(Press-News.org) AMES, Iowa - The field photos show the hard, rough country that some glaciers slide over: rocky domes and bumps in granite, rocky steps and depressions in limestone. The glacier beds dwarf the researchers and their instruments. (As do the high mountains pictured on the various horizons.)
During their trips to glacier beds recently exposed by retreating glaciers in the Swiss Alps (Rhone, Schwarzburg and Tsanfleuron glaciers) and the Canadian Rockies (Castleguard Glacier), four glaciologists used laser and drone technology to precisely measure the rocky beds and record their very different contours.
The researchers turned the measurements into high-resolution digital models of those glacier beds. Then they went to work with manageable but representative subunits of the models to study how glaciers slide along the bedrock base.
"The simplest way to say it is we studied the relationship between the forces at the base of the glacier and how fast the glacier moves," said Neal Iverson, a professor of geological and atmospheric sciences at Iowa State University and the study leader.
Small force changes, big speed changes
The resulting glacier "slip law" developed by the team describes that "relationship between forces exerted by ice and water on the bed and glacier speed," Iverson said. And that slip law could be used by other researchers to better estimate how quickly ice sheets flow into oceans, drop their ice and raise sea levels.
In addition to Iverson, the study team included Christian Helanow, a postdoctoral research associate at Iowa State from 2018 to 2020 and currently a postdoctoral researcher in mathematics at Stockholm University in Sweden; Lucas Zoet, a postdoctoral research associate at Iowa State from 2012 to 2015 and currently an assistant professor of geoscience at the University of Wisconsin-Madison; and Jacob Woodard, a doctoral student in geophysics at Wisconsin.
A grant from the National Science Foundation supported the team's work.
Helanow is the first author of a paper just published online by Science Advances that describes the new slip law for glaciers moving on bedrock.
Helanow's calculations - based on a computer model of the physics of how ice slides over and separates locally from rough bedrock - and the resulting slip law indicate that small changes in force at the glacier bed can lead to big changes in glacier speed.
Measuring to inches
The researchers used two methods to collect high-resolution measurements of the topographies of recently exposed rock glacier beds. They used ground-based lidar mapping technology to take detailed 3D measurements. And, they sent up drones to photograph the beds from various angles, allowing detailed plotting of topography to a resolution of about 4 inches.
"We used actual glacial beds for this model, in their fully 3D, irregular forms," Iverson said. "It turns out that is important."
Previous efforts used idealized, 2D models of glacier beds. The researchers have learned such models are not adequate to derive the slip law for a hard bed.
"The main thing we've done," Helanow said, "is use observed, rather than idealized, glacier beds to see how they impact glacier sliding."
A universal slip law?
The work follows another slip law determined by Zoet and Iverson that was published in April 2020 by the journal Science.
There are a few key differences between the two: The first slip law accounts for the motion of ice moving over soft, deformable ground, while the second addresses glaciers moving over hard beds. (Both bed types are common beneath glaciers and ice sheets.) And, the first is backed by experimental data from a laboratory device that simulates slip at the bed of a glacier, rather than being based on field measurements of former glacier beds and computer modeling.
Even so, the two slip laws ended up having similar mathematical forms.
"They're very similar - whether it's a slip law for soft beds or hard beds," Iverson said. "But it's important to realize that the processes are different, the constants in the equations have quite different values for hard and soft beds."
That has the researchers thinking ahead to more numerical analysis: "These results," they wrote, "may point to a universal slip law that would simplify and improve estimations of glacier discharges to the oceans."
INFORMATION:
Read the paper
"A slip law for hard-bedded glaciers derived from observed bed topography," Science Advances, May 14, 2021
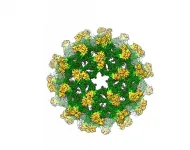
Better designed vaccines for insect-spread viruses like dengue and Zika are likely after researchers discovered models of immature flavivirus particles were originally misinterpreted.
Researchers from The University of Queensland and Monash University have now determined the first complete 3D molecular structure of the immature flavivirus, revealing an unexpected organisation.
UQ researcher Associate Professor Daniel Watterson said the team was studying the insect-specific Binjari virus when they made the discovery.
