(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- The COVID-19 pandemic made it clear technological innovations were urgently needed to detect, treat, and prevent the SARS-CoV-2 virus. A year and a half into this epidemic, waves of successive outbreaks and the dire need for new medical solutions -- especially testing -- continue to exist.
In the Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, researchers from the University of Florida and Taiwan's National Chiao Tung University report a rapid and sensitive testing method for COVID-19 biomarkers.
The researchers, who previously demonstrated detection of biomarkers relevant in epidemics and emergencies, such as the Zika virus, heart attacks, and cerebral spinal fluid leaks, leveraged their expertise to develop a sensor system that provides detection within one second, which is far faster than current COVID-19 detection methods.
"This could alleviate slow COVID-19 testing turnaround time issues," said Minghan Xian, an author and a chemical engineering doctoral candidate at the University of Florida.
Detecting the presence of the virus requires amplifying the numbers of the biomarker, such as the copies of viral ribonucleic acid in the common polymerase chain reaction technique for COVID-19 detection, or amplifying the binding signal for a target biomarker. The group's method amplifies the binding signal for a target biomarker.
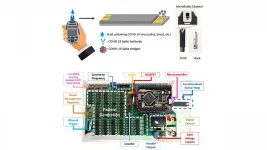
"Our biosensor strip is similar to commercially available glucose test strips in shape, with a small microfluidic channel at the tip to introduce our test fluid," said Xian. "Within the microfluidic channel, a few electrodes are exposed to fluid. One is coated with gold, and COVID-relevant antibodies are attached to the gold surface via a chemical method."
During measurement, sensor strips are connected to a circuit board via a connector, and a short electrical test signal gets sent between the gold electrode bonded with COVID antibody and another auxiliary electrode. This signal is then returned to the circuit board for analysis.
"Our sensor system, a circuit board, uses a transistor to amplify the electrical signal, which then gets converted into a number on the screen," said Xian. "The magnitude of this number depends on the concentration of antigen, the viral protein, present within our test solution."
While the system's sensor strips clearly must be discarded after use, the test circuit board is reusable. This means the cost of testing may be greatly reduced. The versatility of this technology goes far beyond detecting COIVD-19.
"By altering the type of antibodies attached to the gold surface, we can repurpose the system to detect other diseases," said Xian. "The system can serve as a prototype for modularized, inexpensive protein biomarker sensors for expedient real-time feedback within clinical applications, operating rooms, or home use."
INFORMATION:
The article "Fast SARS-COV-2 virus detection using disposable cartridge strips and semiconductor-based biosensor platform" is authored by Minghan Xian, Hao Luo, Xinyi Xia, Chaker Fares, Patrick H. Carey IV, Chan-Wen Chiu, Fan Ren, Siang-Sin Shan, Yu-Te Liao, Shu-Min Hsu, Josephine F. Esquivel-Upshaw, Chin-Wei Chang, Jenshan Lin, Steven C. Ghivizzani, and Stephen J. Pearton. It will appear in Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B on May 18, 2021 (DOI: 10.1116/6.0001060). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1116/6.0001060.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, an AVS journal published by AIP Publishing, is devoted to publishing reports of original research, letters, and review articles covering multiple disciplines with a focus on microelectronics and nanotechnology. See https://avs.scitation.org/journal/jvb.
ABOUT AVS
AVS is an interdisciplinary, professional society with some 4,500 members worldwide. Founded in 1953, AVS hosts local and international meetings, publishes five journals, serves members through awards, training and career services programs and supports networking among academic, industrial, government, and consulting professionals. Its members come from across the fields of chemistry, physics, biology, mathematics, engineering and business and share a common interest in basic science, technology development and commercialization related to materials, interfaces, and processing. https://www.avs.org
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- The COVID-19 pandemic has reinforced the pressing need to mitigate a fast-developing virus as well as antibiotic-resistant bacteria that are growing at alarming rates worldwide.
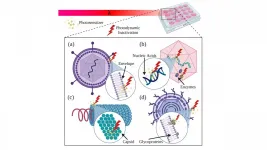
Photodynamic therapy (PDT), or using light to inactivate viruses, bacteria, and other microbes, has garnered promising results in recent decades for treating respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia, and some types of cancer.
