'We're playing Moneyball with building assets'
New tool uses AI to target smarter repairs with limited funds
2021-05-18
(Press-News.org) Researchers have developed a tool to help governments and other organizations with limited budgets spend money on building repairs more wisely.
The new tool uses artificial intelligence (AI) and text mining techniques to analyze written inspection reports and determine which work is most urgently needed.
"Those assessments are now largely subjective, the opinions of people based on experience and training," said Kareem Mostafa, an engineering PhD student at the University of Waterloo who led the project. "We're using actual data on buildings to make spending decisions more objective."
Researchers looked at inspection reports on the roofs of 400 schools managed by the Toronto District School Board. A computer model was developed to search the one- to two-page reports for about 30 keywords, including words such as 'damage' and 'leaks.'
By analyzing the frequency of the keywords, plus factors including the age of roofs, the AI software divided the schools into four categories based on the urgency of repair or replacement. The goal was to give the school board an objective way to target its limited funds, speeding up the assessment process and helping it spend money where it makes the most sense.
"We're playing Moneyball with building assets," Mostafa said. "By using data on buildings instead of opinions, our model also takes potential political headaches out of the process."
Although the software was developed to assess the need for roof repairs, it can be tweaked to help prioritize other kinds of work for organizations with budget limitations and many buildings to maintain.
Mostafa is also working to incorporate other kinds of data, including AI analysis of photographs, into the assessment model.
Tarek Hegazy, a professor of civil and environmental engineering at Waterloo, and Ahmed Attalla, a project manager with the school board, collaborated on the study.
INFORMATION:
A paper on their work, Data mining of school inspection reports to identify the assets with the top renewal priority, appears in the Journal of Building Engineering.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-18
MUSC Hollings Cancer Center lung cancer researcher Gerard Silvestri, M.D., found that a lack of insurance leads to worse cancer survival than for those with Medicare, in a paper published in the May issue of Health Affairs. This work, a joint effort between Silvestri and researchers at the American Cancer Society, highlights the current dire barrier in medical care: Many people cannot take advantage of the newer potentially lifesaving treatments due to the high costs.
Silvestri said the research began last year, inspired by the hotly debated topic of expanding Medicare ...
2021-05-17
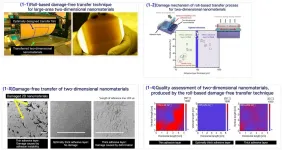
The Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) under the Ministry of Science and ICT developed a roll-based damage-free transfer technique that allows two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials to be transferred into wafer scale without damage. The proposed technique has a variety of applications from transparent displays and semiconductors to displays for self-driving cars, and is expected to accelerate the commercialization of 2D nanomaterial-based high-performance devices.
Dr. Kwang-Seop Kim, principal researcher of the Department of Nano-Mechanics at KIMM, succeeded in developing a technique of transferring 2D nanomaterials, as thin as 1/50,000 of a strand of hair, to a substrate of at least 4 inches (approx. 10 cm) without damage.
The roll-based transfer is a process in ...
2021-05-17
On the evening of May 6, 1937, the largest aircraft ever built by mankind, a towering example of technological prowess, slipped through the stormy skies of New Jersey and prepared to land. The airship Hindenburg was nearing the end of a three-day voyage across the Atlantic Ocean from Frankfurt, Germany. It was a spectacle and a news event. Onlookers and news crews gathered to watch the 800-foot-long behemoth touch down.
And then, in one horrifying half minute, it was all over. Flames erupted from the airship's skin, fed by the flammable hydrogen gas that ...
2021-05-17
One of the especially dangerous health risks of being extremely overweight occurs when an obese person begins to accumulate fat in their liver.
This condition--non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)--is the world's most common chronic liver disease and is the primary underlying cause for liver transplants in children and adults. Without such transplants, which are available to only a small percentage of patients, NAFLD over time can be fatal. In fact, (excluding alcohol-related liver damage) more than 30,000 people a year die from NAFLD.
For years, the primary way to treat NAFLD has ...
2021-05-17
Early preterm births may be dramatically decreased with docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) supplements, with a dose of 1000 mg more effective for pregnant women with low DHA levels than the 200 mg found in some prenatal supplements, according to a study led by researchers from the University of Kansas and the University of Cincinnati and published today in EClinicalMedicine, a clinical journal of The Lancet. Early preterm birth, defined as birth before 34 weeks gestation, is a serious public health issue because these births result in the highest risk of infant mortality and child disability.
"This study tells us that pregnant women should be taking DHA," said Susan E. Carlson, Ph.D., professor of nutrition in the Department ...
2021-05-17
PITTSBURGH, May 17, 2021 - Monoclonal antibodies, a COVID-19 treatment given early after coronavirus infection, cut the risk of hospitalization and death by 60% in those most likely to suffer complications of the disease, according to an analysis of UPMC patients who received the medication compared to similar patients who did not.
UPMC and University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine physician-scientists published the findings today in Open Forum Infectious Diseases, a journal of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. The study involved bamlanivimab, a monoclonal antibody that is now offered only in combination ...
2021-05-17
Cultural diversity -- indicated by linguistic diversity -- and biodiversity are linked, and their connection may be another way to preserve both natural environments and Indigenous populations in Africa and perhaps worldwide, according to an international team of researchers.
"The punchline is, that if you are interested in conserving biological diversity, excluding the Indigenous people who likely helped create that diversity in the first place may be a really bad idea," said Larry Gorenflo, professor of landscape architecture, geography and African studies, Penn State. "Humans are part of ecosystems and I hope this study will usher in a more committed effort to engage Indigenous people in conserving localities containing key biodiversity."
Gorenflo, ...
2021-05-17
Indigenous people have lived in the Bears Ears region of southeastern Utah for millennia. Ancestral Pueblos built elaborate houses, check dams, agricultural terraces and other modifications of the landscape, leaving ecological legacies that persist to this day. Identifying how humans interacted with past environments is critical for informing how best to protect archaeological sites and ecological diversity in the present. This "archaeo-ecosystem" approach would facilitate co-management of public lands in ways that promote Indigenous health, cultural reclamation and sovereignty.
For the first time, a new study evaluated ecological legacies, archaeo-ecosystem restoration and Indigenous ...
2021-05-17
There are roughly 50 billion individual birds in the world, a new big data study by UNSW Sydney suggests - about six birds for every human on the planet.
The study - which bases its findings on citizen science observations and detailed algorithms - estimates how many birds belong to 9700 different bird species, including flightless birds like emus and penguins.
It found many iconic Australian birds are numbered in the millions, like the Rainbow Lorikeet (19 million), Sulphur-crested Cockatoo (10 million) and Laughing Kookaburra (3.4 million). But other natives, like the rare Black-breasted Buttonquail, only have around 100 members left.
The findings are being published this week in the Proceedings ...
2021-05-17
Scientists studying the impact of record heat and drought on intact African tropical rainforests were surprised by how resilient they were to the extreme conditions during the last major El Niño event.
The international study, reported in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences today, found that intact rainforests across tropical Africa continued to remove carbon from the atmosphere before and during the 2015-2016 El Niño, despite the extreme heat and drought.
Tracking trees in 100 different tropical rainforests across six African countries, the researchers found that intact forests across the continent still removed 1.1 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide per year from the atmosphere during the El Niño monitoring ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'We're playing Moneyball with building assets'
New tool uses AI to target smarter repairs with limited funds