Ludwig Cancer research study finds way to revive potent immune cells for cancer therapy
2021-05-24
(Press-News.org) MAY 24, 2021, NEW YORK - A Ludwig Cancer Research study has discovered how to revive a powerful but functionally inert subset of anti-cancer immune cells that are often found within tumors for cancer therapy.
Led by Ludwig Lausanne's Ping-Chih Ho and Li Tang of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, the study describes how an immune factor known as interleukin-10 orchestrates the functional revival of "terminally exhausted" tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes (TILs), which have so far proved impervious to stimulation by immunotherapies. It also demonstrates that the factor, when applied in combination with cell therapies, can eliminate tumors in mouse models of melanoma and colon cancer. The findings are reported in the current issue of Nature Immunology.
"We've found, for the first time, that terminally exhausted TILs can be directly rejuvenated so that their potent anti-cancer activity is restored, and that this rejuvenation is accomplished through the metabolic reprogramming of the cells induced by interleukin-10," said Ho, associate member of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, Lausanne.
Deprived of oxygen and vital nutrients within tumors, the TILs most capable of killing cancer cells are typically pushed into a stubbornly sluggish state known as exhaustion. Recent research has identified two distinct types of exhausted TILs. One, known as "progenitor exhausted" TILs, can recognize cancer cells with nominal efficiency and proliferate in response to the immunotherapy PD-1 blockade. But it is their descendants, "terminally exhausted" TILs, that are best equipped to detect and destroy cancer cells. They are, however, functionally disabled, prone to self-destruction and utterly incapable of proliferation.
"Even PD-1 blockade cannot restore the function of these terminally exhausted TILs," said Ho. "In fact, many patients do not respond to PD-1 blockade because their tumors lack progenitor exhausted TILs and have only terminally exhausted TILs. This is why researchers are looking for ways to revive terminally exhausted T cells for cancer therapy."
Three lines of evidence prompted the current study. First, Ho and his team recently END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study shines light on hazards of Earth's largest volcano
2021-05-24
MIAMI - Scientists from the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science analyzed ground movements measured by Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) satellite data and GPS stations to precisely model where magma intruded and how magma influx changed over time, as well as where faults under the flanks moved without generating significant earthquakes. The GPS network is operated by the U.S. Geological Survey's Hawaii Volcano Observatory.
"An earthquake of magnitude-6 or greater would relieve the stress imparted by the influx of magma along ...
Study: Diet to lower blood pressure also improved other factors in cardiac health
2021-05-24
BOSTON - Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the United States. Public health advocates frequently site Americans' high-sodium diet as one factor in the nation's cardiac health. While sodium has been definitively linked to high-blood pressure -- a key risk factor for CVD -- few rigorously controlled studies make the direct causal link between high sodium intake and cardiovascular damage, heart attack, or stroke.
In a new analysis, researchers from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) examined three cardiovascular biomarkers, which are measurable indicators ...
Impact of school nutrition policies in California varies by children's ethnicity
2021-05-24
California state school nutrition policies and federal policies for school meals have mixed impacts on childhood obesity in children of Pacific Islander (PI), Filipino (FI) and American Indian/Alaska native (AIAN) origins, according to a new study published this week in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Mika Matsuzaki of Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, USA, and colleagues.
Children of PI, FI and AIAN origin are some of the most understudied subgroups experiencing high rates of overweight/obesity. California has enacted policies on foods and beverages available in schools through a series of standards ...
Built environments don't play expected role in weight gain
2021-05-24
People don't gain or lose weight because they live near a fast-food restaurant or supermarket, according to a new study led by the University of Washington. And, living in a more "walkable", dense neighborhood likely only has a small impact on weight.
These "built-environment" amenities have been seen in past research as essential contributors to losing weight or tending toward obesity. The idea appears obvious: If you live next to a fast-food restaurant, you'll eat there more and thus gain weight. Or, if you have a supermarket nearby, you'll shop there, eat healthier and thus lose weight. Live in a neighborhood that makes walking and biking easier and you'll get out, exercise more and burn more calories. ...
Weight-loss treatment prevents accumulation of lipid linked to cardiac mortality
2021-05-24
Researchers at the Karolinska Institutet, University of Oxford and University of Copenhagen have shown that elevated levels of lipids known as ceramides can be associated with a ten-fold higher risk of death from cardiovascular disease. Treatment with liraglutide could keep the ceramide levels in check, compared with placebo. The results have been published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Approximately 16 percent of the Swedish population suffers from obesity (BMI over 30), which is one of the greatest risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction and stroke. The World Health ...
Specialized inhibitory cluster gates plasticity in fear learning
2021-05-24
Has your heart ever started to race at the thought of an upcoming deadline for work? Or has the sight of an unknown object in a dark room made you jump? Well, you can probably thank your amygdala for that.
The small almond-shaped brain structure is central to how we perceive and process fear. As we start to learn to associate fear with cues in our environment, neuronal connections within the amygdala are dynamically altered in a process called synaptic plasticity. Although this physiological mechanism is important for facilitating fear learning, it has mostly been studied in the context of excitatory neurons within the amygdala. Far less is known about the role inhibitory cells ...
COVID-19 infection rates of dentists remain lower than other health professionals
2021-05-24
CHICAGO, May 24, 2021--More than a year after COVID-19 appeared in the U.S., dentists continue to have a lower infection rate than other front-line health professionals, such as nurses and physicians, according to a study published online ahead of the June print issue in the Journal of the American Dental Association. The study, "COVID19 among Dentists in the U.S. and Associated Infection Control: a six-month longitudinal study," is based on data collected June 9 - Nov. 13, 2020.
According to the study, based on the number of dentists with confirmed or probable COVID-19 infections over more than six months, the cumulative infection rate for U.S. dentists is 2.6%. The monthly incidence ...
Simple diagnostic tool predicts individual risk of Alzheimer's
2021-05-24
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed an algorithm that combines data from a simple blood test and brief memory tests, to predict with great accuracy who will develop Alzheimer's disease in the future. The findings are published in Nature Medicine.
Approximately 20-30% of patients with Alzheimer's disease are wrongly diagnosed within specialist healthcare, and diagnostic work-up is even more difficult in primary care. Accuracy can be significantly improved by measuring the proteins tau and beta-amyloid via a spinal fluid sample, or PET scan. However, those methods are expensive and only available at a relatively few specialized memory clinics worldwide. Early and accurate ...
To unpack colonial influence on ecology, researchers propose five strategies
2021-05-24
Ecology, the field of biology devoted to the study of organisms and their natural environments, needs to account for the historical legacy of colonialism that has shaped people and the natural world, researchers argued in a new perspective in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution.
To make ecology more inclusive of the world's diverse people and cultures living in diverse ecosystems, researchers from University of Cape Town, North West University in South Africa and North Carolina State University proposed five strategies to untangle the impacts of colonialism on research and thinking in the field today.
"There are significant biases in our understanding ...
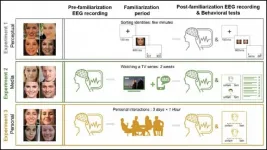
The brain learns faces fastest in person
2021-05-24
The neural representation of a familiar face strengthens faster when you see someone in person, according to a new study published in JNeurosci.
The brain loves faces -- there's even an interconnected network of brain areas dedicated to face-processing. Despite all the research on how the brain sees faces, little is known about how the neural representation of a face changes as it becomes familiar.
To track how familiarity brain signals change, Ambrus et al. measured participants' brain activity with EEG before and after getting to know different ...