Cholesterol levels sustainably lowered using base editing
2021-05-19
(Press-News.org) Base editing is a novel gene editing approach that can precisely change individual building blocks in a DNA sequence. By installing such a point mutation in a specific gene, an international research team led by the University of Zurich has succeeded in sustainably lowering high LDL cholesterol levels in the blood of mice and macaques. This opens up the possibility of curing patients with inherited metabolic liver diseases.
Lipoproteins are complex particles that deliver fat molecules to all tissues of the body through the blood system, supplying energy to the cells. One such lipoprotein, the low-density lipoprotein (LDL), can transport thousands of fat molecules, such as cholesterol, per particle. High levels of LDL in the blood are clinically associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Since LDL can also carry cholesterol into smaller vessels and thus supply more distant tissues, it can increasingly block the artery lumen, which leads to atherosclerosis.
Introducing a single gene mutation blocks an enzyme
An international research team led by the University of Zurich (UZH) has now demonstrated that a novel precise gene editing approach can reduce high LDL cholesterol levels - substantially and sustainably. The scientists introduced a single point mutation in the gene encoding for an enzyme called PCSK9. This protein is involved in the uptake of LDL cholesterol from the blood into the cells. "The genetic change we induced in mice and macaques successfully blocked PCSK9, which led to a significant reduction of the LDL cholesterol concentrations in the blood. This provides a potential therapy for patients suffering from familial hypercholesterolemia, an inherited form of high cholesterol levels," says study leader Gerald Schwank, professor at the Institute for Pharmacology and Toxicology of UZH.
Adaption of RNA technology used in COVID-19 vaccines
The gene editing technology applied by the researchers uses what are known as base editors. These proteins can change individual bases of the DNA molecule - a single "letter" of a genetic "text" - into another. Adenine base editors, for example, convert an adenine (A) into a guanine (G). And base editors do this much more precisely than previous CRISPR-Cas nucleases, which function as molecular scissors. To control the delivery of the base editor tool into the liver of animals, the researchers adapted the RNA technology used in COVID-19 vaccines. However, instead of encapsulating an RNA encoding the spike protein of SARS-CoV2 into lipid nanoparticles, they encapsulated an RNA encoding for the adenine base editor.
Accurate, efficient and safe
The RNA-lipid nanoparticles formulations were introduced into the animals intravenously, leading to liver-specific uptake and transient production of the base editor tool by the cell machinery. "Up to two-thirds of PCSK9 genes were edited in the mice and up to one-third in the non-human primates, leading to a significant reduction in LDL cholesterol levels," says Schwank. In addition, the scientists carefully assessed whether unspecific editing at undesired locations occurred, but found no indications of such off-target events.
RNA-based therapies for metabolic liver diseases
"Our study shows the feasibility of installing single nucleotide base changes in the liver of non-human primates with high efficiency and accuracy. Approximately 30 percent of all disease-causing hereditary mutations are single base mutations that can, in principle, be corrected with base editors," says Schwank. The new approach could therefore be used to treat a large number of patients suffering from inherited metabolic liver diseases, such as hypercholesterolemia, phenylketonuria or urea cycle disorders. Compared to conventional drugs, genome editing has the advantage that induced changes are sustainable. Thus, if a mutation is repaired in a sufficient number of cells, the patient will be permanently cured.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-19
Wednesday 19 May 2021 - New research published today sheds important light on how the production of a key protein in the brain is controlled, which could pave the way for new treatments for a wide range of neurological conditions.
In a study part-funded by Parkinson's UK, researchers investigated a section of genetic material known as antisense long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), which helps fine-tune the production of the protein tau inside brain cells. This precision in tau regulation is crucial for smooth functioning of the nerve cells.
Understanding the mechanism ...
2021-05-19
Unbound nickel atoms and other heavy elements have been observed in very hot cosmic environments, including the atmospheres of ultra-hot exoplanets and evaporating comets that ventured too close to our Sun or other stars. A new study conducted by JU researchers reveals the presence of nickel atoms in the cold gasses surrounding the interstellar comet 2I/Borisov. The team's finding is being published in Nature on 19 May 2021.
Interstellar comets and asteroids are precious to science because, unlike millions of minor bodies that formed in our Solar System, they originate from distant planetary systems. Until very recently, the existence of such cosmic vagabonds has merely ...
2021-05-19
HOUSTON - (May 19, 2021) - A new study from researchers at Rice University has found that bodily inflammation after the death of a spouse can predict future depression.
