(Press-News.org) Sloughed off skin and bodily fluids are things most people would prefer to avoid.
But for marine biologist like Cheryl Lewis Ames, Associate Professor of Applied Marine Biology in the Graduate School of Agricultural Science at Tohoku University (Japan), such remnants of life have become a magical key to detecting the unseen.
Any organism living in the ocean will inevitably leave behind traces containing their DNA - environmental DNA (eDNA) - detectable in water samples collected from the ocean
Only recently has molecular sequencing technology become advanced enough to conduct eDNA analysis in the field to identify species that may be endangered, invasive or dangerous, and could otherwise go unnoticed.
Ames chose sampling sites in the Florida Keys (USA) where species of upside-jellyfish Cassiopea occur to test out their newly developed Fieldable eDNA sequencing kit - called FeDS.
Using eDNA for multiple species identification is a multistep process known as metabarcoding. Since the mixed DNA template must first be amplified using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), metabarcoding experiments in the field have only recently been possible thanks to battery-operated thermocyclers and other portable devices.
Determining the identity of a species from small bits of DNA filtered from seawater requires the use of a Next Generation Sequencer (NGS), a machine that traditionally takes up the whole desktop counter in a laboratory and requires an electrical outlet. A novelty of the portable technology used in this study - Nanopore MinION -- is that as pieces of DNA pass through a microscopic pore in the device, differences in electrical current determine the unique code of each DNA strand.
Instead of the typically large sequencing machines used to complete such a task, Ames and her team were testing a Nanopore system the size of a cellphone, powered by a laptop computer. A drop of the prepared eDNA mixture added to the portable sequencer reveals on the screen the genetic code of all the DNA passing through it in real-time.
Then, DNA sequences are searched against a huge database of sequences to determined which species are represented by the eDNA collected onsite that day. Upgraded "offline" versions of the necessary software and pre-downloading of the reference database to the laptop meant that the whole metabarcoding process could be conducted beyond the walls of a laboratory, away from internet connection.
Ames and the team detected 53 species of jellyfish including Cassiopea, the upside-down jellyfish, two venomous species of box jellyfish, many species with hydroid forms, and two species of stalked jellyfish which were previously unreported in the Florida Keys, indicating that the process could reveal species that would otherwise go unnoticed.
"My hope is that one day this system is used for sting mitigation, almost like a weather forecast app that also reports 'jellyfish stings risk' at certain beaches," said Ames.
Ames has spent much of her time conducting research in areas where jelly stings are common, and warnings about whether venomous jellies are in the area could prevent countless injuries to swimmers. Besides practical purposes in fisheries and conservation, the fact that a sample of ocean water can reveal the organisms in the vicinity is truly a marvel.
INFORMATION:
Researchers at the University of Zurich show how climate mitigation scenarios can be improved by taking into account that the financial system can play both an enabling or a hampering role on the path to a sustainable economic system.
To limit global warming, a profound transformation of energy, production and consumption in our economies is required. The scale of the transformation means that the financial system must have a proactive role. New green investments are needed, as well as a reallocation of capital from high to low-carbon activities. The Central Banks and Supervisors Network for Greening the Financial ...
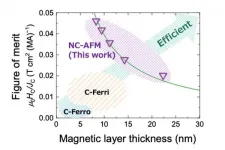
Researchers at Tohoku University and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have discovered a new spintronic phenomenon - a persistent rotation of chiral-spin structure.
Their discovery was published in the journal Nature Materials on May 13, 2021.
Tohoku University and JAEA researchers studied the response of chiral-spin structure of a non-collinear antiferromagnet Mn3Sn thin film to electron spin injection and found that the chiral-spin structure shows persistent rotation at zero magnetic field. Moreover, their frequency can be tuned by the applied current.
"The electrical control of magnetic ...