"We were using Australia's safe-to-handle Binjari virus, which we combine with more dangerous viral genes to make safer and more effective vaccines," Dr Watterson ...
ITHACA, NY, May 13, 2021 -- Cyanobacteria are one of the unsung heroes of life on Earth. They first evolved to perform photosynthesis about 2.4 billion years ago, pumping tons of oxygen into the atmosphere - a period known as the Great Oxygenation Event - which enabled the evolution of multicellular life forms.
Led by BTI faculty member END ...
The United States has witnessed a steep rise in reports, arrests, and media coverage of teachers' sexual misconduct with students. A new study investigated the impact of perpetrators' gender, sexuality, and age on perceptions of teacher sexual misconduct. The study found that
responses to teachers' misconduct varied according to certain characteristics, which can influence whether victims report the misconduct.
The study, by researchers at Prairie View A&M University and the University of Nevada, Reno, appears in Feminist Criminology.
"Because sexual abuse of a child or adolescent in any context has substantial psychological, emotional, and physical consequences for the victim, teachers' sexual misconduct is a serious public health ...
Developing self-healing materials is nothing new for Nancy Sottos, lead of the Autonomous Materials Systems Group at the END ...
Three billion years ago, light first zipped through chlorophyll within tiny reaction centers, the first step plants and photosynthetic bacteria take to convert light into food.
Heliobacteria, a type of bacteria that uses photosynthesis to generate energy, has reaction centers thought to be similar to those of the common ancestors for all photosynthetic organisms. Now, a University of Michigan team has determined the first steps in converting light into energy for this bacterium.
"Our study highlights the different ways in which nature has made use of the basic reaction ...
May 14, 2021 - Two thirds of all pediatric spinal fractures, especially in the adolescent population, occur in motor vehicle accidents (MVAs) where seatbelts are not utilized, reports a study in Spine. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Over 60 percent of pediatric spinal fractures occur in children ages 15 to 17, coinciding with the beginning of legal driving," according to the new research by Dr. Vishal Sarwahi, MD, of Cohen Children's Medical Center, New Hyde Park, NY, and colleagues. They emphasize the need for measures to increase seatbelt usage, particularly by younger drivers, and outline the potential trauma that can be avoided through proper seatbelt use.
Seatbelts save lives... and ...
May 14, 2021 - Two years ago, the Veterans Affairs healthcare system (VA) began rolling out a new benefit, enabling Veterans to receive urgent care from a network of community providers - rather than visiting a VA emergency department or clinic. Progress toward expanding community care services for Veterans is the focus of a special supplement to the May issue of Medical Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The urgent care benefit "provides a new way to deliver unscheduled, low-acuity acute care to Veterans," according to the ...
A team led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and Children's National Hospital has developed a unique pre-clinical model that enables the study of long-term HIV infection, and the testing of new therapies aimed at curing the disease.
Ordinary mice cannot be infected with HIV, so previous HIV mouse models have used mice that carry human stem cells or CD4 T cells, a type of immune cell that can be infected with HIV. But these models tend to have limited utility because the human cells soon perceive the tissues of their mouse hosts as "foreign," ...
The question of why we dream is a divisive topic within the scientific community: it's hard to prove concretely why dreams occur and the neuroscience field is saturated with hypotheses. Inspired by techniques used to train deep neural networks, Erik Hoel (@erikphoel), a research assistant professor of neuroscience at Tufts University, argues for a new theory of dreams: the overfitted brain hypothesis. The hypothesis, described May 14 in a review in the journal Patterns, suggests that the strangeness of our dreams serves to help our brains better generalize our day-to-day experiences.
"There's obviously an incredible number of theories of why we dream," says Hoel. "But I wanted to bring to ...
Rodents and pigs share with certain aquatic organisms the ability to use their intestines for respiration, finds a study publishing May 14th in the journal Med. The researchers demonstrated that the delivery of oxygen gas or oxygenated liquid through the rectum provided vital rescue to two mammalian models of respiratory failure.
"Artificial respiratory support plays a vital role in the clinical management of respiratory failure due to severe illnesses such as pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome," says senior study author Takanori Takebe (@TakebeLab) of the Tokyo Medical and Dental University and the Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center. "Although the side effects and safety need to be thoroughly ...