Microbes metabolizing toxic substances were found in the burning coal seams of Kuzbass
Microbes that metabolize substances harmful to humans were found in the burning coal seams of Kuzbass
2021-05-25
(Press-News.org) Geothermal ecosystems, such as volcanoes and hot terrestrial and deep-sea springs, are characterized by severe conditions. The temperatures are high and the environment could be extremely acidic or very alkaline. Moreover, there are chemically active compounds in them that can be fatal to living organisms, because they are capable of destroying the membrane of an ordinary cell.
"Exclusively very adapted microorganisms can exist here. They do not only have unique protective systems but are also able to get energy from chemical transformations of those substances that are available to them. Humans are actively using the peculiarities of their metabolism, for example some enzymes help biologists to amplify DNA molecules in a test tube," says Vitaly Kadnikov, Ph.D., senior researcher at the Federal Research Centre "Fundamentals of Biotechnology" of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the principal investigator of the grant from the Russian Science Foundation.
New and so far poorly understood analogs of these natural ecosystems (called simply thermal) are places of hydrocarbon production, that is, oil wells and coal pits. The latter is the research object of a group of scientists from the Federal Research Centre "Fundamentals of Biotechnology" of RAS (Moscow) and Tomsk State University (Tomsk). The authors studied quarries near the city of Kiselevsk, Kemerovo region, and took samples of soil layers from places where there were signs of an underground fire-heated soil, smoke and where steam is coming out to the surface. They characterized the chemical and mineralogical composition of the samples to understand what substances could be used for energy by the bacteria that colonize the coal. Then biologists determined the composition of microbial communities from each layer by analyzing the DNA from it, namely, the gene sequence of one of the ribosome subunits usually used for such purposes.
It turned out that more than a dozen groups of microorganisms live in the Kuzbass quarry, the bacteria mostly. Archaea which are considered to be common inhabitants of extreme ecosystems turned out to be no more than 3%; they are all chemolithoautotrophs converting ammonia into nitrite. The latter compound became "food" for another small group of organisms that metabolize it into nitrate, which people use, for example, as fertilizer.
The representatives of the Chlorobacteria predominated among the bacteria, often found in ecosystems with a high carbon dioxide content; they are also capable of converting poisonous carbon monoxide into CO2. This might be applied for new air purification technologies wherever a furnace is used. Some bacteria found in coal seams can oxidize hydrogen with water formation.
There have also been found microbes that utilize methane as a growth substrate. Many of the identified organisms can fix carbon dioxide and grow autotrophically, but there have been those that feed on the dead remains of their fellows. The Kuzbass quarry turned out to be a well-balanced microbial community, surpassing similar objects studied earlier in China, the US, and Altai in diversity.
"Our research is another step towards understanding how these relatively young ecosystems emerged, what connections they have and whether we can use them. They have much in common with those that form around hot springs. Who knows, maybe they comprise very specific organisms that will help to develop new ways of obtaining valuable biotechnological products by using hydrogen and carbon monoxide generated during coal gasification," says Vitaly Kadnikov.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-25
BOSTON - In a surprising discovery, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) identified a mechanism that protects the brain from the effects of hypoxia, a potentially lethal deprivation of oxygen. This serendipitous finding, which they report in Nature Communications, could aid in the development of therapies for strokes, as well as brain injury that can result from cardiac arrest, among other conditions.
However, this study began with a very different objective, explains senior author Fumito Ichinose, MD, PhD, an attending physician in the Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine at MGH, and principal investigator in ...
2021-05-25
Bottom Line: In a new recommendation statement, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that clinicians offer pregnant adolescents and adults effective behavioral counseling interventions aimed at promoting healthy weight gain and preventing excess gestational weight gain in pregnancy. Excess weight at the beginning of pregnancy and excess gestational weight gain have been associated with adverse maternal and infant health outcomes such as a large for gestational age infant, cesarean delivery or preterm birth. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care ...
