Researchers identify a gene that causes canine hereditary deafness in puppies
2021-05-21
(Press-News.org) Finnish researchers have been the first to determine the cause for the nonsyndromic early-onset hereditary canine hearing loss in Rottweilers. The gene defect was identified in a gene relevant to the sense of hearing. The study can also promote the understanding of mechanisms of hearing loss in human.
Hearing loss is the most common sensory impairment and a complex problem in humans, with varying causes, severity and age of onset. Deafness and hearing loss are fairly common also in dogs, but gene variants underlying the hereditary form of the disorder are so far poorly known.
Researchers from the University of Helsinki and the Folkhalsan Research Center focused on a rare type of hearing loss observed in Rottweilers. It begins early in puppyhood and progresses to deafness at the age of few months. A similar type of hearing loss was also seen in a small number of mixed-breed dogs, of which the majority had Rottweiler ancestry.
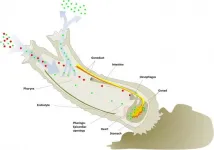
"We identified the variant in the LOXHD1 gene, which plays a key role in the function of the cilia of the cochlear sensory cells. While the exact mechanism of deafness is not known, variants of the same gene cause hereditary hearing loss in humans and mice as well," says Docent Marjo Hytonen from the University of Helsinki and the Folkhalsan Research Center.
Hearing impairment caused by the LOXHD1 gene defect is a recessively inherited trait, which means that to develop the disorder, the dog must have two copies of the defective gene, one from the father and one from the dam.
"Through our collaboration partner, we had the chance to investigate the prevalence and breed specificity of the gene variant in a unique global dataset of some 800,000 dogs. No surveys of similar scope have previously been published," says Professor Hannes Lohi from the University of Helsinki and the Folkhalsan Research Center.
New individual dogs that had inherited the gene defect and were also found to be deaf were identified in the screening.
"This enhances the significance of our finding. Thanks to our gene discovery, dogs used for breeding can now be tested for the defect. This makes it possible to avoid combinations that could result in puppies who will lose their hearing."
The recent study is part of a research programme led by Professor Lohi and investigating the genetic background of hereditary diseases. Currently ongoing are several projects whose goals include the determination of genetic causes for hearing loss.
According to Marjo Hytonen, the preliminary results are promising.
"We have observed that both previously unknown hereditary congenital hearing loss and adult-onset hearing loss occur in several dog breeds. In addition to dogs, the preliminary findings open new avenues for investigating human hereditary hearing defects."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-21
If you've been to your local beach, you may have noticed the wind tossing around litter such as an empty potato chip bag or a plastic straw. These plastics often make their way into the ocean, affecting not only marine life and the environment but also threatening food safety and human health.
Eventually, many of these plastics break down into microscopic sizes, making it hard for scientists to quantify and measure them. Researchers call these incredibly small fragments "nanoplastics" and "microplastics" because they are not visible to the naked eye. Now, in a multiorganizational effort led by the National Institute of Standards and ...
2021-05-21
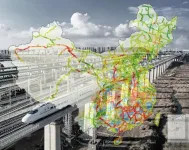
Just half a degree Celsius less warming would save economic losses of Chinese railway infrastructure by approximately $0.63 billion per year, according to a new paper published by a collaborative research team based in Beijing Normal University and the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China.
The study, which appears in Transportation Research Part D recently, found that the rainfall-induced disaster risk of railway infrastructure has increased with increasing extreme rainfall days during the decades 1981-2016. Limiting global ...
2021-05-21
Ending our dependence on coal is essential for effective climate protection. Nevertheless, efforts to phase out coal trigger anxiety and resistance, particularly in mining regions. The governments of both Canada and Germany have involved various stakeholders to develop recommendations aimed at delivering just transitions and guiding structural change. In a new study, researchers at the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) compare the stakeholder commissions convened by the two countries, drawing on expert interviews with their members, and examine how governments use commissions to legitimize their transition policies.