"Inflammation and future depressive symptoms among recently bereaved spouses" will appear in the June 2021 edition of the journal Psychoneuroendocrinology. Lead author Lydia Wu, a Rice psychology graduate student, and Christopher Fagundes, associate professor of psychology and principal investigator for the Biobehavioral Mechanisms Explaining Disparities (BMED) lab at Rice, led the study. The research team evaluated 99 people who lost their spouses within 2-3 months of the study on a number of factors, including physical ...
2021-05-19
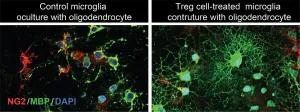
PITTSBURGH, May 19, 2021 - Specialized immune cells that accumulate in the brain in the days and weeks after a stroke promote neural functions in mice, pointing to a potential immunotherapy that may boost recovery after the acute injury is over, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine neurologists found.
The study, published today in the journal Immunity, demonstrated that a population of specialized immune cells, called regulatory T (Treg) cells, serve as tissue repair engineers to promote functional recovery after stroke. Boosting Treg cells using an antibody complex treatment, ...
2021-05-19
The yeast Candida albicans can cause itchy, painful urinary tract and vaginal yeast infections. For women in low-resource settings who lack access to healthcare facilities, these infections create substantial social and economic burdens. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Omega have developed color-changing threads that turn bright pink in the presence of C. albicans. When embedded in tampons or sanitary napkins, they could allow women to quickly and discreetly self-diagnose vulvovaginal yeast infections, the researchers say.
According to the Mayo Clinic, about 75% of women will experience a yeast infection, or vulvovaginal candidiasis, at least ...
2021-05-19
Researchers have found the elusive genetic element controlling the elongated grains and glumes of a wheat variety identified by the renowned botanist Carl Linnaeus more than 250 years ago.
The findings relating to Polish wheat, Triticum polonicum, could translate into genetic improvements and productivity in the field.
Wheat, in bread, pasta, and other forms, is a vital energy and protein source for humans. Each individual grain is nestled within the glumes and other leaf-like organs called lemma and palea which affect the grain's final size, shape, and weight.
Characterised by Linnaeus in 1762, Polish wheat has long grains, glumes, ...
2021-05-19
The sun delivers more energy to Earth in one hour than humanity consumes over an entire year. Scientists worldwide are searching for materials that can cost-effectively and efficiently capture this carbon-free energy and convert it into electricity.
Perovskites, a class of materials with a unique crystal structure, could overtake current technology for solar energy harvesting. They are cheaper than materials used in current solar cells, and they have demonstrated remarkable photovoltaic properties -- behavior that allows them to very efficiently convert sunlight into electricity.
Revealing the nature of perovskites at the atomic scale is critical to understanding their promising capabilities. ...
2021-05-19
Scientists, governments and corporations worldwide are racing against the clock to fight climate change, and part of the solution might be in our soil. By adding carbon from the atmosphere to depleted soil, farmers can both increase their yields and reduce emissions. A cover story in Chemical & Engineering News, the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, explores what it would take to get this new practice off the ground.
Historically, agricultural soil has provided crops with the nutrients needed to grow, write Senior Editors Melody Bomgardner and Britt Erickson. Today, most soil is considered degraded, leading farmers to rely on fertilizer, irrigation and pesticides, all of which are costly. Scientific advancements ...
2021-05-19
Des Plaines, IL - The Canadian Syncope Risk Score (CSRS) is an accurate validated prediction score for emergency department patients with unexplained syncope. These are the results of a study titled Multivariable risk scores for predicting short-term outcomes for emergency department patients with unexplained syncope: A systematic review, to be published in the May issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM) journal, peer-reviewed journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
Syncope is a common presentation to an emergency department, with patients at risk of experiencing an adverse event within 30 days. Without a standardized risk stratification system of patients, there will be health care ...
2021-05-19
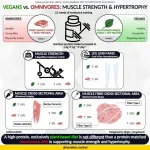
Protein intake is more important than protein source if the goal is to gain muscle strength and mass. This is the key finding of a study that compared the effects of strength training in volunteers with a vegan or omnivorous diet, both with protein content considered adequate.
In the study, which was conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil, 38 healthy young adults, half of whom were vegans and half omnivores, were monitored for 12 weeks. In addition to performing exercises to increase muscle strength and mass, the volunteers followed either a mixed diet with both ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cholesterol levels sustainably lowered using base editing