New research could lead to better treatment for epilepsy
2021-05-20
(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered that the way in which neurons are connected within regions of the brain, can be a better indicator of disease progression and treatment outcomes for people with brain disorders such as epilepsy.
Many brain diseases lead to cell death and the removal of connections within the brain. In a new study, published in Human Brain Mapping, a group of scientists, led by Dr Marcus Kaiser from the School of Medicine at the University of Nottingham, looked at epilepsy patients undergoing surgery.
They found that changes in the local network within brain regions can be a better predictor of disease progression, and also whether surgery will be successful or not.
The team found that looking at connectivity within regions of the brain, showed superior results to the current approach of only observing fibre tract connectivity between brain regions. Dividing the surface of the brain into 50,000 network nodes of comparable size, each brain region could be studied as a local network with 100-500 nodes. These local networks showed distinct changes compared to a control group not suffering from epileptic seizures.
Using a non-invasive technique called diffusion tensor imaging - a special measurement protocol for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanners - the team of scientists demonstrated that fibres within and between brain regions are removed for patients.
However, they found that connectivity within regions was a better predictor of whether surgical removal of brain tissue was successful in preventing future seizures.
Explaining the work, Dr Kaiser, Professor of Neuroinformatics at the University of Nottingham, says: "When someone has an epileptic seizure, it 'spreads' through the brain. We found that local network changes occurred for regions along the main spreading pathways for seizures. Importantly, regions far away from the starting point of the seizure, for example in the opposite brain hemisphere, were involved.
"This indicates that the increased brain activity during seizures leads to changes in a wide range of brain regions. Furthermore, the longer patients suffered, the more regions showed local changes and the more severe were these changes."
The researchers at Nottingham, Newcastle, Qingdao, Shanghai, and Munich Universities, along with the company Biomax, evaluated the scans of 33 temporal lobe epilepsy patients and 36 control subjects.
Project partners used the NeuroXM™ knowledge management platform to develop a knowledge model for high-resolution connectivity with more than 50,000 cortical nodes and several millions of connections and corresponding automated processing pipelines accessible through Biomax's neuroimaging product NICARA™.
Project manager Dr Markus Butz-Ostendorf from Biomax: "Our software can be easily employed at hospitals and can also be combined with other kinds of data from genetics or from other imaging approaches such as PET, CT, or EEG."
Commenting on the fact that local changes were more informative of surgery outcome, Professor Yanjiang Wang, who is one of the corresponding authors, and Ms Xue Chen, both from China University of Petroleum (East China), explained: "Local connectivity was not only better in overall predictions but particularly successful in identifying patients where surgery did not lead to any improvement, identifying 95% of such cases compared to 90% when used connectivity between regions".
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-20
More than 90 years ago, astronomer Edwin Hubble observed the first hint of the rate at which the universe expands, called the Hubble constant.
Almost immediately, astronomers began arguing about the actual value of this constant, and over time, realized that there was a discrepancy in this number between early universe observations and late universe observations.
Early in the universe's existence, light moved through plasma--there were no stars yet--and from oscillations similar to sound waves created by this, scientists deduced that the Hubble constant was about 67. This means the universe expands about 67 kilometers per second faster every 3.26 million light-years.
But this observation differs when scientists look at the universe's ...
2021-05-20
BOSTON - Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers are presenting dozens of research studies at the 2021 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). The studies will be presented during the virtual program on June 4-8, 2021. ASCO is the world's largest clinical cancer research meeting, attracting more than 30,000 oncology professionals from around the world.
Toni K. Choueiri, MD, the director of the Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology at Dana-Farber, will present results from the randomized, double-blind, phase III KEYNOTE-564 trial evaluating pembrolizumab versus placebo after surgery in patients with renal cell carcinoma (abstract LBA5) during ASCO's Plenary Session on Sunday, June ...
2021-05-20
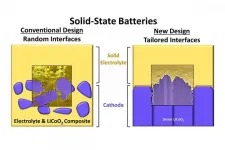
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Solid-state batteries pack a lot of energy into a small space, but their electrodes are not good at keeping in touch with their electrolytes. Liquid electrolytes reach every nook and cranny of an electrode to spark energy, but liquids take up space without storing energy and fail over time. Researchers are now putting solid electrolytes in touch with electrodes made of strategically arranged materials - at the atomic level - and the results are helping drive better solid-state battery technologies.
