(Press-News.org) In the latest National Autism Indicators Report, researchers from Drexel University's A.J. Drexel Autism Institute examined surveys of family members of autistic adults who use Developmental Disability services, and found needs for additional supports like respite care and assistance to plan for crisis and emergencies, especially among families whose adult lived with them.
Data from the surveys showed over one quarter of families with autistic adults who use Developmental Disability services and live with family do not have enough services or supports for themselves, according to the report. And over half of these families indicated a need for respite care to enable them to take a break from caregiving.
Four in 10 families had not discussed preparation for handing crises or emergencies within the previous year at a care team meeting, whether the autistic adult lived with family or apart from family in a group home or other setting. Researchers noted this may have left families ill-equipped to handle illness and unforeseen changes in caregiving needs during the COVID-19 pandemic.
"During the pandemic, families of autistic adults faced complications related to loss of direct support providers, loss of structure provided by daytime activities and a need for extreme precautions due to increased risk of serious illness in this population," said Lindsay Shea, DrPH, leader of the Life Course Outcomes Research Program and director of the Policy and Analytics Center at the Autism Institute. "The pandemic highlighted just how dangerous lack of emergency preparation can be for families of autistic adults. Who will care for your loved one if you become sick and require hospitalization?"
Lead author Anne Roux, a research scientist at the Autism Institute, and her team looked at data from several thousand families across states that participated in the Adult Family Survey and the Family/Guardian Survey conducted in 2018-2019 as part of the National Core Indicators - a collaborative effort to collect data to help improve the quality of states' Developmental Disability services.
Gaps in Resources
This is the first National Autism Indicators Report to examine the needs of families whose loved ones use Developmental Disability services, as little data is available that specifically explores the needs of caregivers. Past reports have shown that households of youth on the autism spectrum were more likely to experience financial hardship. While this latest report on families found that only 37% of families with an adult living with them received payment for the care they provided, despite the fact that they may be less able to work due to need for supervision and additional caregiving demands.
Among families whose autistic adult did not live with them, 10% reported abuse or neglect within the past year. Many of these individuals live in congregate group settings in which families sometimes feel they have little choice about which staff provide care for the adult.
"This rate seems very concerning. Having competent, trained direct support staff can make a huge difference in the confidence of family members who are relying on hired personnel to provide skilled care and supervision," said Roux. "The top concern of parents of autistic adults is what will happen to their son or daughter when they are no longer able to care for them. You're talking about a group of people with disabilities who have high rates of additional physical and mental health conditions and high levels of support needs for managing distressed behavior. Families need to be involved in planning for the delivery of essential services and supports. No family member wants to turn over this level of care to strangers."
Yet, few policies govern services and supports for families, and not enough planning or resources are devoted to addressing the dilemma of aging caregivers within a growing population of adults on the autism spectrum.
Barriers to Community Participation
Although many families reported their loved one participated in activities in the community, only one-third had any type of paid daytime activities. About 40% of adults who lived with family, and 60% of those who lived apart from family, were engaged in facility-based work in settings that did not include people without disabilities. Hispanic autistic adults were less likely to participate in community-based activities or to have paid work compared to those who were non-Hispanic white, Black or other/mixed race.
About one in every three families felt like their adult did not have enough support to be able to work or volunteer in the community. "Despite this, families reported high levels of satisfaction with the supports and services their adult received," Roux said. "At the same time families reported barriers to community participation including stigma in the community or not having adequate staffing to support the adult to do activities in the community."
The report is a snapshot of a segment of autistic adults who are receiving services. The researchers know there is likely a sizable population of adults with autism who don't receive Developmental Disability services and really need them.
"Some states don't provide Developmental Disability services for adults with autism unless they also have intellectual disability. These policies ignore the fact that many autistic adults are cognitively-able but still have tremendous challenges navigating the social, organizational and communication demands of adult life," Roux explained.
"It's critical that we put in place state policies that appropriately recognize and adequately meet the unique needs of the growing group of adults on the autism spectrum who need state Developmental Disability services, including the family members who are such vital care partners," said Shea.
The National Autism Indicators Report series is written in a format that can be understood by non-scientists who need the information, particularly decision- and policy makers. Autism Institute researchers aim to fill a need and desire for usable information. The purpose of indicators is to describe where people are now and have a comparison for measuring changes in the future.
States' developmental disability services lacking for autistic adults and their families
National Autism Indicators Report: Families of autistic adults who use Developmental Disability services face gaps in services and supports, lack of emergency planning and barriers to community participation.
2021-05-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A COVID-fighter's guide to T cells
2021-05-25
LA JOLLA--In a new paper, scientists from La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) bring together research findings from COVID-19 researchers around the world. The results are striking: human T cells can target more than 1,400 sites on the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
"Our lab and many others have shown this very broad and diverse T cell response," says LJI Research Assistant Professor Daniela Weiskopf, Ph.D., co-author of the Cell Host & Microbe review.
This kind of research review, called a "meta-analysis," pools the results of multiple studies, and the researchers give close consideration to how the studies were conducted.
