The brain learns faces fastest in person
The brain signal linked to face familiarity is strongest after getting to know someone in-person
2021-05-24
(Press-News.org) The neural representation of a familiar face strengthens faster when you see someone in person, according to a new study published in JNeurosci.
The brain loves faces -- there's even an interconnected network of brain areas dedicated to face-processing. Despite all the research on how the brain sees faces, little is known about how the neural representation of a face changes as it becomes familiar.
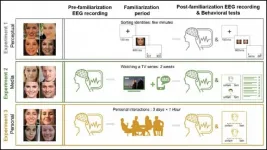
To track how familiarity brain signals change, Ambrus et al. measured participants' brain activity with EEG before and after getting to know different faces. Participants were exposed to faces in one of three ways: perceptual exposure (a sorting game), media exposure (watching a TV show), and in-person (chatting with lab members). A jolt of brain activity appeared on the EEG around 400 milliseconds after viewing a face; the strength of the signal was tied to the familiarity of the face. The type of exposure affected how much the signal changed: in-person exposure strengthened it the most, followed by media exposure. Perceptual exposure had very little impact on the familiarity signal. These results emphasize the importance of in-person interactions when getting to know new people.
INFORMATION:
Paper title: Getting to Know You: Emerging Neural Representations During Face Familiarization
About JNeurosci
JNeurosci, the Society for Neuroscience's first journal, was launched in 1981 as a means to communicate the findings of the highest quality neuroscience research to the growing field. Today, the journal remains committed to publishing cutting-edge neuroscience that will have an immediate and lasting scientific impact, while responding to authors' changing publishing needs, representing breadth of the field and diversity in authorship.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world's largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 37,000 members in more than 90 countries and over 130 chapters worldwide.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-24
A strange phenomenon happens with modern blue whales, humpback whales and gray whales: they have teeth in the womb but are born toothless. Replacing the teeth is baleen, a series of plates composed of thin, hair- and fingernail-like structures growing from the roof of their mouths that act as a sieve for filter feeding small fish and tiny shrimp-like krill.
The disappearing embryonic teeth are testament to an evolutionary history from ancient whales that had teeth and consumed larger prey. Modern baleen whales on the other hand use their fringed baleen to strain their miniscule prey from water, hence the term filter feeding.
A new study that utilized high-resolution computed tomography (CT) to ...
2021-05-24
East Hanover, NJ. May 24, 2021. A recent qualitative study of rehabilitation professionals caring for people with spatial neglect enabled researchers to identify interventions to improve rehabilitation outcomes. Experts reported that implementation of spatial neglect care depends on interventions involving family support and training, promotion of interdisciplinary collaboration, development of interprofessional vocabulary, and continuous treatment and follow-up assessment through care transitions.
The article, "Barriers and Facilitators to Rehabilitation Care of Individuals with Spatial ...
2021-05-24
Scientists at the University of York have made significant progress in the development of a nasal spray treatment for patients with Parkinson's disease.
Researchers have developed a new gel that can adhere to tissue inside the nose alongside the drug levodopa, helping deliver treatment directly to the brain.
Levodopa is converted to dopamine in the brain, which makes-up for the deficit of dopamine-producing cells in Parkinson's patients, and helps treat the symptoms of the disease. Over extended periods of time, however, levodopa becomes less effective, and increased doses are needed.
Professor David Smith, from the ...
2021-05-24
Extra funding should be made available for early years care in the wake of the pandemic, researchers say.
Experts at the University of Leeds, University of Oxford and Oxford Brookes University have made the call after assessing the benefits of early childhood education and care (ECEC) for children under three during COVID-19.
They found children who attended childcare outside the home throughout the first UK lockdown made greater gains in language and thinking skills, particularly if they were from less advantaged backgrounds.
And now they are making several policy recommendations ...
2021-05-24
Research Study Key Takeaways:
Ridesharing can reduce a passenger's risk of being a target of sexual assault by providing a more reliable and timely transportation option for traveling to a safer place.
The entry of Uber into a city contributes to a 6.3% reduction in rape incidents.
A 1% increase in Uber pickups in a neighborhood translates to a more than 3% decrease in the likelihood of sexual assaults.
CATONSVILLE, MD, May 24, 2021 - Contrary to portraits painted in popular media, new research involving ridesharing services shows they provide an additional level of protection for potential sexual assault victims, particularly ...
2021-05-24
Regular physical activity has positive effects on children's developing brain circuits, finds a Boston Children's Hospital study using neuroimaging data from nearly 6,000 early adolescents. Physical activity of any kind was associated with more efficiently organized, flexible, and robust brain networks, the researchers found. The more physical activity, the more "fit" the brain.
Findings were published in Cerebral Cortex on May 14.
"It didn't matter what kind of physical activity children were involved in - it only mattered that they were active," says Caterina Stamoulis, PhD, principal ...
2021-05-24
The first detailed cross-section of a galaxy broadly similar to the Milky Way, published today, reveals that our galaxy evolved gradually, instead of being the result of a violent mash-up. The finding throws the origin story of our home into doubt.
The galaxy, dubbed UGC 10738, turns out to have distinct 'thick' and 'thin' discs similar to those of the Milky Way. This suggests, contrary to previous theories, that such structures are not the result of a rare long-ago collision with a smaller galaxy. They appear to be the product of more peaceful change.
And that is a game-changer. It means that our spiral galaxy home isn't the product of a freak accident. Instead, it ...
2021-05-24
SPOKANE, Wash.-- Breast cancer screening took a sizeable hit during the COVID-19 pandemic, suggests new research that showed that the number of screening mammograms completed in a large group of women living in Washington State plummeted by nearly half. Published today in JAMA Network Open, the study found the steepest drop-offs among women of color and those living in rural communities.
"Detecting breast cancer at an early stage dramatically increases the chances that treatment will be successful," said lead study author Ofer Amram, an assistant professor in the Washington ...
2021-05-24
What The Study Did: Researchers used clinical data to examine differences in breast cancer screenings before and during the COVID-19 pandemic overall and among sociodemographic groups. Data included completed screening mammograms within a large statewide nonprofit community health care system from April 2018 through December 2020.
Authors: Ofer Amram, Ph.D., of Washington State University in Spokane, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.10946)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
2021-05-24
What The Study Did: This follow-up study of a randomized clinical trial examines the association between survival and C-reactive protein levels in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who were treated with tocilizumab.
Authors: Xavier Mariette, M.D., Ph.D., of the Hôpital Bicêtre in Bicêtre, France, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.2209)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The brain learns faces fastest in person
The brain signal linked to face familiarity is strongest after getting to know someone in-person