2021-05-25
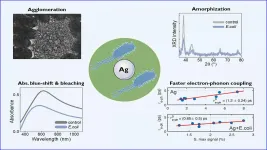
WASHINGTON, May 25, 2021 -- For millennia, silver has been utilized for its antimicrobial and antibacterial properties. Although its use as a disinfectant is widely known, the effects of silver's interaction with bacteria on the silver itself are not well understood.
As antibiotic-resistant bacteria become more and more prevalent, silver has seen steep growth in its use in things like antibacterial coatings. Still, the complex chain of events that lead to the eradication of bacteria is largely taken for granted, and a better understanding of this process can provide clues on how to best apply it.
In Chemical Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Italy, the United States, and Singapore studied the impacts an interaction with bacteria has on silver's ...
2021-05-25
What The Study Did: This study evaluates the association between bitter taste receptor types (supertasters who experience greater intensity of bitter tastes; tasters; and nontasters who experience low intensity of bitter tastes or no bitter tastes) and outcomes after infection with SARS-CoV-2.
Authors: Henry P. Barham, MD, Sinus and Nasal Specialists of Louisiana in Baton Rouge, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11410)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
2021-05-25
What The Study Did: Researchers examined if circulating sex hormones are associated with disease severity in patients with COVID-19.
Authors: Sandeep Dhindsa, M.D., of the St Louis University School of Medicine and Abhinav Diwan, M.D., of the Washington University School of Medicine, both in St. Louis, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11398)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
2021-05-25
What The Study Did: Rates of depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts and posttraumatic stress disorder among current and former coal miners in the United States were examined in this study.
Authors: Drew Harris, M.D., of the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11110)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and ...
2021-05-25
Throughout the pandemic, doctors have seen evidence that men with COVID-19 fare worse, on average, than women with the infection. One theory is that hormonal differences between men and women may make men more susceptible to severe disease. And since men have much more testosterone than women, some scientists have speculated that high levels of testosterone may be to blame.
But a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests that, among men, the opposite may be true: that low testosterone levels in the blood are linked to more severe disease. The study could not prove ...
2021-05-25
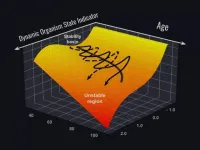
The research team of Gero, a Singapore-based biotech company in collaboration with Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo NY, announces a publication in Nature Communications, a journal of Nature portfolio, presenting the results of the study on associations between aging and the loss of the ability to recover from stresses.
Recently, we have witnessed the first promising examples of biological age reversal by experimental interventions. Indeed, many biological clock types properly predict more years of life for those who choose healthy lifestyles or quit unhealthy ones, such as smoking. What has been still unknown is how quickly biological age is changing over time for the same individual. And especially, how one would distinguish between the ...
2021-05-25
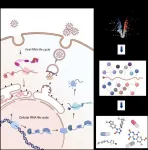
An international and multidisciplinary team led by researchers at the University of Oxford, University of Glasgow, and University of Heidelberg, has uncovered the interactions that SARS-CoV-2 RNA establishes with the host cell, many of which are fundamental for infection. These discoveries pave the way for the development of new therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 with broad-range antiviral potential.
The genetic information of SARS-CoV-2 is encoded in an RNA molecule instead DNA. This RNA must be multiplied, translated, and packaged into new viral particles to produce the viral progeny. Despite the complexity of these processes, SARS-CoV-2 only encodes a handful ...
2021-05-25
Swedish and Danish journalists describe their role as monitorial to a greater extent than journalists from other Nordic countries. Journalists from Norway and Iceland state they have the least experience of political influence and thus differ from Finnish journalists. This is shown by a new comparative study published by Nordicom at the University of Gothenburg.
In a new study, researchers examine the similarities and differences in Nordic journalists' perceptions of the role of journalists and different kinds of influence on journalistic work. They also compare the Nordic perceptions with journalists in the rest of Europe. The study is ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Microbes metabolizing toxic substances were found in the burning coal seams of Kuzbass
Microbes that metabolize substances harmful to humans were found in the burning coal seams of Kuzbass