In the case of COVID-19, a global meta-analysis of T cell response studies is especially helpful because different patient populations ...
Study shows how fungi and bacteria can activate genes associated with head and neck cancer
2021-05-25
An in vitro study conducted by a group of researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Araraquara, Brazil, shows how fungi and bacteria can activate genes associated with head and neck tumors, as the metabolism of biofilms (communities in which these microorganisms self-organize in a structured and coordinated manner) stimulate tumor cells by favoring the cell signaling pathways required for tumor development and resistance to treatment. The findings include entirely novel information on the links between microbial biofilms and cell behavior in head and neck cancer.
The researchers discovered that metabolites secreted by biofilms, termed the secretome, can modulate the expression of proto-oncogenes and cell cycle genes associated with tumor cell growth and survival. Their analysis ...
Microbes metabolizing toxic substances were found in the burning coal seams of Kuzbass
2021-05-25
Geothermal ecosystems, such as volcanoes and hot terrestrial and deep-sea springs, are characterized by severe conditions. The temperatures are high and the environment could be extremely acidic or very alkaline. Moreover, there are chemically active compounds in them that can be fatal to living organisms, because they are capable of destroying the membrane of an ordinary cell.
"Exclusively very adapted microorganisms can exist here. They do not only have unique protective systems but are also able to get energy from chemical transformations of those substances that are available to them. Humans are actively using the ...
Serendipitous discovery could lead to treatment for strokes, cardiac arrest
2021-05-25
BOSTON - In a surprising discovery, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) identified a mechanism that protects the brain from the effects of hypoxia, a potentially lethal deprivation of oxygen. This serendipitous finding, which they report in Nature Communications, could aid in the development of therapies for strokes, as well as brain injury that can result from cardiac arrest, among other conditions.
However, this study began with a very different objective, explains senior author Fumito Ichinose, MD, PhD, an attending physician in the Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine at MGH, and principal investigator in ...
New USPSTF recommendation on behavioral counseling interventions for healthy weight in pregnancy
2021-05-25
Bottom Line: In a new recommendation statement, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that clinicians offer pregnant adolescents and adults effective behavioral counseling interventions aimed at promoting healthy weight gain and preventing excess gestational weight gain in pregnancy. Excess weight at the beginning of pregnancy and excess gestational weight gain have been associated with adverse maternal and infant health outcomes such as a large for gestational age infant, cesarean delivery or preterm birth. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care ...
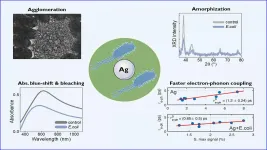
Silver attacks bacteria, gets 'consumed'
2021-05-25
WASHINGTON, May 25, 2021 -- For millennia, silver has been utilized for its antimicrobial and antibacterial properties. Although its use as a disinfectant is widely known, the effects of silver's interaction with bacteria on the silver itself are not well understood.
As antibiotic-resistant bacteria become more and more prevalent, silver has seen steep growth in its use in things like antibacterial coatings. Still, the complex chain of events that lead to the eradication of bacteria is largely taken for granted, and a better understanding of this process can provide clues on how to best apply it.
In Chemical Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Italy, the United States, and Singapore studied the impacts an interaction with bacteria has on silver's ...
Association between bitter taste receptor types, clinical outcomes among patients with COVID-19
2021-05-25
What The Study Did: This study evaluates the association between bitter taste receptor types (supertasters who experience greater intensity of bitter tastes; tasters; and nontasters who experience low intensity of bitter tastes or no bitter tastes) and outcomes after infection with SARS-CoV-2.
Authors: Henry P. Barham, MD, Sinus and Nasal Specialists of Louisiana in Baton Rouge, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11410)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
Association of circulating sex hormones with COVID-19 severity
2021-05-25
What The Study Did: Researchers examined if circulating sex hormones are associated with disease severity in patients with COVID-19.
Authors: Sandeep Dhindsa, M.D., of the St Louis University School of Medicine and Abhinav Diwan, M.D., of the Washington University School of Medicine, both in St. Louis, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11398)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Mental illness among US coal miners
2021-05-25
What The Study Did: Rates of depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts and posttraumatic stress disorder among current and former coal miners in the United States were examined in this study.
Authors: Drew Harris, M.D., of the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11110)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and ...
For men, low testosterone means high risk of severe COVID-19
2021-05-25
Throughout the pandemic, doctors have seen evidence that men with COVID-19 fare worse, on average, than women with the infection. One theory is that hormonal differences between men and women may make men more susceptible to severe disease. And since men have much more testosterone than women, some scientists have speculated that high levels of testosterone may be to blame.
But a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests that, among men, the opposite may be true: that low testosterone levels in the blood are linked to more severe disease. The study could not prove ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] States' developmental disability services lacking for autistic adults and their familiesNational Autism Indicators Report: Families of autistic adults who use Developmental Disability services face gaps in services and supports, lack of emergency planning and barriers to community participation.