuroscience field is saturated with hypotheses. Inspired by techniques used to train deep neural networks, Erik Hoel (@erikphoel), a research assistant professor of neuroscience at Tufts University, argues for a new theory of dreams: the overfitted brain hypothesis. The hypothesis, described May 14 in a review in the journal Patterns, suggests that the strangeness of our dreams serves to help our brains better generalize our day-to-day experiences.
"There's obviously an incredible number of theories of why we dream," says Hoel. "But I wanted to bring to ...
Mammals can use their intestines to breathe
2021-05-14
Rodents and pigs share with certain aquatic organisms the ability to use their intestines for respiration, finds a study publishing May 14th in the journal Med. The researchers demonstrated that the delivery of oxygen gas or oxygenated liquid through the rectum provided vital rescue to two mammalian models of respiratory failure.
"Artificial respiratory support plays a vital role in the clinical management of respiratory failure due to severe illnesses such as pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome," says senior study author Takanori Takebe (@TakebeLab) of the Tokyo Medical and Dental University and the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center. "Although the side effects and safety need to be thoroughly ...
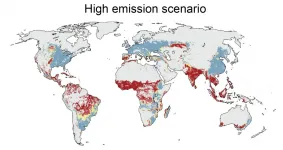
Climate change threatens one-third of global food production
2021-05-14
Climate change is known to negatively affect agriculture and livestock, but there has been little scientific knowledge on which regions of the planet would be touched or what the biggest risks may be. New research led by Aalto University assesses just how global food production will be affected if greenhouse gas emissions are left uncut. The study is published in the prestigious journal One Earth on Friday 14 May.
'Our research shows that rapid, out-of-control growth of greenhouse gas emissions may, by the end of the century, lead to more than a third of current global food production falling into conditions in which no food is produced today - that is, out of safe climatic space,' explains Matti Kummu, professor of global water and food issues at Aalto University.
According ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Scientists rewrite the genesis of mosquito-borne virusesBetter designed vaccines for insect-spread viruses like dengue and Zika now possible