A new study, led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign materials science and engineering professor Paul Braun, postdoctoral research associate Beniamin Zahiri, and Xerion Advanced Battery Corp. director of research and development ...
2021-05-20
The University of Maryland (UMD) co-published a new review paper in the Annual Review of Resource Economics to examine pollinators from both an economic and ecological perspective, providing much needed insight into the complexities of valuing pollination. Pollinators are not only a critical component of a healthy ecosystem, but they are also necessary to produce certain foods and boost crop yields. While native and wild pollinators (whether they be certain bee species, other insects and animals, or just the wind) still play an important role, managed honey bee colonies are commercially trucked around the U.S. to meet the need for pollination services in agricultural products. Recent reports of ...
2021-05-20
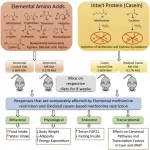
BATON ROUGE, Louisiana - A diet that improves the biomarkers of metabolic health, and that could potentially slow the aging process, has moved a step closer to reality.
"We've known for years that restricting the amino acid methionine in the diet produces immediate and lasting improvements in nearly every biomarker of metabolic health," said Thomas W. Gettys, PhD, Professor and Director, Nutrient Sensing and Adipocyte Signaling Laboratory at Pennington Biomedical Research Center. "The problem is that methionine-restricted diets have been difficult to implement because they taste so bad."
Until now. Restricting methionine normally involves diets formulated with elemental (e.g., individual) amino acids. Individual amino acids are the building blocks ...
2021-05-20
May 20, 2021 - Women with a history of weight cycling - losing and regaining 10 pounds or more, even once - have increased rates of insomnia and other sleep problems, reports a study in The Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing, official journal of the Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"History of weight cycling was prospectively associated with several measures of poor sleep, including short sleep duration, worse sleep quality, greater insomnia, greater sleep disturbances, ...
2021-05-20
Melting glaciers and polar ice sheets are among the dominant sources of sea-level rise, yet until now, the water beneath them has remained hidden from airborne ice-penetrating radar.
With the detection of groundwater beneath Hiawatha Glacier in Greenland, researchers have opened the possibility that water can be identified under other glaciers from the air at a continental scale and help improve sea-level rise projections. The presence of water beneath ice sheets is a critical component currently missing from glacial melt scenarios that may greatly impact how quickly seas rise - for example, by enabling big chunks of ice to calve ...
2021-05-20
New research led by the University of Kent's School of Psychology has found that some brain activity methods used to detect incriminating memories do not work accurately in older adults.
Findings show that concealed information tests relying on electrical activity of the brain (electroencephalography [EEG]) are ineffective in older adults because of changes to recognition-related brain activity that occurs with aging.
EEG-based forensic memory detection is based on the logic that guilty suspects will hold incriminating knowledge about crimes they have committed, and therefore their brains will elicit a recognition response ...
2021-05-20
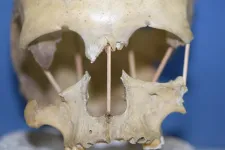
For the first time, researchers have successfully sequenced the entire genome from the skull of Peştera Muierii 1, a woman who lived in today's Romania 35,000 years ago. Her high genetic diversity shows that the out of Africa migration was not the great bottleneck in human development but rather this occurred during and after the most recent Ice Age. This is the finding of a new study led by Mattias Jakobsson at Uppsala University and being published in Current Biology.
"She is a bit more like modern-day Europeans than the individuals in Europe 5,000 years earlier, but the difference is much less than we had thought. We can see that she is not a direct ancestor of modern Europeans, but she is a predecessor of the hunter-gathers that lived in Europe until the end of the last ...
2021-05-20
DURHAM, N.C. - A newly identified group of antibodies that binds to a coating of sugars on the outer shell of HIV is effective in neutralizing the virus and points to a novel vaccine approach that could also potentially be used against SARS-CoV-2 and fungal pathogens, researchers at the Duke Human Vaccine Institute report.
In a study appearing online May 20 in the journal Cell, the researchers describe an immune cell found in both monkeys and humans that produces a unique type of anti-glycan antibody. This newly described antibody has the ability to attach ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New research could lead to better treatment for epilepsy