In the study, the researchers identify similarities and ...
2021-05-21
The work, carried out by Pilar Madrigal and Sandra Jurado, from the UMH-CSIC Neurosciences Institute in Alicante, a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council and Miguel Hernández University, has been published in Communications Biology, a Nature group´s journal.
"Our in-depth analysis of the oxytocin-vasopressin circuit in the mouse brain has revealed that these two molecules have distinct dynamics throughout embryonic development. It is likely that these adaptations modulate the functional properties of different brain regions according to their developmental stage, contributing to the refinement ...
2021-05-21
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University have developed a nanosensor-based hardware and software complex for measurement of cardiac micropotential energies without filtering and averaging-out cardiac cycles in real time. The device allows registering early abnormalities in the function of cardiac muscle cells, which otherwise can be recorded only during open-heart surgery or by inserting an electrode in a cardiac cavity through a vein. Such changes can lead to sudden cardiac death (SCD). Nowadays, there are no alternatives to the Tomsk device for a number of key characteristics in Russia and the world. The research findings of four-year measurement of cardiac micropotential energies using this device ...
2021-05-21
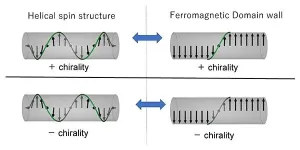
Using magnets, a collaborative group have furthered our understanding of chirality.
Their research was published in the journal Physical Review Letters on April 28, 2021.
Chirality is the lack of symmetry in matter. Human hands, for example, express chirality. A mirror image of your right hand differs from your left, giving it two distinguishable chiral states.
Chirality is an important issue in a myriad of scientific fields, ranging from high-energy physics to biology.
Within our bodies, some molecules, such as amino acids, show only one chiral state. In other words, they are homo-chiral. It is crucial to understand how this information is transferred and ...
2021-05-21
Type 2 diabetes patients who also have asthma are benefitting from a diabetes medication, typically given to help the pancreas produce more insulin, that also improves asthma symptoms and may reduce lung and airway inflammation.
These types of medication -- GLP-1 receptor agonists -- are a newer class of FDA-approved therapeutics that are generally used in addition to metformin for control of blood sugar or to induce weight loss in patients with obesity.
Researchers from Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School and University Hospital Zurich in Switzerland used electronic health record (EHR) data of patients with asthma and type 2 diabetes who initiated treatment with GLP-1R agonists, finding lower rates of asthma exacerbations ...
2021-05-21
'Don't forget the mask' - although most people nowadays follow this advice, professionals express different opinions about the effectiveness of face masks. An international team led by researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry in Mainz, Germany, has now used observational data and model calculations to answer open questions. The study shows under which conditions and in which way masks actually reduce individual and population-average risks of being infected with COVID-19 and help mitigate the corona pandemic. In most environments and situations, ...
2021-05-21
PHILADELPHIA--A five-year community outreach and engagement effort by the Abramson Cancer Center at the University of Pennsylvania (ACC) to increase enrollment of Black patients into cancer clinical trials more than doubled the percentage of participants, improving access and treatment for a group with historically low representation in cancer research. The percentage of patients enrolled into a treatment clinical trial, for example, increased from 12 to 24 percent. A significant increase was also observed in non-therapeutic interventional and non-interventional trials.
The findings were published today in an abstract to be presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology annual meeting on June 5. (Abstract #100). [ADD ...
2021-05-21
New York, NY (May 21, 2021) --Women who were highly exposed to ultra-fine particles in air pollution during their pregnancy were more likely to have children who developed asthma, according to a study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine in May. This is the first time asthma has been linked with prenatal exposure to this type of air pollution, which is named for its tiny size and which is not regulated or routinely monitored in the United States.
Slightly more than 18 percent of the children born to these mothers developed asthma in their preschool years, compared ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers identify a gene that causes canine hereditary deafness in puppies