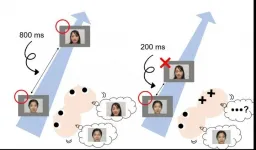
It has previously been reported that human visual system has a temporal limitation in processing visual information when perceiving things that occur less than half a second apart. This temporal deficit is known as "attentional blink" and has been demonstrated in a large number of studies. These studies reported that adults could recognize two things when these two were temporally separated over 500 ms, but adults overlooked the second thing when the temporal interval was less than 500 ms. Recently, this attentional blink phenomenon has been observed in even preverbal infants less than one-year old.
In the study ...
Finnish researchers have been the first to determine the cause for the nonsyndromic early-onset hereditary canine hearing loss in Rottweilers. The gene defect was identified in a gene relevant to the sense of hearing. The study can also promote the understanding of mechanisms of hearing loss in human.
Hearing loss is the most common sensory impairment and a complex problem in humans, with varying causes, severity and age of onset. Deafness and hearing loss are fairly common also in dogs, but gene variants underlying the hereditary form of the disorder are so far poorly ...
If you've been to your local beach, you may have noticed the wind tossing around litter such as an empty potato chip bag or a plastic straw. These plastics often make their way into the ocean, affecting not only marine life and the environment but also threatening food safety and human health.
Eventually, many of these plastics break down into microscopic sizes, making it hard for scientists to quantify and measure them. Researchers call these incredibly small fragments "nanoplastics" and "microplastics" because they are not visible to the naked eye. Now, in a multiorganizational effort led by the National Institute of Standards and ...
Just half a degree Celsius less warming would save economic losses of Chinese railway infrastructure by approximately $0.63 billion per year, according to a new paper published by a collaborative research team based in Beijing Normal University and the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China.
The study, which appears in Transportation Research Part D recently, found that the rainfall-induced disaster risk of railway infrastructure has increased with increasing extreme rainfall days during the decades 1981-2016. Limiting global ...
Ending our dependence on coal is essential for effective climate protection. Nevertheless, efforts to phase out coal trigger anxiety and resistance, particularly in mining regions. The governments of both Canada and Germany have involved various stakeholders to develop recommendations aimed at delivering just transitions and guiding structural change. In a new study, researchers at the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) compare the stakeholder commissions convened by the two countries, drawing on expert interviews with their members, and examine how governments use commissions to legitimize their transition policies.
In the study, the researchers identify similarities and ...
The work, carried out by Pilar Madrigal and Sandra Jurado, from the UMH-CSIC Neurosciences Institute in Alicante, a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council and Miguel Hernández University, has been published in Communications Biology, a Nature group´s journal.
"Our in-depth analysis of the oxytocin-vasopressin circuit in the mouse brain has revealed that these two molecules have distinct dynamics throughout embryonic development. It is likely that these adaptations modulate the functional properties of different brain regions according to their developmental stage, contributing to the refinement ...
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University have developed a nanosensor-based hardware and software complex for measurement of cardiac micropotential energies without filtering and averaging-out cardiac cycles in real time. The device allows registering early abnormalities in the function of cardiac muscle cells, which otherwise can be recorded only during open-heart surgery or by inserting an electrode in a cardiac cavity through a vein. Such changes can lead to sudden cardiac death (SCD). Nowadays, there are no alternatives to the Tomsk device for a number of key characteristics in Russia and the world. The research findings of four-year measurement of cardiac micropotential energies using this device ...
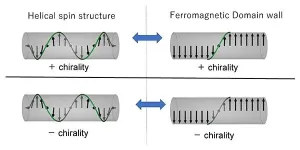
Using magnets, a collaborative group have furthered our understanding of chirality.
Their research was published in the journal Physical Review Letters on April 28, 2021.
Chirality is the lack of symmetry in matter. Human hands, for example, express chirality. A mirror image of your right hand differs from your left, giving it two distinguishable chiral states.
Chirality is an important issue in a myriad of scientific fields, ranging from high-energy physics to biology.
Within our bodies, some molecules, such as amino acids, show only one chiral state. In other words, they are homo-chiral. It is crucial to understand how this information is transferred and ...