In Applied Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers at Texas A&M University and the University of São Paulo in Brazil ...
Academic institutions need to do much more to support faculty members with disabilities and to create an environment in which they can thrive, argues a commentary published May 18 in the journal Trends in Neurosciences. The paper was written by Justin Yerbury, a cell and molecular neurobiologist who has amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and his wife, Rachel Yerbury, a research psychologist.
"We want people to understand how tough life is for people with a disability," says Justin Yerbury (@jjyerbury), a professor at the University of Wollongong in Australia. "When you add academia on top of ...
Twice as many eligible patients got screened for hepatitis C when it was already ordered for them compared to those who had to request it, according to a new study by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Additionally, the patients in the study - whose average age was 63 - completed their screenings much more often when they were contacted via mail as opposed to electronic messaging. The study was published today in BMJ.
"We think that sending the lab order with outreach was so successful because it ...
University of California scientists have discovered genetic data that will help food crops like tomatoes and rice survive longer, more intense periods of drought on our warming planet.
Over the course of the last decade, the research team sought to create a molecular atlas of crop roots, where plants first detect the effects of drought and other environmental threats. In so doing, they uncovered genes that scientists can use to protect the plants from these stresses.
Their work, published today in the journal Cell, achieved a high degree of understanding of the root functions because it combined genetic data from different cells of tomato roots grown both indoors and outside.
"Frequently, ...
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that adults ages 45 to 75 be screened for colorectal cancer, lowering the age for screening that was previously 50 to 75. The USPSTF also recommends that clinicians selectively offer screening to adults 76 to 85 years of age. Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death for both men and women in the United States. In 2016, 26% of eligible adults had never been screened and nearly one-third were not up to date with screening in 2018. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services and this statement replaces its 2016 recommendation.
To access the embargoed study: ...
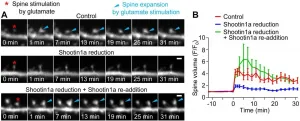
Ikoma, Japan - In neurons, changes in the size of dendritic spines - small cellular protrusions involved in synaptic transmission - are thought to be a key mechanism underlying learning and memory. However, the specific way in which these structural changes occur remains unknown. In a study published in Cell Reports, researchers from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have revealed that the binding of cell adhesion molecules with actin, via an important linker protein in the structural backbone of synapses, is vital for this process of structural plasticity.
Actin proteins make up an important part of a cell's structure, or cytoskeleton, and allow for dynamic changes in this structure by forming ...
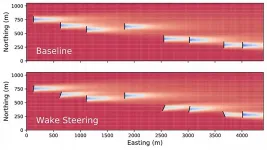
WASHINGTON, May 18, 2021 -- Wake steering is a strategy employed at wind power plants involving misaligning upstream turbines with the wind direction to deflect wakes away from downstream turbines, which consequently increases the net production of wind power at a plant.
In Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, by AIP Publishing, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) illustrate how wake steering can increase energy production for a large sampling of commercial land-based U.S. wind power plants.
While some plants showed less potential for wake steering due to unfavorable meteorological conditions or turbine layout, several wind power plants were ideal candidates ...
What The Study Did: Telemedicine use grew rapidly during the COVID-19 pandemic but there was geographic variation in its use so researchers in this study examined the association of county-level telemedicine use with community factors among people with commercial or Medicare Advantage insurance.
Authors: Ateev Mehrotra, M.D., M.P.H., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10330)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and ...
What The Study Did: Demographic information from 105 randomized clinical trials for primary open-angle glaucoma was combined to compare the rate of participation between individuals from racial/ethnic minority groups with white individuals.
Authors: Deepkumar G. Patel, D.D.S., M.P.H., of New York Ophthalmology Associates in Manhattan, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.8348)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
Research to be published tomorrow in the journal Nature Communications is the first study to quantify the costs of storm damage caused by sea level rise driven specifically by human-induced climate change. Researchers from Stevens Institute of Technology, Climate Central, Rutgers University and other institutions found this self-inflicted damage to be $8.1 billion of Hurricane Sandy's damage and an additional 71,000 people and 36,000 homes exposed to Sandy's flooding.
Hurricane Sandy struck the northeast U.S. coast in 2012, causing widespread destruction estimated at ...